
The equation of common tangent to the parabola ${y^2} = 4ax{\text{ and }}{x^2} = 4by$ is
$
{\text{A}}{\text{. }}x{a^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} + y{b^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} + {(ab)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}} = 0 \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. }}\dfrac{1}{{{a^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}}} + \dfrac{y}{{{b^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{{(ab)}^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}}} = 0 \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. }}y{a^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} + x{b^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} - {(ab)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}} = 0 \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. }}\dfrac{1}{{{b^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}}} + \dfrac{y}{{{a^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{{(ab)}^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}}} = 0 \\
$
Answer
614.7k+ views
Hint: In this question ${y^2} = 4ax$ is a parabola whose axis is x-axis and ${x^2} = 4by$ is also a parabola whose axis is y-axis. We have to write their respective equations of tangents. Since, it is given that tangents are common, use the equation in a slope so we can equate slopes and y-intercept of both parabolas to get an equation of common tangent to both.
Complete step-by-step answer:
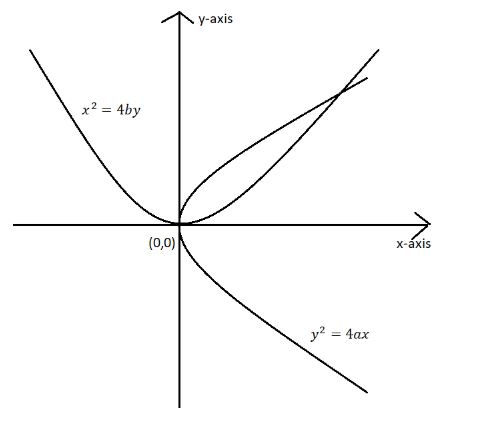
We know equation of tangent to parabola to ${y^2} = 4ax$ is given by
$ \Rightarrow y = mx + \dfrac{a}{m}{\text{ \{ }}m{\text{ is the slope of tangent\} eq}}{\text{.1}}$
And the equation of tangent to parabola to ${x^2} = 4by$ is given by
$
\Rightarrow x = {m_1}y + \dfrac{a}{{{m_1}}}{\text{ \{ }}{m_1} = {\text{slope of tangent\} }} \\
\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{1}{{{m_1}}}x + \dfrac{a}{{{{({m_1})}^2}}}{\text{ eq}}{\text{.2}} \\
$
For common tangent, eq.1 and eq.2 represent the same line. Therefore, the same slope and the same y-intercept.
$
\therefore m = \dfrac{1}{{{m_1}}}{\text{ eq}}{\text{.3}} \\
{\text{and }}\dfrac{a}{m} = - \dfrac{b}{{{m_1}^2}}{\text{ eq}}{\text{.4}} \\
$
Now considering eq.4 using relation of eq.3, we get
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{m} = - \dfrac{b}{{{{({m_1})}^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{m} = - b{m^2} \\
\Rightarrow a = - b{m^3} \\
\Rightarrow m = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{b}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}{\text{ eq}}{\text{.5}} \\
$
Now, put value of$m$from eq.5 into eq.1 we get the equation of common tangent to both the given parabola
$
\Rightarrow y = mx + \dfrac{a}{m} \\
\Rightarrow y = mx + \dfrac{a}{m} \\
\Rightarrow y = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{b}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}x + \dfrac{a}{{{{\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{b}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}}}{\text{ \{ }}m = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{b}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}\} \\
\Rightarrow y = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{b}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}x + a{\left( {\dfrac{{ - b}}{a}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \\
$
Now on rearranging the terms of above equation to get answer in form of given options
Using property$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{a^m}}}{{{a^n}}} = {a^{m - n}}$
We can rewrite above equation as
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{b}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}x + {(a)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}{\left( { - b} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \\
\Rightarrow {(b)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}y = {\left( { - a} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}x + {(a)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}{\left( { - b} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}{(b)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \\ $
Now using property${a^m}.{a^n} = {a^{m + n}}$, we can write above equation as
$ \Rightarrow {\left( a \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}x + {(b)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}y + {(a)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}{(b)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {\left( a \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}x + {(b)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}y + {(ab)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}} = 0 \\ $
Hence, option A. is correct.
Note: Whenever you get this type of question the key concept to solve this is to learn equation of tangents of different curves in different conditions like in this question we require tangent of parabola in different scenario($y = mx + \dfrac{a}{m}$ and $x = {m_1}y + \dfrac{a}{{{m_1}}}{\text{ }}$).
Complete step-by-step answer:

We know equation of tangent to parabola to ${y^2} = 4ax$ is given by
$ \Rightarrow y = mx + \dfrac{a}{m}{\text{ \{ }}m{\text{ is the slope of tangent\} eq}}{\text{.1}}$
And the equation of tangent to parabola to ${x^2} = 4by$ is given by
$
\Rightarrow x = {m_1}y + \dfrac{a}{{{m_1}}}{\text{ \{ }}{m_1} = {\text{slope of tangent\} }} \\
\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{1}{{{m_1}}}x + \dfrac{a}{{{{({m_1})}^2}}}{\text{ eq}}{\text{.2}} \\
$
For common tangent, eq.1 and eq.2 represent the same line. Therefore, the same slope and the same y-intercept.
$
\therefore m = \dfrac{1}{{{m_1}}}{\text{ eq}}{\text{.3}} \\
{\text{and }}\dfrac{a}{m} = - \dfrac{b}{{{m_1}^2}}{\text{ eq}}{\text{.4}} \\
$
Now considering eq.4 using relation of eq.3, we get
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{m} = - \dfrac{b}{{{{({m_1})}^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{m} = - b{m^2} \\
\Rightarrow a = - b{m^3} \\
\Rightarrow m = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{b}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}{\text{ eq}}{\text{.5}} \\
$
Now, put value of$m$from eq.5 into eq.1 we get the equation of common tangent to both the given parabola
$
\Rightarrow y = mx + \dfrac{a}{m} \\
\Rightarrow y = mx + \dfrac{a}{m} \\
\Rightarrow y = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{b}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}x + \dfrac{a}{{{{\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{b}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}}}{\text{ \{ }}m = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{b}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}\} \\
\Rightarrow y = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{b}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}x + a{\left( {\dfrac{{ - b}}{a}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \\
$
Now on rearranging the terms of above equation to get answer in form of given options
Using property$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{a^m}}}{{{a^n}}} = {a^{m - n}}$
We can rewrite above equation as
$ \Rightarrow y = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - a}}{b}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}x + {(a)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}{\left( { - b} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \\
\Rightarrow {(b)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}y = {\left( { - a} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}x + {(a)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}{\left( { - b} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}{(b)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \\ $
Now using property${a^m}.{a^n} = {a^{m + n}}$, we can write above equation as
$ \Rightarrow {\left( a \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}x + {(b)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}y + {(a)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}{(b)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {\left( a \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}x + {(b)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}y + {(ab)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}} = 0 \\ $
Hence, option A. is correct.
Note: Whenever you get this type of question the key concept to solve this is to learn equation of tangents of different curves in different conditions like in this question we require tangent of parabola in different scenario($y = mx + \dfrac{a}{m}$ and $x = {m_1}y + \dfrac{a}{{{m_1}}}{\text{ }}$).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




