
The emitter-base junction of a transistor is__________ biased while the collector-base junction is ____________ biased.
A. Reverse, forward
B. Reverse, reverse
C. Forward, forward
D. Forward, reverse
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: Transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electrons signals and electron power. In the n-p-n transistor the emitter base is forward and the collector base is reversed in the n-p-n junction diode.
Complete answer:
Consider an n-p-n transistor,
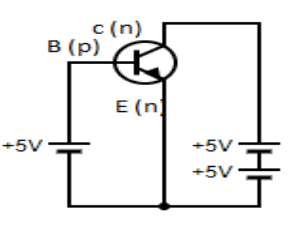
In the above figure, the base is connected to the p transistor, whereas collector and emitter are connected to the n transistor. In base emitter transistors the current is flowing forward biased, whereas, in collector and emitter transistors the current is passing in reverse biased.Thus, the emitter-base junction is forward biased and collector-base junction is reverse biased.
The correct answer is option D.
Additional information: In n-p-n transistor, there are three terminals namely base, emitter and collector. In this transistor the flow of electrons is from emitter to collector, the base diode is slightly doped, the emitter diode is moderately doped and the collector diode is heavily doped. Base is the most important factor in n-p-n transistors.
In an n-p-n transistor is the movement of negative electrons, through the base region which constitute transistor action. Emitter base injects a large amount of charge carrier to the base. Section which collects the majority of charge carriers and supplied by the emitter is called collector. Emitter size is more than base but less than the collector.
Note: : In n-p-n emitter to base causes the flow of electron to n type. Biasing to the transistor ensures that it operates in the active region. The emitter base is forward biased in the n-p-n transistor; the collector base is reversed biased in the n-p-n transistor.
Complete answer:
Consider an n-p-n transistor,

In the above figure, the base is connected to the p transistor, whereas collector and emitter are connected to the n transistor. In base emitter transistors the current is flowing forward biased, whereas, in collector and emitter transistors the current is passing in reverse biased.Thus, the emitter-base junction is forward biased and collector-base junction is reverse biased.
The correct answer is option D.
Additional information: In n-p-n transistor, there are three terminals namely base, emitter and collector. In this transistor the flow of electrons is from emitter to collector, the base diode is slightly doped, the emitter diode is moderately doped and the collector diode is heavily doped. Base is the most important factor in n-p-n transistors.
In an n-p-n transistor is the movement of negative electrons, through the base region which constitute transistor action. Emitter base injects a large amount of charge carrier to the base. Section which collects the majority of charge carriers and supplied by the emitter is called collector. Emitter size is more than base but less than the collector.
Note: : In n-p-n emitter to base causes the flow of electron to n type. Biasing to the transistor ensures that it operates in the active region. The emitter base is forward biased in the n-p-n transistor; the collector base is reversed biased in the n-p-n transistor.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




