
The equivalent capacity between A and B in the given circuit is (\[{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}} = 4 \mu F \], \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}} = 12 \mu F \], \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}} = 8 \mu F \], \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}} = 4 \mu F \], \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}} = 8 \mu F \])
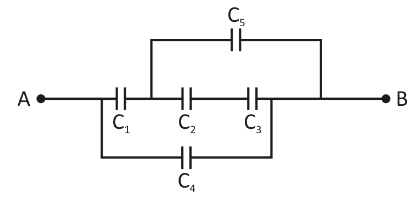
A. \[24\mu F\]
B. \[36\mu F\]
C. \[\dfrac{{16}}{3}\mu F\]
D. \[\dfrac{8}{3}\mu F\]

Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: In this question, the given figure can be represented or drawn as the balance wheatstone bridge. Find the capacitance of the upper arm and the lower arm of the circuit then by using both capacitance find the equivalent capacitance of the circuit.
Complete step by step answer:
The given figure can be redrawn into equivalent circuit as shown:
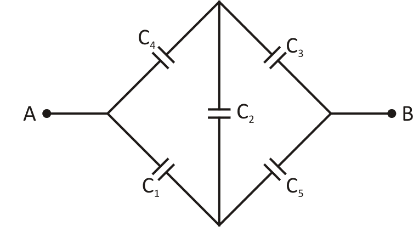
Here, the wheatstone bridge is balanced. So,\[12\mu F\] becomes ineffective. Capacitance of the upper arm and \[{C_3}\] are in series, \[\dfrac{1}{{{C_U}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{C_4}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_3}}}\]
Where ${C_U}$ is the upper arm capacitance and
\[{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}} = 4 \mu F\] , \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}} =12 \mu F\],
\[{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}} = 8 \mu F\], \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}} = 4 \mu F \], \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}} = 8 \mu F \]
\[\dfrac{1}{{{C_U}}} = \dfrac{1}{4} + \dfrac{1}{8} \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{{{C_U}}} = \dfrac{{2 + 1}}{8}\\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{{{C_U}}} = \dfrac{3}{8}\mu F\]
\[\Rightarrow {C_U} = \dfrac{8}{3}\mu F\]
Capacitance of the lower arm is \[{C_1}\] and \[C{}_5\] are in series,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{C_L}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{C_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_5}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{{{C_L}}} = \dfrac{1}{4} + \dfrac{1}{8} \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{{{C_L}}} = \dfrac{{2 + 1}}{8}\\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{{{C_L}}} = \dfrac{3}{8}\mu F\]
\[\Rightarrow{C_L} = \dfrac{8}{3}\mu F\]
${C_L}$ is the lower arm capacitance. Now, \[{C_U}\] and \[{C_L}\] are in parallel.
The equivalent capacitance ${C_{eq}}$ between points A and B is
\[{C_{eq}} = {C_U} + {C_L}\]
\[\Rightarrow{C_{eq}} = \dfrac{8}{3} + \dfrac{8}{3} \\
\therefore{C_{eq}}= \dfrac{{16}}{3}\mu F\]
Hence, option C is correct.
Note:In this question we are asked to find the equivalent capacitance of the given circuit. Here, we redraw the figure as a balance wheatstone bridge and solve the question step by step and first try to find capacitance of upper arm then lower arm. So, we are able to find out the total equivalent capacitance of the circuit. Without finding the upper arm and lower arm capacitance we cannot find the equivalent capacitance.
Complete step by step answer:
The given figure can be redrawn into equivalent circuit as shown:

Here, the wheatstone bridge is balanced. So,\[12\mu F\] becomes ineffective. Capacitance of the upper arm and \[{C_3}\] are in series, \[\dfrac{1}{{{C_U}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{C_4}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_3}}}\]
Where ${C_U}$ is the upper arm capacitance and
\[{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}} = 4 \mu F\] , \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}} =12 \mu F\],
\[{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}} = 8 \mu F\], \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}} = 4 \mu F \], \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}} = 8 \mu F \]
\[\dfrac{1}{{{C_U}}} = \dfrac{1}{4} + \dfrac{1}{8} \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{{{C_U}}} = \dfrac{{2 + 1}}{8}\\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{{{C_U}}} = \dfrac{3}{8}\mu F\]
\[\Rightarrow {C_U} = \dfrac{8}{3}\mu F\]
Capacitance of the lower arm is \[{C_1}\] and \[C{}_5\] are in series,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{C_L}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{C_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_5}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{{{C_L}}} = \dfrac{1}{4} + \dfrac{1}{8} \\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{{{C_L}}} = \dfrac{{2 + 1}}{8}\\
\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{{{C_L}}} = \dfrac{3}{8}\mu F\]
\[\Rightarrow{C_L} = \dfrac{8}{3}\mu F\]
${C_L}$ is the lower arm capacitance. Now, \[{C_U}\] and \[{C_L}\] are in parallel.
The equivalent capacitance ${C_{eq}}$ between points A and B is
\[{C_{eq}} = {C_U} + {C_L}\]
\[\Rightarrow{C_{eq}} = \dfrac{8}{3} + \dfrac{8}{3} \\
\therefore{C_{eq}}= \dfrac{{16}}{3}\mu F\]
Hence, option C is correct.
Note:In this question we are asked to find the equivalent capacitance of the given circuit. Here, we redraw the figure as a balance wheatstone bridge and solve the question step by step and first try to find capacitance of upper arm then lower arm. So, we are able to find out the total equivalent capacitance of the circuit. Without finding the upper arm and lower arm capacitance we cannot find the equivalent capacitance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




