
The first reaction in photorespiration is
A. Carboxylation
B. Decarboxylation
C. Oxygenation
D. Phosphorylation
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: Generally, RuBisCO enzyme has the affinity towards $CO_2$ to produce 3-phosphoglyceric acid form RuBP but sometimes BuBP reacts with oxygen ($O_2$).
Complete answer: RuBisCO or Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase is an enzyme that generally reacts with RuBP or Ribulose bisphosphate in the presence of carbon dioxide ($CO_2$) to form 3-phosphoglyceric acid. This is the first step of the Calvin cycle – Carboxylation. This is called so because in this step $CO_2$ is get trapped by RuBisCO but sometimes this RuBisCO enzyme can react with oxygen ($O_2$).
The substrate for the reaction is the same that is RuBP but the products are different – 2-phosphoglycolate and 3-phosphoglyceric acid. This is called photorespiration.
Here oxygen trapping is done thus the first step of photorespiration is Oxygenation.
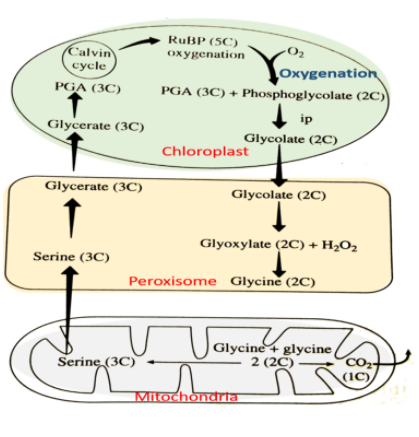
Additional information: The 2-phosphoglycolate is a very toxic product and cell cannot metabolise it. So, to bypass this photorespiration takes place in some higher plans.
The photorespiration takes place in three cells in plant tissue – chloroplast, peroxisome, and mitochondria.
1. The first step is taken place in the chloroplast.
2. The second step is taken place in peroxisome where glycolate is transformed into glycine.
3. The third step is taken place in mitochondria where glycine is transformed into serine.
4. Then the serine comes to peroxisome from mitochondria and forms glycerate.
5. Then this glycerate enters the chloroplast again and forms 3-phosphoglycerate which enters the Calvin cycle. This is the whole process of photorespiration.
So, the correct answer is option C. Oxygenation.
Note: The photorespiration takes place in chloroplast, peroxisome, and mitochondria of the plant cells.
Complete answer: RuBisCO or Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase is an enzyme that generally reacts with RuBP or Ribulose bisphosphate in the presence of carbon dioxide ($CO_2$) to form 3-phosphoglyceric acid. This is the first step of the Calvin cycle – Carboxylation. This is called so because in this step $CO_2$ is get trapped by RuBisCO but sometimes this RuBisCO enzyme can react with oxygen ($O_2$).
The substrate for the reaction is the same that is RuBP but the products are different – 2-phosphoglycolate and 3-phosphoglyceric acid. This is called photorespiration.
Here oxygen trapping is done thus the first step of photorespiration is Oxygenation.

Additional information: The 2-phosphoglycolate is a very toxic product and cell cannot metabolise it. So, to bypass this photorespiration takes place in some higher plans.
The photorespiration takes place in three cells in plant tissue – chloroplast, peroxisome, and mitochondria.
1. The first step is taken place in the chloroplast.
2. The second step is taken place in peroxisome where glycolate is transformed into glycine.
3. The third step is taken place in mitochondria where glycine is transformed into serine.
4. Then the serine comes to peroxisome from mitochondria and forms glycerate.
5. Then this glycerate enters the chloroplast again and forms 3-phosphoglycerate which enters the Calvin cycle. This is the whole process of photorespiration.
So, the correct answer is option C. Oxygenation.
Note: The photorespiration takes place in chloroplast, peroxisome, and mitochondria of the plant cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




