
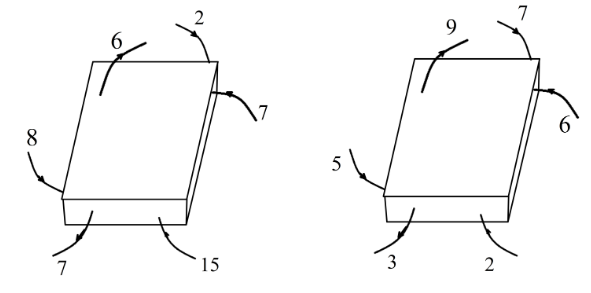
The figure shows two situations in which a Gaussian cube is placed in an electric field. The arrows and values indicate the directions and magnitudes (in \[N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}\] ) of the electric fields. What is the net charge (in the two situations) inside the cube?
A . (1) negative, (2) positive
B. (1) negative, (2) zero
C. (1) positive, (2) positive
D. (1) negative, (2) negative

Answer
528k+ views
Hint: Gauss’s law states that the total electric flux due to closed surface is equal to the \[\dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\] times charge enclosed by the surface. Gauss’s law is given by, \[\phi = \oint\limits_s {\vec E} .d\vec S = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\] where, \[\vec E\] is the electric field, \[S\] is the closed surface placed in the electric field.Direction of \[S\] is always normal to it.
Complete step by step answer:
If flux is positive that means if the field line exits then charge inside the surface is positive and if flux is negative that means if the field line is entering the surface then charge inside the surface is negative. So, if we find the net electric field line entering/exiting the Gaussian cube then we can easily say either the flux is positive or negative. From there we can find either the charge inside the surface is positive or negative.
Thus, from the first situation: let’s find the net field line entering/exiting the cube.So, we have here for the first Gaussian cube field line entering the cube is equal to,
\[{E_{enter}} = 7 + 2 + 8 + 15 = 31N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}\]
The field exiting the cube is equal to, \[{E_{exit}} = 7 + 6 = 13N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}\]
Hence, the net field line entering the surface is greater than the field line leaving the cube.
\[{E_{enter}} > {E_{exit}}\]
So, flux must be negative. Hence, the charge inside the cube must be negative.
Now, for the second situation: field line entering the cube is equal to,
\[{E_{enter}} = 7 + 6 + 2 + 5 = 20N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}\]
The field exiting the cube is equal to,
\[{E_{exit}} = 9 + 3 = 12N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}\]
Hence, the net field line entering the surface is greater than the field line leaving the cube.
\[{E_{enter}} > {E_{exit}}\]
So, flux must be negative and the charge inside the cube must be negative.Thus, for both the cubes charge inside is negative.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note: For a positive charge field line always exits from the charge So, the flux through a closed surface is positive (\[\phi = + ve\]) since field due to a positive charge is given by, \[k\dfrac{q}{{{r^2}}}\]. But, for a negative charge the field line always enters towards the charge. So, the flux through a closed surface is negative(\[\phi = - ve\]) since field due to a negative charge is given by, \[k\dfrac{{ - q}}{{{r^2}}}\].
Complete step by step answer:
If flux is positive that means if the field line exits then charge inside the surface is positive and if flux is negative that means if the field line is entering the surface then charge inside the surface is negative. So, if we find the net electric field line entering/exiting the Gaussian cube then we can easily say either the flux is positive or negative. From there we can find either the charge inside the surface is positive or negative.
Thus, from the first situation: let’s find the net field line entering/exiting the cube.So, we have here for the first Gaussian cube field line entering the cube is equal to,
\[{E_{enter}} = 7 + 2 + 8 + 15 = 31N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}\]
The field exiting the cube is equal to, \[{E_{exit}} = 7 + 6 = 13N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}\]
Hence, the net field line entering the surface is greater than the field line leaving the cube.
\[{E_{enter}} > {E_{exit}}\]
So, flux must be negative. Hence, the charge inside the cube must be negative.
Now, for the second situation: field line entering the cube is equal to,
\[{E_{enter}} = 7 + 6 + 2 + 5 = 20N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}\]
The field exiting the cube is equal to,
\[{E_{exit}} = 9 + 3 = 12N{m^2}{C^{ - 1}}\]
Hence, the net field line entering the surface is greater than the field line leaving the cube.
\[{E_{enter}} > {E_{exit}}\]
So, flux must be negative and the charge inside the cube must be negative.Thus, for both the cubes charge inside is negative.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note: For a positive charge field line always exits from the charge So, the flux through a closed surface is positive (\[\phi = + ve\]) since field due to a positive charge is given by, \[k\dfrac{q}{{{r^2}}}\]. But, for a negative charge the field line always enters towards the charge. So, the flux through a closed surface is negative(\[\phi = - ve\]) since field due to a negative charge is given by, \[k\dfrac{{ - q}}{{{r^2}}}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




