
The figure illustrates how $B$, the flux density inside a sample of ferromagnetic material varies with external magnetic field ${B_0}$. For the sample to be suitable for making a permanent magnet OQ should be large or should it be small?
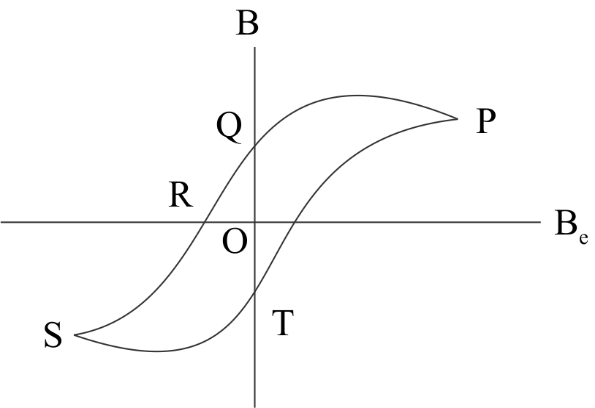
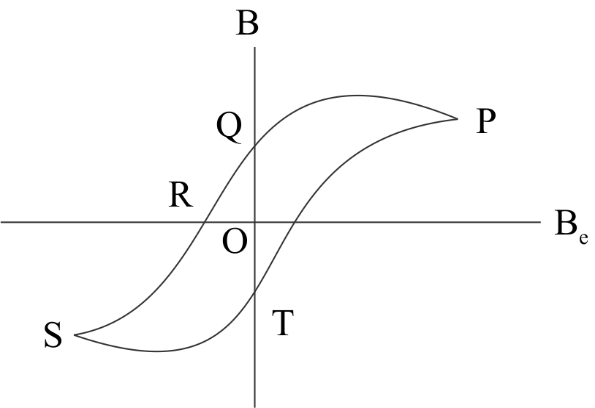
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we need to understand how the hysteresis loop of a ferromagnetic material differs for both hard and soft magnets. The variation of magnetic flux with external magnetic fields gives us the hysteresis loop.
Complete step by step answer
The materials used for making a permanent magnet should have high retentivity and coercivity so that the magnet is able to retain its magnetism when roughly handled or at extreme temperature changes. The given diagram is called the hysteresis loop, which shows us the change in magnetic flux density through a ferromagnetic material when it is placed in an external magnetic field. First, the magnetization of the material starts until it reaches the point P where it reaches the saturation stage with all the dipoles aligned. Further increase in the external magnetic field ${B_0}$ has no effect on $B$.
If ${B_0}$ is now gradually reduced to zero, $B$ does not retrace the curve back, instead it follows the curve PQ. However at point Q some amount of magnetization still remains even though the external magnetic field is reduced to zero. This is known as the residual or remnant magnetization called the retentivity of the material. So greater the retentivity, more is the material suitable for making a permanent magnet. These kinds of materials are called hard magnets. Usually the hysteresis loop for hard magnets are of greater area but smaller height.
So, for a sample to be suitable for making a permanent magnet, OQ should be small.
Note: Usually soft magnets are used to manufacture electromagnets. Since they have low retentivity and coercivity, and low hysteresis loss, they can easily lose their magnetization power once the flow of current stops.
Complete step by step answer
The materials used for making a permanent magnet should have high retentivity and coercivity so that the magnet is able to retain its magnetism when roughly handled or at extreme temperature changes. The given diagram is called the hysteresis loop, which shows us the change in magnetic flux density through a ferromagnetic material when it is placed in an external magnetic field. First, the magnetization of the material starts until it reaches the point P where it reaches the saturation stage with all the dipoles aligned. Further increase in the external magnetic field ${B_0}$ has no effect on $B$.
If ${B_0}$ is now gradually reduced to zero, $B$ does not retrace the curve back, instead it follows the curve PQ. However at point Q some amount of magnetization still remains even though the external magnetic field is reduced to zero. This is known as the residual or remnant magnetization called the retentivity of the material. So greater the retentivity, more is the material suitable for making a permanent magnet. These kinds of materials are called hard magnets. Usually the hysteresis loop for hard magnets are of greater area but smaller height.
So, for a sample to be suitable for making a permanent magnet, OQ should be small.
Note: Usually soft magnets are used to manufacture electromagnets. Since they have low retentivity and coercivity, and low hysteresis loss, they can easily lose their magnetization power once the flow of current stops.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




