
The equi-convex lens has a focal length$f$. If it is cut perpendicular to the principal axis passing through the optical centre, then the focal length of each half is.
$\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{.}\dfrac{f}{2} \\
& \text{B}\text{. }f \\
& \text{C}\text{.}\dfrac{3f}{2} \\
& \text{D}.2f \\
\end{align}$
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: Cutting an equi-convex lens through the optical centre and perpendicular to its principal axis, we will get the two halves as a plano-convex lens i.e. lens with one surface plane and other surface convex.
Formula used:
We know that the lens’ maker formula is given by the equation
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\left( n-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}-\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}} \right)$
Where,
$f$ is the focal length of lens
$n$ is the refractive index of material used
${{R}_{1}}$ is the radius of curvature of sphere 1
${{R}_{2}}$ is the radius of curvature of sphere 2.
Complete step-by-step answer:
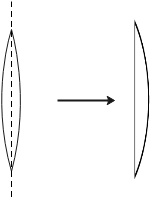
Assuming the direction of light along positive x-direction.
Now,
For equi-convex lens,
${{R}_{1}}=R,{{R}_{2}}=-R\And \text{focal length}=f$
So, from lens’ maker formula,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\left( n-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{R}-\dfrac{1}{-R} \right)\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2\left( n-1 \right)}{R} \\
& \Rightarrow f=\dfrac{R}{2\left( n-1 \right)}\text{ }\cdots \cdots E{{q}^{n}}.\to \left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
For plano-convex lens,
${{R}_{1}}=R,{{R}_{2}}=\infty \And \text{ focal length}=f'$
So, from lens’ maker formula,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f'}=\left( n-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{R}-\dfrac{1}{\infty } \right)\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f'}=\dfrac{n-1}{R} \\
& \Rightarrow f'=\dfrac{R}{n-1}\text{ }\cdots \cdots E{{q}^{n}}.\to \left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, dividing $E{{q}^{n}}.\to \left( 2 \right)$ by$E{{q}^{n}}.\to \left( 1 \right)$, we get
\[\dfrac{f'}{f}=\dfrac{\dfrac{R}{n-1}}{\dfrac{R}{2\left( n-1 \right)}}\Rightarrow \dfrac{f'}{f}=2\Rightarrow f'=2f\]
So, the focal length of the equi-convex lens gets doubled when it is cut through the optical centre perpendicular to the principal axis.
Hence, the correct answer is $\left( \text{D} \right)$.
Additional information:
The optical centre of a lens is a point inside it through which a ray of light passes undeviated while the principal axis is an imaginary axis which passes through the optical centre and on this axis focal points are located.
Note: Students should notice here that the lens is cut perpendicular to its principal axis, then the focal length is doubled. If it is cut parallel to the principal axis then the focal length will remain unchanged because the curvature of both the surfaces will remain unchanged and thus from the lens’ maker formula, focal length is unaffected. Field of view for the lens will change in this case.
Formula used:
We know that the lens’ maker formula is given by the equation
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\left( n-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}-\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}} \right)$
Where,
$f$ is the focal length of lens
$n$ is the refractive index of material used
${{R}_{1}}$ is the radius of curvature of sphere 1
${{R}_{2}}$ is the radius of curvature of sphere 2.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Assuming the direction of light along positive x-direction.
Now,
For equi-convex lens,
${{R}_{1}}=R,{{R}_{2}}=-R\And \text{focal length}=f$
So, from lens’ maker formula,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\left( n-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{R}-\dfrac{1}{-R} \right)\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2\left( n-1 \right)}{R} \\
& \Rightarrow f=\dfrac{R}{2\left( n-1 \right)}\text{ }\cdots \cdots E{{q}^{n}}.\to \left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
For plano-convex lens,
${{R}_{1}}=R,{{R}_{2}}=\infty \And \text{ focal length}=f'$
So, from lens’ maker formula,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f'}=\left( n-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{R}-\dfrac{1}{\infty } \right)\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f'}=\dfrac{n-1}{R} \\
& \Rightarrow f'=\dfrac{R}{n-1}\text{ }\cdots \cdots E{{q}^{n}}.\to \left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, dividing $E{{q}^{n}}.\to \left( 2 \right)$ by$E{{q}^{n}}.\to \left( 1 \right)$, we get
\[\dfrac{f'}{f}=\dfrac{\dfrac{R}{n-1}}{\dfrac{R}{2\left( n-1 \right)}}\Rightarrow \dfrac{f'}{f}=2\Rightarrow f'=2f\]
So, the focal length of the equi-convex lens gets doubled when it is cut through the optical centre perpendicular to the principal axis.
Hence, the correct answer is $\left( \text{D} \right)$.
Additional information:
The optical centre of a lens is a point inside it through which a ray of light passes undeviated while the principal axis is an imaginary axis which passes through the optical centre and on this axis focal points are located.
Note: Students should notice here that the lens is cut perpendicular to its principal axis, then the focal length is doubled. If it is cut parallel to the principal axis then the focal length will remain unchanged because the curvature of both the surfaces will remain unchanged and thus from the lens’ maker formula, focal length is unaffected. Field of view for the lens will change in this case.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




