
The equipotential surface of a dipole is:
A. A sphere whose centre coincides with the centre of electric dipole.
B. A plane surface inclined at an angle of with the axis of the electric dipole.
C. A plane surface passing through the centre of the electric dipole and perpendicular to the axis of the electric dipole.
D. Any plane surface parallel to the axis of electric dipole.
Answer
614.1k+ views
Hint: Equipotential surface is a surface in which the potential is constant throughout.
Complete step by step answer:
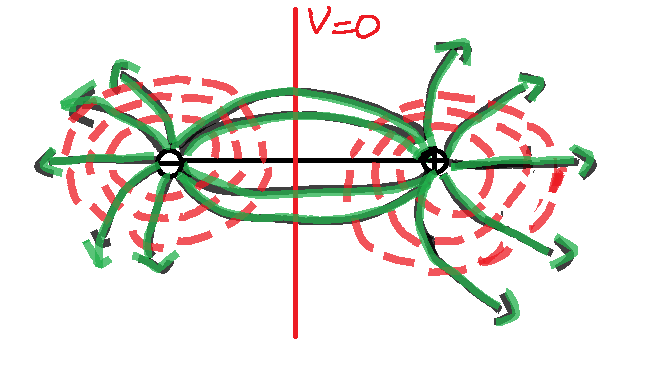
The above figure shows how an equipotential surface of a dipole looks like. The green lines signifies the electric field and the red lines signifies the equipotential surface around the dipole.
The two charges in a dipole form its own electric field and the field density will be more along the axis of dipole, since the dipole consists of opposite charges. So the equipotential surface will be present at the centre of the dipole, which is a line perpendicular to the axis of the dipole and potential value is zero along the line.
So the answer to the question is option (C)- A plane surface passing through the centre of the electric dipole and perpendicular to the axis of the electric dipole.
Note: Equipotential surfaces are like contour lines on a map which traces lines of equal altitude. Altitude refers to electric potential or voltage. Equipotential lines are always perpendicular to the electric field, so that the work done in moving a charge along these lines is zero. In three dimensions the lines from equipotential surfaces.
Complete step by step answer:

The above figure shows how an equipotential surface of a dipole looks like. The green lines signifies the electric field and the red lines signifies the equipotential surface around the dipole.
The two charges in a dipole form its own electric field and the field density will be more along the axis of dipole, since the dipole consists of opposite charges. So the equipotential surface will be present at the centre of the dipole, which is a line perpendicular to the axis of the dipole and potential value is zero along the line.
So the answer to the question is option (C)- A plane surface passing through the centre of the electric dipole and perpendicular to the axis of the electric dipole.
Note: Equipotential surfaces are like contour lines on a map which traces lines of equal altitude. Altitude refers to electric potential or voltage. Equipotential lines are always perpendicular to the electric field, so that the work done in moving a charge along these lines is zero. In three dimensions the lines from equipotential surfaces.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




