
The emf of the cell is 2V and its internal resistance is 2 ohm. A resistance of 8 ohm is joined to the battery in parallel. This is connected to the secondary circuit of the potentiometer. If 1V standard cell balances for 100 cm of potentiometer wire, the balance point of the above cell is.
A. 120 cm
B. 240 cm
C. 160 cm
D. 116 cm
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: So we have the total circuit resistance (internal + external resistance) and the voltage. We will use the formula based on a law of electricity. It is Ohm’s Law or in this case, I = E/R. using potential gradient and potential difference between two points A and B we will solve the question.
Complete step by step answer:
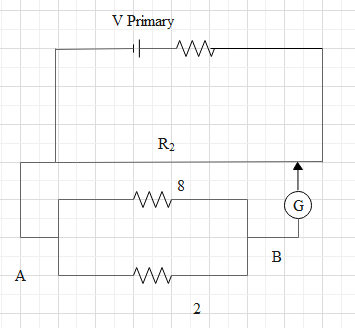
For 1V,
\[\begin{align}
& 1=k\left( 100 \right)........(1) \\
& k=\dfrac{1}{100}V/Cm \\
\end{align}\]
Where k is potential gradient.
Firstly we will form a balanced situation.
After connecting the battery (that is balanced condition) and using the formula for current.
$\begin{align}
& i=\dfrac{E}{r+R}=\dfrac{2}{2+8}=0.2A \\
& {{V}_{A}}-2i+2={{V}_{B}},{{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{B}}=2i-2=2\times 0.2-2 \\
& =1.6V \\
& \therefore {{V}_{B}}-{{V}_{A}}=1.6V \\
& {{V}_{B}}-{{V}_{A}}=k{{l}_{2}}............(2) \\
\end{align}$
Dividing equation (1) by (2).
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{{{V}_{B}}-{{V}_{A}}}=\dfrac{100}{{{l}_{2}}};\dfrac{1}{1.6}=\dfrac{100}{{{l}_{2}}} \\
& {{l}_{2}}=160 cm \\
\end{align}$
The balance point of the above cell is 160 cm.
Therefore the correct option is C.
Additional information:
A potentiometer varies the quantity of current through an electrical or electronic circuit. It is an instrument used to measure an unknown e.m.f by comparison with known e.m.f. example: the quantity control on your radio may be a potentiometer.
Sensitivity of potentiometer: the littlest electric potential which will be measured with the assistance of Potentiometer. A potentiometer is claimed to be more sensitive, if it measures a little electric potential more accurately. Sensitivity of the potentiometer depends on potential gradient.
When we get this balance point, we can then multiply the resistance of the length along the resistance wire where we have zero deflection times the working current of the potentiometer (the resistance wire is of a uniform area, so its resistance per unit length is constant).
Note:
Potential Gradient can be defined as the decrease in potential per unit length. It can be calculated as V / L, where V is the potential difference between two points and L is the distance between two points. We find the balance point (that point along the slide wire where there is zero deflection on the galvanometer) to determine the unknown EMF of a cell/battery that is connected to a potentiometer.
Complete step by step answer:

For 1V,
\[\begin{align}
& 1=k\left( 100 \right)........(1) \\
& k=\dfrac{1}{100}V/Cm \\
\end{align}\]
Where k is potential gradient.
Firstly we will form a balanced situation.
After connecting the battery (that is balanced condition) and using the formula for current.
$\begin{align}
& i=\dfrac{E}{r+R}=\dfrac{2}{2+8}=0.2A \\
& {{V}_{A}}-2i+2={{V}_{B}},{{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{B}}=2i-2=2\times 0.2-2 \\
& =1.6V \\
& \therefore {{V}_{B}}-{{V}_{A}}=1.6V \\
& {{V}_{B}}-{{V}_{A}}=k{{l}_{2}}............(2) \\
\end{align}$
Dividing equation (1) by (2).
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{{{V}_{B}}-{{V}_{A}}}=\dfrac{100}{{{l}_{2}}};\dfrac{1}{1.6}=\dfrac{100}{{{l}_{2}}} \\
& {{l}_{2}}=160 cm \\
\end{align}$
The balance point of the above cell is 160 cm.
Therefore the correct option is C.
Additional information:
A potentiometer varies the quantity of current through an electrical or electronic circuit. It is an instrument used to measure an unknown e.m.f by comparison with known e.m.f. example: the quantity control on your radio may be a potentiometer.
Sensitivity of potentiometer: the littlest electric potential which will be measured with the assistance of Potentiometer. A potentiometer is claimed to be more sensitive, if it measures a little electric potential more accurately. Sensitivity of the potentiometer depends on potential gradient.
When we get this balance point, we can then multiply the resistance of the length along the resistance wire where we have zero deflection times the working current of the potentiometer (the resistance wire is of a uniform area, so its resistance per unit length is constant).
Note:
Potential Gradient can be defined as the decrease in potential per unit length. It can be calculated as V / L, where V is the potential difference between two points and L is the distance between two points. We find the balance point (that point along the slide wire where there is zero deflection on the galvanometer) to determine the unknown EMF of a cell/battery that is connected to a potentiometer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




