
The empirical formula of a monobasic acid is $C{{H}_{2}}O$. The vapour density of its ethyl ester is 44. What is the molecular formula of the acid?
A. ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}{{O}_{2}}$
B. $C{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$
C. ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$
D. ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}{{O}_{3}}$
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Think about the formula that relates vapour density and molecular weight. Relate and visualize the structures and of the respective ester as well as the acid. Find weight of alkyl group attached
Complete answer:
We know the general formulae and structures that define an acid and an ester. Let us consider the structures of the acid with the given empirical formula along with the structure of its ethyl ester.
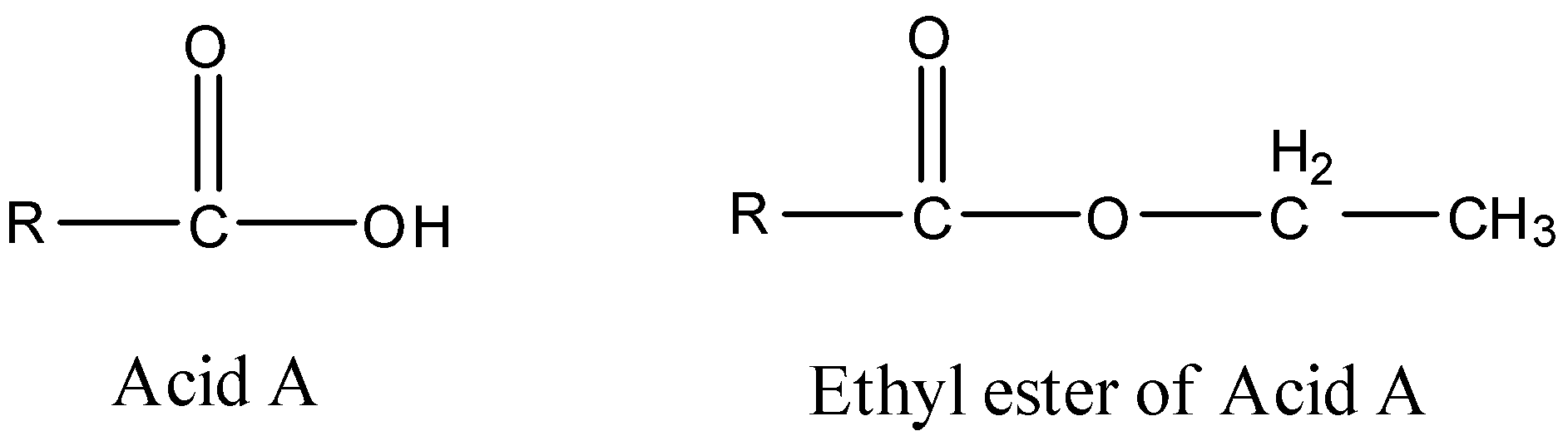
Here, we can see that the acidic hydrogen atom on the acid is replaced by the ethyl group of the aster, and the only unknown left is the parent alkyl group on both the molecules. To calculate that, we will first have to calculate the molecular mass of the ester.
We know that the molecular mass is twice the vapour density. So:
\[\text{molecular mass of ethyl ester of acid A = 2}\times \text{vapour density}\]
We have been given the vapour density of the ethyl ester of acid A as 44, so its molecular weight will be:
\[\begin{align}
& \text{molecular mass}=2\times 44 \\
& \text{molecular mass}=88 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we will find the mass of the unknown alkyl group present in the aster as well as the acid. The total molecular mass of the ester will be equal to the sum of the unknown alkyl group and the mass of the moiety $COO({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})$. First, let us find the molecular mass of this moiety before putting it in the formula.
$\begin{align}
& \text{molecular mass of }COO({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})=(3\times 12)+(2\times 16)+(5\times 1) \\
& \text{molecular mass of }COO({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})=36+32+5 \\
& \text{molecular mass of }COO({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})=73 \\
\end{align}$
So, the mass of the alkyl group will be:
\[\begin{align}
& \text{molecular mass of ester = mass of alkyl group + mass of }COO({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})\text{ moiety} \\
& 88=\text{mass of alkyl group + }73 \\
& \text{mass of alkyl group}=88-73 \\
& \text{mass of alkyl group}=15 \\
\end{align}\]
Now that we have this, let us find the total mass of the acid A.
Total mass of acid A = mass of alkyl group + mass of $-COOH$ group
Total mass of acid A = 15 + 45
Total mass of acid A = 60
Now, to find the molecular formula, we know that:
\[\dfrac{\text{molecular formula}}{\text{empirical formula}}=\dfrac{\text{molecular weight}}{\text{empirical weight}}\]
The empirical weight of the given acid will be:
\[\begin{align}
& \text{empirical weight = }(1\times 12)+(2\times 1)+(1\times 16) \\
& \text{empirical weight = }12+2+16 \\
& \text{empirical weight = }30 \\
\end{align}\]
Putting all the values that we have obtained in the equation mentioned, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\text{molecular formula}}{C{{H}_{2}}O}=\dfrac{60}{30} \\
& \text{molecular formula}=2(C{{H}_{2}}O) \\
& \text{molecular formula}={{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}{{O}_{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the answer to this question is ‘A. ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}{{O}_{2}}$’.
Note:
Remember that here, the molecular formula gives no indication towards the structure of the compound. It is only because we know it is an acid that we are able to visualize its structure. The actual structural molecular formula of the compound concerned is $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$ which is the formula for acetic acid. Be careful and visualize the structure of the compounds given properly.
Complete answer:
We know the general formulae and structures that define an acid and an ester. Let us consider the structures of the acid with the given empirical formula along with the structure of its ethyl ester.

Here, we can see that the acidic hydrogen atom on the acid is replaced by the ethyl group of the aster, and the only unknown left is the parent alkyl group on both the molecules. To calculate that, we will first have to calculate the molecular mass of the ester.
We know that the molecular mass is twice the vapour density. So:
\[\text{molecular mass of ethyl ester of acid A = 2}\times \text{vapour density}\]
We have been given the vapour density of the ethyl ester of acid A as 44, so its molecular weight will be:
\[\begin{align}
& \text{molecular mass}=2\times 44 \\
& \text{molecular mass}=88 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we will find the mass of the unknown alkyl group present in the aster as well as the acid. The total molecular mass of the ester will be equal to the sum of the unknown alkyl group and the mass of the moiety $COO({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})$. First, let us find the molecular mass of this moiety before putting it in the formula.
$\begin{align}
& \text{molecular mass of }COO({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})=(3\times 12)+(2\times 16)+(5\times 1) \\
& \text{molecular mass of }COO({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})=36+32+5 \\
& \text{molecular mass of }COO({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})=73 \\
\end{align}$
So, the mass of the alkyl group will be:
\[\begin{align}
& \text{molecular mass of ester = mass of alkyl group + mass of }COO({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})\text{ moiety} \\
& 88=\text{mass of alkyl group + }73 \\
& \text{mass of alkyl group}=88-73 \\
& \text{mass of alkyl group}=15 \\
\end{align}\]
Now that we have this, let us find the total mass of the acid A.
Total mass of acid A = mass of alkyl group + mass of $-COOH$ group
Total mass of acid A = 15 + 45
Total mass of acid A = 60
Now, to find the molecular formula, we know that:
\[\dfrac{\text{molecular formula}}{\text{empirical formula}}=\dfrac{\text{molecular weight}}{\text{empirical weight}}\]
The empirical weight of the given acid will be:
\[\begin{align}
& \text{empirical weight = }(1\times 12)+(2\times 1)+(1\times 16) \\
& \text{empirical weight = }12+2+16 \\
& \text{empirical weight = }30 \\
\end{align}\]
Putting all the values that we have obtained in the equation mentioned, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\text{molecular formula}}{C{{H}_{2}}O}=\dfrac{60}{30} \\
& \text{molecular formula}=2(C{{H}_{2}}O) \\
& \text{molecular formula}={{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}{{O}_{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the answer to this question is ‘A. ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}{{O}_{2}}$’.
Note:
Remember that here, the molecular formula gives no indication towards the structure of the compound. It is only because we know it is an acid that we are able to visualize its structure. The actual structural molecular formula of the compound concerned is $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$ which is the formula for acetic acid. Be careful and visualize the structure of the compounds given properly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




