
The enzyme, which combines with non-protein part to form a functional enzyme is known as
(a)Coenzyme
(b)Apoenzyme
(c)Holoenzyme
(d)Prosthetic group
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: This kind of enzyme is a catalytically active enzyme that includes an inactive enzyme and a non-polypeptide group of cofactors. Typical examples of such kinds of enzymes are DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase which contain multiple protein subunits.
Complete answer:
The enzyme, which combines with the non-protein part to form a functional enzyme is known as the holoenzyme.
Let's begin the explanation by first understanding what an enzyme is.
A highly specific biomolecule possessing the ability to catalyze biochemical reactions is called an ‘enzyme.’ Enzymes are proteinaceous in nature. They can be simple proteins, for example, lactase, maltase, sucrase, and malate isomerase. But sometimes they can be present in the form of conjugated proteins. Such enzymes are known as ‘holoenzymes’. Holoenzyme consists of a protein part and a non-protein part. The protein part of the enzyme is called ‘apoenzyme’ while the non-protein part is called ‘prosthetic group’ (cofactor). One such example is aminotransferase + pyridoxal phosphate.
Additional Information: -FAD and FMN are examples of coenzymes that contain riboflavin as a prosthetic group. Rate of enzyme activity increases in the presence of coenzymes.
-The cofactor is non-proteinaceous in nature. It can be metal ions or other inorganic ions.
-Prosthetic groups can be organic such as lipids, sugar, and vitamins, or inorganic such as metal ions, but they can never be composed of amino acids.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Holoenzyme.’
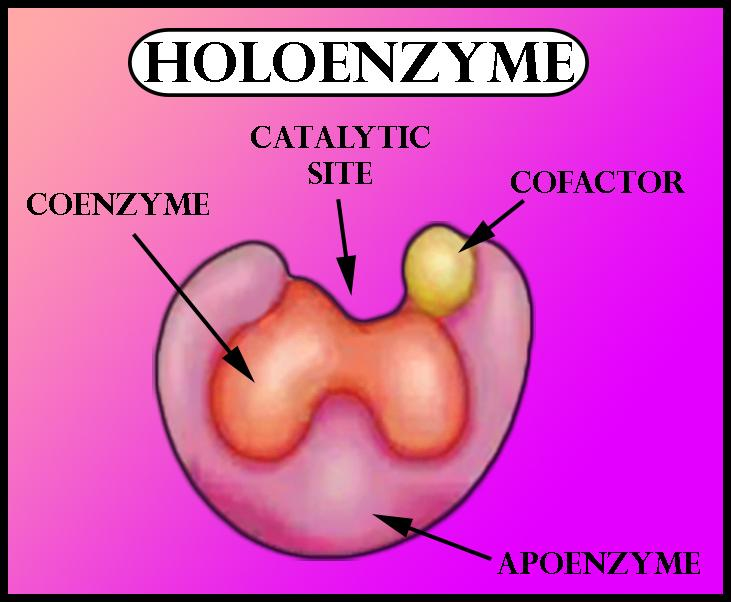
Note: -Coenzymes are a type of cofactor which are organic in nature. Examples of coenzymes are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and ascorbic acid.
-The apoenzyme is often present in an inactive form. Binding with an organic or inorganic cofactor leads to its activation.
-Prosthetic groups are tightly bound, specific non-polypeptide units that are required for the biological functioning of some proteins.
Complete answer:
The enzyme, which combines with the non-protein part to form a functional enzyme is known as the holoenzyme.
Let's begin the explanation by first understanding what an enzyme is.
A highly specific biomolecule possessing the ability to catalyze biochemical reactions is called an ‘enzyme.’ Enzymes are proteinaceous in nature. They can be simple proteins, for example, lactase, maltase, sucrase, and malate isomerase. But sometimes they can be present in the form of conjugated proteins. Such enzymes are known as ‘holoenzymes’. Holoenzyme consists of a protein part and a non-protein part. The protein part of the enzyme is called ‘apoenzyme’ while the non-protein part is called ‘prosthetic group’ (cofactor). One such example is aminotransferase + pyridoxal phosphate.
Additional Information: -FAD and FMN are examples of coenzymes that contain riboflavin as a prosthetic group. Rate of enzyme activity increases in the presence of coenzymes.
-The cofactor is non-proteinaceous in nature. It can be metal ions or other inorganic ions.
-Prosthetic groups can be organic such as lipids, sugar, and vitamins, or inorganic such as metal ions, but they can never be composed of amino acids.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Holoenzyme.’

Note: -Coenzymes are a type of cofactor which are organic in nature. Examples of coenzymes are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and ascorbic acid.
-The apoenzyme is often present in an inactive form. Binding with an organic or inorganic cofactor leads to its activation.
-Prosthetic groups are tightly bound, specific non-polypeptide units that are required for the biological functioning of some proteins.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




