
The elevator shown in figure is descending, with an acceleration of $2m/{s^2}$. The mass of the block A is 0.5 kg. The force exerted by the block A on the block B is -
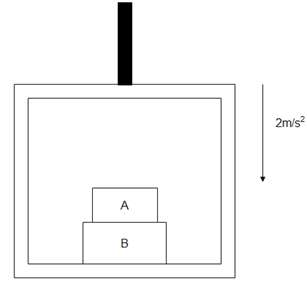

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: While we travel in an elevator that goes down we feel that we had lost some weight and when the elevator goes up we feel weight gain. But the actual mass of us is the same in both cases. It's all due to the variation of normal reactions in both the cases. This can be solved from the ground reference frame.
Formula used:
$\eqalign{
& mg - N = ma \cr
& N = mg - ma \cr
& N = W - ma \cr} $
Complete answer:
When elevator is not moving let the weight of the block be W
$W = mg$
Where m is the mass of block A and g is the acceleration due to gravity
Now when elevator starts moving down with acceleration ‘a’
Normal reaction N acts upward
Weight W acts downward
Force $m \times a$ acts downward
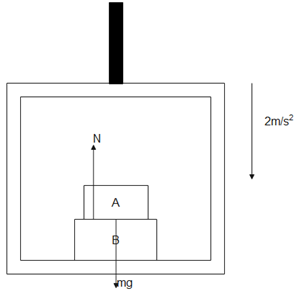
From ground frame of reference
Balancing the forces gives us
$\eqalign{
& mg - N = ma \cr
& \Rightarrow N = mg - ma \cr
& \Rightarrow N=W - ma \cr
& \Rightarrow N = 0.5g - 0.5a \cr
& \Rightarrow N = 5 - \left( {0.5 \times 2} \right) \cr
& \therefore N = 5 - 1 = 4Newton \cr} $
Hence force exerted by block A on block B is 4 newton.
Additional information:
Same question can be solved by the elevator frame of reference. Here pseudo force comes into action. Since elevator blocks system is moving down with acceleration ‘a’ pseudo force will be acting upward and it will be $m \times a$
Upward forces = $N + ma$
Downward forces = $mg$
Equating both the forces we get
$N = W - ma$
Hence both methods will give us the same answer.
Note:
It is to be noted that only weight seems to be increased but not mass. Because mass is always constant wherever we go but weights vary as resultant acceleration varies. A freely falling body feels no weight due to the same property as resultant acceleration would be (g-g =0)zero. This is called weightlessness. Same applies with the astronaut in the satellite where he feels weightlessness.
Formula used:
$\eqalign{
& mg - N = ma \cr
& N = mg - ma \cr
& N = W - ma \cr} $
Complete answer:
When elevator is not moving let the weight of the block be W
$W = mg$
Where m is the mass of block A and g is the acceleration due to gravity
Now when elevator starts moving down with acceleration ‘a’
Normal reaction N acts upward
Weight W acts downward
Force $m \times a$ acts downward

From ground frame of reference
Balancing the forces gives us
$\eqalign{
& mg - N = ma \cr
& \Rightarrow N = mg - ma \cr
& \Rightarrow N=W - ma \cr
& \Rightarrow N = 0.5g - 0.5a \cr
& \Rightarrow N = 5 - \left( {0.5 \times 2} \right) \cr
& \therefore N = 5 - 1 = 4Newton \cr} $
Hence force exerted by block A on block B is 4 newton.
Additional information:
Same question can be solved by the elevator frame of reference. Here pseudo force comes into action. Since elevator blocks system is moving down with acceleration ‘a’ pseudo force will be acting upward and it will be $m \times a$
Upward forces = $N + ma$
Downward forces = $mg$
Equating both the forces we get
$N = W - ma$
Hence both methods will give us the same answer.
Note:
It is to be noted that only weight seems to be increased but not mass. Because mass is always constant wherever we go but weights vary as resultant acceleration varies. A freely falling body feels no weight due to the same property as resultant acceleration would be (g-g =0)zero. This is called weightlessness. Same applies with the astronaut in the satellite where he feels weightlessness.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




