
The electric potential energy of a uniformly charged thin spherical shell of radius R having total charge Q is
$\begin{align}
& a)\dfrac{K{{Q}^{2}}}{2R} \\
& b)\dfrac{K{{Q}^{2}}}{6R} \\
& c)\dfrac{K{{Q}^{2}}}{8R} \\
& d)\dfrac{K{{Q}^{2}}}{16R} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: The electric potential energy of the above shell asked is basically the energy required to form the assembly of the charge total charge Q on the shell. To find the energy of the spherical shell we will bring small charge dq from infinity to the shell having initially some charge q. Further will integrate the work done in bringing the charge at the charge to the shell assuming the initial charge is zero.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To begin with let us consider a spherical shell of radius R and having charge q. hence the electrostatic potential on the shell is $V=\dfrac{Kq}{R}\text{,where K is the permittivity of free space}$
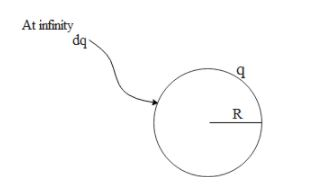
Now let us say we bring small charge dq from infinity such that the final charge on the thin spherical shell is Q. Hence the work done to form an assembly of such charge is given by,
$E=\int\limits_{{{Q}_{0}}}^{Q}{\dfrac{Kqdq}{R}}\text{,where }{{\text{Q}}_{\text{0}}}\text{ is the initial charge on the shell}$ .
We want to calculate the energy of formation of the shell from the beginning, hence the initial charge on the shell must be zero. Therefore we get the above equation as,
$\begin{align}
& W=\int\limits_{0}^{Q}{\dfrac{Kqdq}{R}}\text{since K and R are constant,} \\
& W=\dfrac{K}{R}\int\limits_{0}^{Q}{qdq} \\
& W=\dfrac{K}{R}\left[ \dfrac{{{q}^{2}}}{2} \right]_{0}^{Q} \\
& W=\dfrac{K{{Q}^{2}}}{2R} \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option a”.
Note: K is the permittivity of free space. Its value is given to be as $\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{\circ }}}=9\times {{10}^{9}}Nm/{{C}^{2}}$. It is to be noted that the above scenario is taking place in vacuum. If the same had to happen in some other medium than the energy required would have been lesser than the value we obtained for work done in vacuum.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To begin with let us consider a spherical shell of radius R and having charge q. hence the electrostatic potential on the shell is $V=\dfrac{Kq}{R}\text{,where K is the permittivity of free space}$

Now let us say we bring small charge dq from infinity such that the final charge on the thin spherical shell is Q. Hence the work done to form an assembly of such charge is given by,
$E=\int\limits_{{{Q}_{0}}}^{Q}{\dfrac{Kqdq}{R}}\text{,where }{{\text{Q}}_{\text{0}}}\text{ is the initial charge on the shell}$ .
We want to calculate the energy of formation of the shell from the beginning, hence the initial charge on the shell must be zero. Therefore we get the above equation as,
$\begin{align}
& W=\int\limits_{0}^{Q}{\dfrac{Kqdq}{R}}\text{since K and R are constant,} \\
& W=\dfrac{K}{R}\int\limits_{0}^{Q}{qdq} \\
& W=\dfrac{K}{R}\left[ \dfrac{{{q}^{2}}}{2} \right]_{0}^{Q} \\
& W=\dfrac{K{{Q}^{2}}}{2R} \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option a”.
Note: K is the permittivity of free space. Its value is given to be as $\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{\circ }}}=9\times {{10}^{9}}Nm/{{C}^{2}}$. It is to be noted that the above scenario is taking place in vacuum. If the same had to happen in some other medium than the energy required would have been lesser than the value we obtained for work done in vacuum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




