
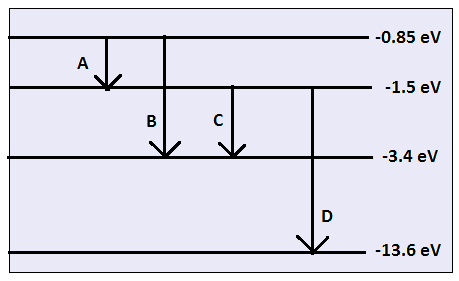
The energy level diagram of the given element is given below. Identify by doing necessary calculation which transition corresponds to the emission of a spectral line of wavelength 102.7 nm.

Answer
498k+ views
Hint: The amount of energy associated with the photon of radiation is directly proportional to the frequency of incident light which is expressed as $E = h\nu $. It shows that higher the frequency of incident light the higher the energy corresponds to photons.
Complete answer:
As we know the relation between energy of photon and frequency of incident light is $E = h\nu $.
Where is defined as a universal constant, known as planck's constant. Value of planck's constant is $6.626 \times {10^{ - 34}}$ Js.
As we know frequency is also expressed in terms of light constant and wavelength of radiation.
$\nu = \dfrac{c}{\lambda }$
So, final equation of energy in terms of wavelength becomes-
$E = \dfrac{{hc}}{\lambda }$
For element A
${E_1} = - 1.5$
${E_2} = - 0.85$
Therefore, difference in energy is
$\Delta {\rm E} = \left( {{E_2} - {E_1}} \right)$
$\Delta {\rm E} = - 0.85 - \left( { - 1.5} \right)$
After solving the above equation, we get $\Delta {\rm E} = 0.65$
Now calculate the wavelength of transition
$\lambda = \dfrac{{hc}}{E}$
$\lambda = \dfrac{{6.626 \times {{10}^{ - 34}} \times 3.0 \times {{10}^8}}}{{0.65 \times 1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}}$
After solving this above equation, we get
$\lambda = 19.038 \times {10^{ - 7}}m$
In terms of nanometer value of wavelength is-
$\lambda = 1903.8nm$
For element B
${E_1} = - 3.4$
${E_2} = - 0.85$
Therefore, difference in energy is
$\Delta {\rm E} = \left( {{E_2} - {E_1}} \right)$
$\Delta {\rm E} = - 0.85 - \left( { - 3.4} \right)$
After solving the above equation, we get $\Delta {\rm E} = 2.55$
Now calculate the wavelength of transition
$\lambda = \dfrac{{hc}}{E}$
$\lambda = \dfrac{{6.626 \times {{10}^{ - 34}} \times 3.0 \times {{10}^8}}}{{2.55 \times 1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}}$
After solving this above equation, we get
$\lambda = 4.8529 \times {10^{ - 7}}m$
In terms of nanometer value of wavelength is-
$\lambda = 485.2nm$
For element C
${E_1} = - 3.4$
${E_2} = - 1.5$
Therefore, difference in energy is
$\Delta {\rm E} = \left( {{E_2} - {E_1}} \right)$
$\Delta {\rm E} = - 1.5 - \left( { - 3.4} \right)$
After solving the above equation, we get $\Delta {\rm E} = 1.9$
Now calculate the wavelength of transition
$\lambda = \dfrac{{hc}}{E}$
$\lambda = \dfrac{{6.626 \times {{10}^{ - 34}} \times 3.0 \times {{10}^8}}}{{1.9 \times 1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}}$
After solving this above equation, we get
$\lambda = 6.5131 \times {10^{ - 7}}m$
In terms of nanometer value of wavelength is-
$\lambda = 651nm$
For element D
${E_1} = - 13.6$
${E_2} = - 1.5$
Therefore, difference in energy is
$\Delta {\rm E} = \left( {{E_2} - {E_1}} \right)$
$\Delta {\rm E} = - 1.5 - \left( { - 13.6} \right)$
After solving the above equation, we get $\Delta {\rm E} = 12.1$
Now calculate the wavelength of transition
$\lambda = \dfrac{{hc}}{E}$
$\lambda = \dfrac{{6.626 \times {{10}^{ - 34}} \times 3.0 \times {{10}^8}}}{{12.1 \times 1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}}$
After solving this above equation, we get
$\lambda = 1.0227 \times {10^{ - 7}}m$
In terms of nanometer value of wavelength is-
$\lambda = 102.27nm$
Hence, from the above calculation transition of element D from $ - 1.5$ ev to $ - 13.6$ ev corresponds with the emission of wavelength of $102.27nm$.
Note:
Make sure to convert the wavelength of the radiation into nanometers and convert the unit of $\Delta {\rm E}$ from volts to electron-volts by multiplying it by $1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}$.
Complete answer:
As we know the relation between energy of photon and frequency of incident light is $E = h\nu $.
Where is defined as a universal constant, known as planck's constant. Value of planck's constant is $6.626 \times {10^{ - 34}}$ Js.
As we know frequency is also expressed in terms of light constant and wavelength of radiation.
$\nu = \dfrac{c}{\lambda }$
So, final equation of energy in terms of wavelength becomes-
$E = \dfrac{{hc}}{\lambda }$
For element A
${E_1} = - 1.5$
${E_2} = - 0.85$
Therefore, difference in energy is
$\Delta {\rm E} = \left( {{E_2} - {E_1}} \right)$
$\Delta {\rm E} = - 0.85 - \left( { - 1.5} \right)$
After solving the above equation, we get $\Delta {\rm E} = 0.65$
Now calculate the wavelength of transition
$\lambda = \dfrac{{hc}}{E}$
$\lambda = \dfrac{{6.626 \times {{10}^{ - 34}} \times 3.0 \times {{10}^8}}}{{0.65 \times 1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}}$
After solving this above equation, we get
$\lambda = 19.038 \times {10^{ - 7}}m$
In terms of nanometer value of wavelength is-
$\lambda = 1903.8nm$
For element B
${E_1} = - 3.4$
${E_2} = - 0.85$
Therefore, difference in energy is
$\Delta {\rm E} = \left( {{E_2} - {E_1}} \right)$
$\Delta {\rm E} = - 0.85 - \left( { - 3.4} \right)$
After solving the above equation, we get $\Delta {\rm E} = 2.55$
Now calculate the wavelength of transition
$\lambda = \dfrac{{hc}}{E}$
$\lambda = \dfrac{{6.626 \times {{10}^{ - 34}} \times 3.0 \times {{10}^8}}}{{2.55 \times 1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}}$
After solving this above equation, we get
$\lambda = 4.8529 \times {10^{ - 7}}m$
In terms of nanometer value of wavelength is-
$\lambda = 485.2nm$
For element C
${E_1} = - 3.4$
${E_2} = - 1.5$
Therefore, difference in energy is
$\Delta {\rm E} = \left( {{E_2} - {E_1}} \right)$
$\Delta {\rm E} = - 1.5 - \left( { - 3.4} \right)$
After solving the above equation, we get $\Delta {\rm E} = 1.9$
Now calculate the wavelength of transition
$\lambda = \dfrac{{hc}}{E}$
$\lambda = \dfrac{{6.626 \times {{10}^{ - 34}} \times 3.0 \times {{10}^8}}}{{1.9 \times 1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}}$
After solving this above equation, we get
$\lambda = 6.5131 \times {10^{ - 7}}m$
In terms of nanometer value of wavelength is-
$\lambda = 651nm$
For element D
${E_1} = - 13.6$
${E_2} = - 1.5$
Therefore, difference in energy is
$\Delta {\rm E} = \left( {{E_2} - {E_1}} \right)$
$\Delta {\rm E} = - 1.5 - \left( { - 13.6} \right)$
After solving the above equation, we get $\Delta {\rm E} = 12.1$
Now calculate the wavelength of transition
$\lambda = \dfrac{{hc}}{E}$
$\lambda = \dfrac{{6.626 \times {{10}^{ - 34}} \times 3.0 \times {{10}^8}}}{{12.1 \times 1.6 \times {{10}^{ - 19}}}}$
After solving this above equation, we get
$\lambda = 1.0227 \times {10^{ - 7}}m$
In terms of nanometer value of wavelength is-
$\lambda = 102.27nm$
Hence, from the above calculation transition of element D from $ - 1.5$ ev to $ - 13.6$ ev corresponds with the emission of wavelength of $102.27nm$.
Note:
Make sure to convert the wavelength of the radiation into nanometers and convert the unit of $\Delta {\rm E}$ from volts to electron-volts by multiplying it by $1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




