
What would be the final product of this reaction sequence?
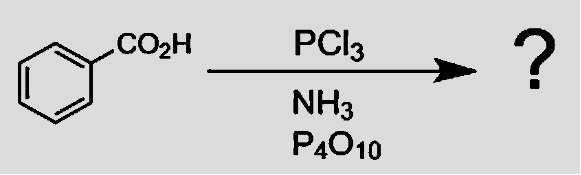

Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, we should recall the concept of nucleophilic substitution reactions. It is the type of reaction that involves the replacement of one atom or molecule of a compound with another atom or molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
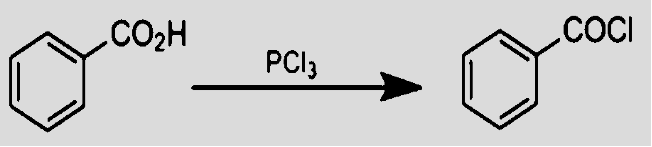
- Reaction of the carboxylic acid with phosphorus chloride yields acyl chloride. With $PC{{l}_{5}}$, the reaction is quite simple utilizing a one-mole reactant and yielding products. The major advantage of this reaction is that there is only one side product i.e. phosphonic acid which is non-toxic, is easily removed by filtration whereas reaction with $PC{{l}_{5}}$ gives two side products making the reaction more volatile.
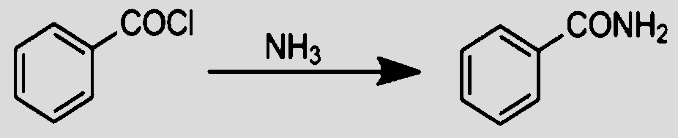
- Reaction of an acyl chloride with ammonia takes place in two stages. In the first stage, we initially get $HCl$, with the hydrogen atom coming from $N{{H}_{3}}$ group. Since ammonia and amines are basic, they react with $HCl$ to produce salt. Therefore, in the second stage, we get benzamide.
- Amides dehydrated with ${{P}_{4}}{{O}_{10}}$ yield cyanides. Since ${{P}_{4}}{{O}_{10}}$ is known to be a very strong dehydrating agent, it reacts itself with water molecules to form phosphoric acid. That enables it to remove free water molecules by a simple hydrolysis reaction. Amide reacts with it to give its substituted nitriles and Cyanide as a major product is formed.
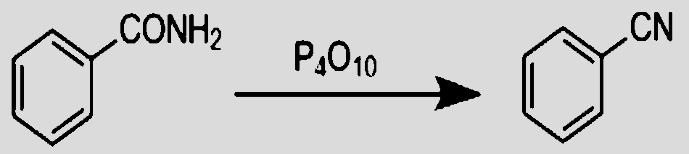
Note: It is important to note that in each case, the nucleophile approaches the given substrate to the leaving group. The leaving group is pushed out of the transition state on the opposite side of the carbon-nucleophile bond, forming the required product.
Complete step by step answer:
- Reaction of the carboxylic acid with phosphorus chloride yields acyl chloride. With $PC{{l}_{5}}$, the reaction is quite simple utilizing a one-mole reactant and yielding products. The major advantage of this reaction is that there is only one side product i.e. phosphonic acid which is non-toxic, is easily removed by filtration whereas reaction with $PC{{l}_{5}}$ gives two side products making the reaction more volatile.

- Reaction of an acyl chloride with ammonia takes place in two stages. In the first stage, we initially get $HCl$, with the hydrogen atom coming from $N{{H}_{3}}$ group. Since ammonia and amines are basic, they react with $HCl$ to produce salt. Therefore, in the second stage, we get benzamide.

- Amides dehydrated with ${{P}_{4}}{{O}_{10}}$ yield cyanides. Since ${{P}_{4}}{{O}_{10}}$ is known to be a very strong dehydrating agent, it reacts itself with water molecules to form phosphoric acid. That enables it to remove free water molecules by a simple hydrolysis reaction. Amide reacts with it to give its substituted nitriles and Cyanide as a major product is formed.
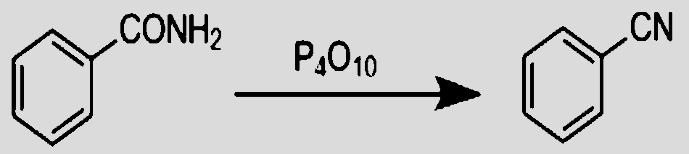
Note: It is important to note that in each case, the nucleophile approaches the given substrate to the leaving group. The leaving group is pushed out of the transition state on the opposite side of the carbon-nucleophile bond, forming the required product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




