
The equivalent resistance between the points A and B will be (each resistance is $15\Omega $).
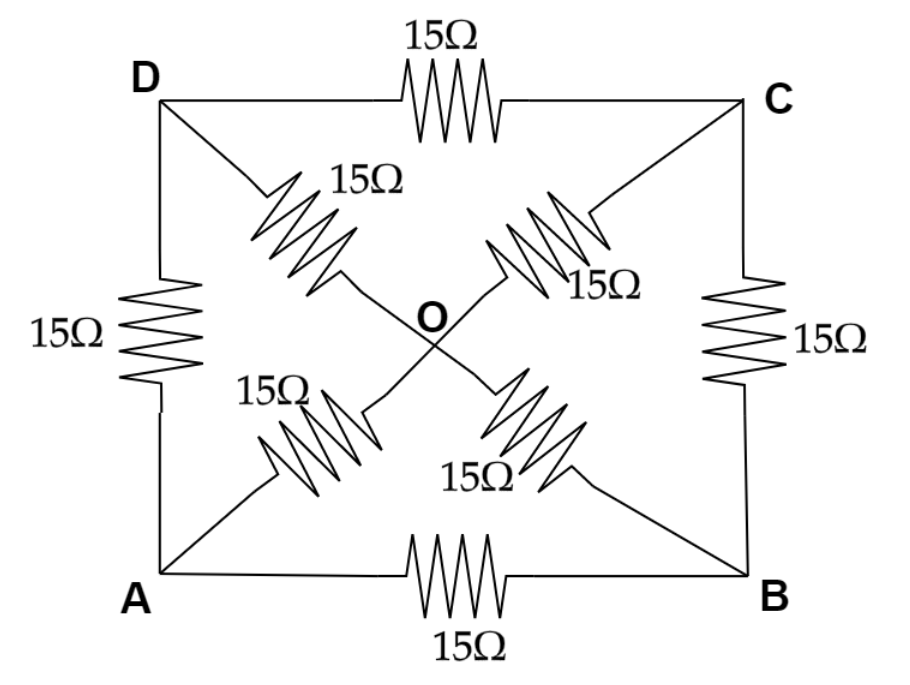
$\left( A \right)30\Omega $
$\left( B \right)8\Omega $
$\left( C \right)10\Omega $
$\left( D \right)40\Omega $

Answer
495.3k+ views
Hint: First of all using envelope theory we will have to open the circuit from the center and now find total resistance in each branch. First find the total resistance along the branch DC, then ADCB and lastly the resistance of branch AOB. Now draw a final simplified diagram and with the help of that diagram calculate the total equivalent resistance between the points A and B.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the problem we know that there is a circuit diagram and we need to calculate the equivalent resistance at the point between A and B and each resistance is equal and that is $15\Omega $ .
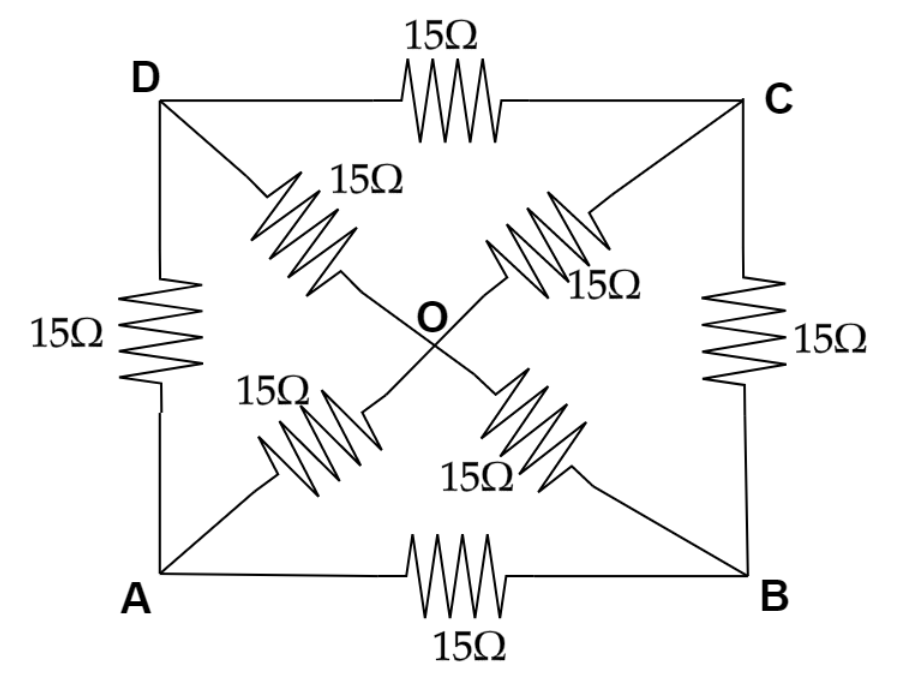
Now applying Envelope theory at the center O then we can now open the circuit from the centre so we will get,
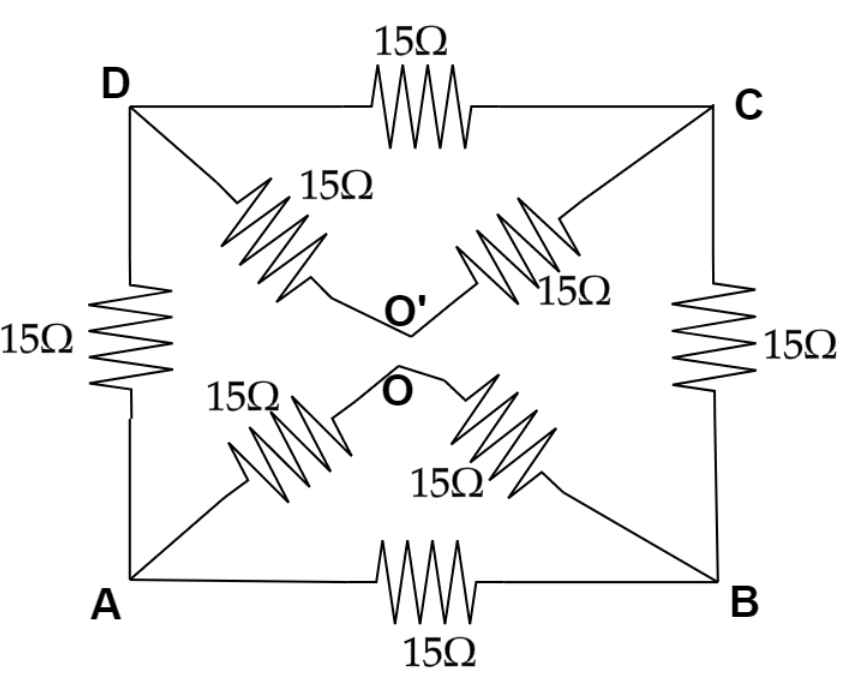
Now we will get two different loops after using envelope theory and name them ai O’ and O respectively.
Now with the help of a diagram we can now calculate the total resistance of the respective branch.
At branch DC the total resistance will be,
$RDC = \left( {15\Omega } \right)DC||\left[ {\left( {15\Omega } \right)DO' + \left( {15\Omega } \right)CO'} \right]$
Now on further simplifying we will get,
$RDC = 15\Omega ||30\Omega $
As we know, $\operatorname{R} {\text{eq = R1||R2 = }}\dfrac{{{\text{R1}} \times {\text{R2}}}}{{{\text{R1 + R2}}}}$
Putting this formula in the above equation we will get,
$RDC = \dfrac{{15\Omega \times 30\Omega }}{{15\Omega + 30\Omega }}$
$ \Rightarrow RDC = \dfrac{{450\Omega }}{{45\Omega }}$
Hence the total resistance between D and C is $10\Omega $.
Now the circuit will look like,
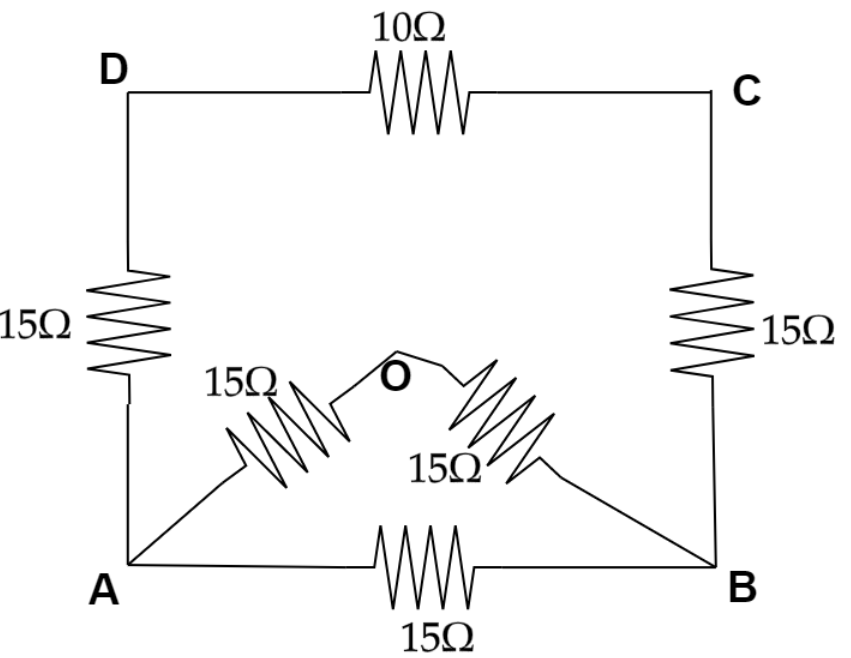
Now calculating the total resistance between A and B which is the resistance of the upper part ADCB we will get,
$RADCB = RAD + RDC + RDB$
From the figure, putting the value of resistance we will get,
$RADCB = 15\Omega + 10\Omega + 15\Omega $
$ \Rightarrow RADCB = 40\Omega $
Now the total resistance in between A and B that is resistance of middle part AOB, we will get,
$RAOB = RAO + ROB$
From the figure, putting the value of resistance we will get,
$RAOB = 15\Omega + 15\Omega $
$ \Rightarrow RAOB = 30\Omega $
Now the circuit will become,
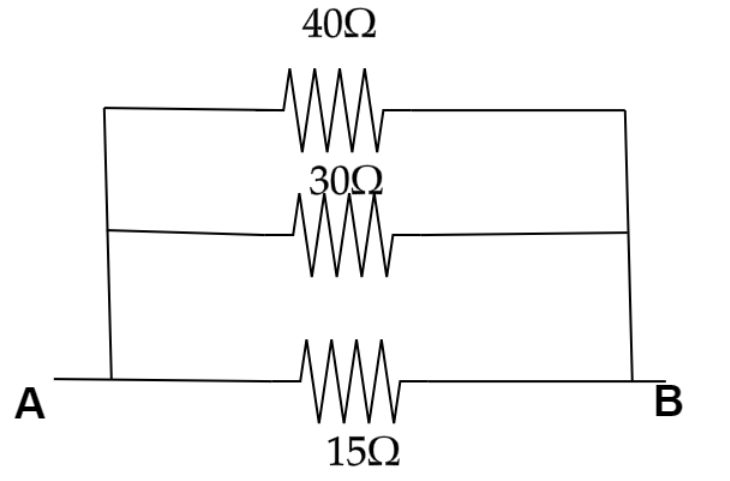
Therefore the equivalent resistance between A and B we will get,
$\dfrac{1}{{\operatorname{R} {\text{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{RADCB}} + \dfrac{1}{{RAOB}} + \dfrac{1}{{RAB}}$
Now putting the value from the diagram we will get,
$\dfrac{1}{{\operatorname{R} {\text{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{40\Omega }} + \dfrac{1}{{30\Omega }} + \dfrac{1}{{15\Omega }}$
On solving we will get,
$\dfrac{1}{{\operatorname{R} {\text{eq}}}} = \dfrac{{3 + 4 + 8}}{{120\Omega }}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\operatorname{R} {\text{eq}}}} = \dfrac{{15}}{{120\Omega }}$
Reversing the above equation we will get,
$\operatorname{R} {\text{eq}} = \dfrac{{120\Omega }}{{15}}$
Hence the equivalent resistance between A and B is $8\Omega $. Therefore the correct option is $\left( B \right)$.
Note:
While solving this kind of problem, we always have to draw the simplified circuit in each step so that we will not commit a mistake. We can solve this problem in many different ways. We can use the delta star method to open the circuit in a simplified version.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the problem we know that there is a circuit diagram and we need to calculate the equivalent resistance at the point between A and B and each resistance is equal and that is $15\Omega $ .

Now applying Envelope theory at the center O then we can now open the circuit from the centre so we will get,

Now we will get two different loops after using envelope theory and name them ai O’ and O respectively.
Now with the help of a diagram we can now calculate the total resistance of the respective branch.
At branch DC the total resistance will be,
$RDC = \left( {15\Omega } \right)DC||\left[ {\left( {15\Omega } \right)DO' + \left( {15\Omega } \right)CO'} \right]$
Now on further simplifying we will get,
$RDC = 15\Omega ||30\Omega $
As we know, $\operatorname{R} {\text{eq = R1||R2 = }}\dfrac{{{\text{R1}} \times {\text{R2}}}}{{{\text{R1 + R2}}}}$
Putting this formula in the above equation we will get,
$RDC = \dfrac{{15\Omega \times 30\Omega }}{{15\Omega + 30\Omega }}$
$ \Rightarrow RDC = \dfrac{{450\Omega }}{{45\Omega }}$
Hence the total resistance between D and C is $10\Omega $.
Now the circuit will look like,

Now calculating the total resistance between A and B which is the resistance of the upper part ADCB we will get,
$RADCB = RAD + RDC + RDB$
From the figure, putting the value of resistance we will get,
$RADCB = 15\Omega + 10\Omega + 15\Omega $
$ \Rightarrow RADCB = 40\Omega $
Now the total resistance in between A and B that is resistance of middle part AOB, we will get,
$RAOB = RAO + ROB$
From the figure, putting the value of resistance we will get,
$RAOB = 15\Omega + 15\Omega $
$ \Rightarrow RAOB = 30\Omega $
Now the circuit will become,

Therefore the equivalent resistance between A and B we will get,
$\dfrac{1}{{\operatorname{R} {\text{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{RADCB}} + \dfrac{1}{{RAOB}} + \dfrac{1}{{RAB}}$
Now putting the value from the diagram we will get,
$\dfrac{1}{{\operatorname{R} {\text{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{40\Omega }} + \dfrac{1}{{30\Omega }} + \dfrac{1}{{15\Omega }}$
On solving we will get,
$\dfrac{1}{{\operatorname{R} {\text{eq}}}} = \dfrac{{3 + 4 + 8}}{{120\Omega }}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\operatorname{R} {\text{eq}}}} = \dfrac{{15}}{{120\Omega }}$
Reversing the above equation we will get,
$\operatorname{R} {\text{eq}} = \dfrac{{120\Omega }}{{15}}$
Hence the equivalent resistance between A and B is $8\Omega $. Therefore the correct option is $\left( B \right)$.
Note:
While solving this kind of problem, we always have to draw the simplified circuit in each step so that we will not commit a mistake. We can solve this problem in many different ways. We can use the delta star method to open the circuit in a simplified version.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




