
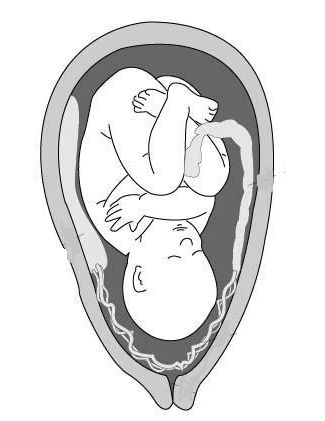
The figure shows a foetus in the uterus. Define implantation.

Answer
525k+ views
Hint: Implantation refers to the attachment of the fertilized egg to the uterine lining and it is also defined as the stage of parental development. It is the early stage of pregnancy
Complete answer:
In humans, implantation is the period of conception where the foetus adheres to the uterine wall. The conceptus is known as a blastocyst at this point of prenatal development. The embryo receives oxygen and nutrients from the mother through this adhesion, allowing it to mature. In humans, implantation of a fertilized ovum is most likely to occur nine days after ovulation; however, this will vary between six and twelve days.
The reception-ready period of the uterine endometrium, which lasts about 4 days, is often referred to as the "implantation window." The implantation window begins approximately 6 days after the height of luteinizing hormone levels.
The signs and effects of implantation are the body's way of letting you know that you're pregnant. While several women experience no discomfort during the procedure, some show light bleeding and abdominal cramps.
The distinction between implantation symptoms and your cycle can be perplexing, particularly because blood is shed from the uterine lining in both cases while most women do not experience bleeding during implantation, some do, with 15 to 25% having light, spotty blood. This blood usually begins pink and darkens, and unlike your period, it does not circulate or produce clots. It should be over in a day or two.
Note:
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is detected in urine by home pregnancy testing.
- Before implantation, the pregnant body begins to produce this hormone. For the first 8 weeks, levels in the blood and urine doubled almost every 24 hours, peaking at about 10 weeks.
- In women with 28-day menstrual periods, home pregnancy testing can detect hCG in the urine 12–15 days after ovulation.
Complete answer:
In humans, implantation is the period of conception where the foetus adheres to the uterine wall. The conceptus is known as a blastocyst at this point of prenatal development. The embryo receives oxygen and nutrients from the mother through this adhesion, allowing it to mature. In humans, implantation of a fertilized ovum is most likely to occur nine days after ovulation; however, this will vary between six and twelve days.
The reception-ready period of the uterine endometrium, which lasts about 4 days, is often referred to as the "implantation window." The implantation window begins approximately 6 days after the height of luteinizing hormone levels.
The signs and effects of implantation are the body's way of letting you know that you're pregnant. While several women experience no discomfort during the procedure, some show light bleeding and abdominal cramps.
The distinction between implantation symptoms and your cycle can be perplexing, particularly because blood is shed from the uterine lining in both cases while most women do not experience bleeding during implantation, some do, with 15 to 25% having light, spotty blood. This blood usually begins pink and darkens, and unlike your period, it does not circulate or produce clots. It should be over in a day or two.
Note:
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is detected in urine by home pregnancy testing.
- Before implantation, the pregnant body begins to produce this hormone. For the first 8 weeks, levels in the blood and urine doubled almost every 24 hours, peaking at about 10 weeks.
- In women with 28-day menstrual periods, home pregnancy testing can detect hCG in the urine 12–15 days after ovulation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




