
The fertilization cone, which pulls the sperm into the egg, is formed from
(a)Acrosome of the sperm
(b)Acrosomal process of the sperm
(c)Vitelline layer of the egg
(d)Plasma membrane of the egg
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: During fertilization, sperm cells undergo a reaction process to penetrate the female egg cell. Glycoproteins on the outer surface of the sperm then bind with glycoproteins on the zona pellucida of the ovum in order to fertilize it.
Complete answer:
The fertilization cone is formed from the plasma membrane of the egg, which draws the sperm into the egg. While fertilization, a sperm should first combine with the plasma membrane of the female ovum, then penetrate to fertilize it. Fusing to the ovum usually causes a little problem, whereas penetrating through the egg's hard shell or extracellular matrix can present more of a problem to the sperm. Therefore, sperm cells go through a process known as the acrosome reaction, in which glycoproteins on the outer surface of the sperm then bind with glycoproteins on the zona pellucida of the ovum in order to fertilize it.
Additional Information: After the sperm goes to the cytoplasm of the oocyte, the tail and the outer coating of the sperm disintegrate and the cortical reaction occurs, preventing other sperm from fertilizing an equivalent egg. The oocyte now goes through its second meiotic division giving rise to the haploid ovum and releasing a polar body. The sperm nucleus then fuses with the ovum, allowing fusion of their genetic material.
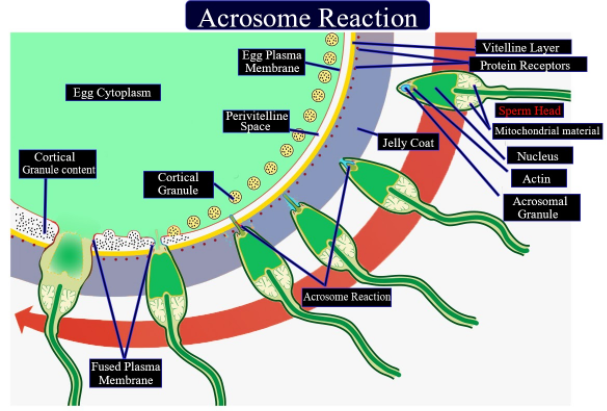
So, the correct answer is ‘Plasma membrane of the egg’.
Note: At the start of the process, the sperm undergoes a series of changes, as freshly ejaculated sperm is unable or poorly ready to fertilize. The sperm must undergo capacitation within the female's reproductive tract over several hours, which increases its motility and destabilizes its membrane.
Complete answer:
The fertilization cone is formed from the plasma membrane of the egg, which draws the sperm into the egg. While fertilization, a sperm should first combine with the plasma membrane of the female ovum, then penetrate to fertilize it. Fusing to the ovum usually causes a little problem, whereas penetrating through the egg's hard shell or extracellular matrix can present more of a problem to the sperm. Therefore, sperm cells go through a process known as the acrosome reaction, in which glycoproteins on the outer surface of the sperm then bind with glycoproteins on the zona pellucida of the ovum in order to fertilize it.
Additional Information: After the sperm goes to the cytoplasm of the oocyte, the tail and the outer coating of the sperm disintegrate and the cortical reaction occurs, preventing other sperm from fertilizing an equivalent egg. The oocyte now goes through its second meiotic division giving rise to the haploid ovum and releasing a polar body. The sperm nucleus then fuses with the ovum, allowing fusion of their genetic material.

So, the correct answer is ‘Plasma membrane of the egg’.
Note: At the start of the process, the sperm undergoes a series of changes, as freshly ejaculated sperm is unable or poorly ready to fertilize. The sperm must undergo capacitation within the female's reproductive tract over several hours, which increases its motility and destabilizes its membrane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




