
The electric field produced by a positive charge is always directed outwards of the positive charge, while the electric produced by a negative charge is always directed inwards to the negative charge.
A). $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}d}{\left( 1+\sqrt{3} \right)}\text{ from +3q charge, yes}$
B). $\dfrac{\sqrt{5}d}{\left( 1+\sqrt{3} \right)}\text{ from +3q charge, yes}$
C). $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}d}{\left( 1+\sqrt{2} \right)}\text{ from +3q charge, yes}$
D). $\dfrac{\sqrt{2}d}{\left( 1+\sqrt{3} \right)}\text{ from +3q charge, yes}$

Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: Each charge at the end of the rod will produce its own electric field. Since both, the charges at the end are positive charges, the field will be directed outside. The charge Q, which is free to move along the rod, will be repelled by both the charges. The charge Q will situate itself at a point on the rod, where there is less repulsion. Since the magnitude of the electric field produced by the +3q charge is more than the +1q, the charge Q will be closer to the +1q charge than the +3q charge.
Formula Used:
According Coulomb’s law the force of attraction or repulsion between two charges ${{q}_{1\text{ }}}and\text{ }{{\text{q}}_{2}}$ separated by a distance r is given as,
$\overrightarrow{F}=k\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}{{q}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}\widehat{r}$
Where
k is a proportionality constant whose value is $9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$
$\hat{r}$ is the unit vector along the distance r.
Complete step by step answer:
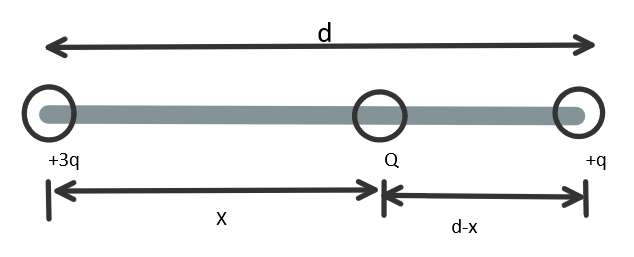
In the question we have a long horizontal, insulating rod which has charges $\text{3q and q}$ fixed at its end, a charge Q is placed on the rod, which can slide along the rod. So in order to find the equilibrium position of the charge Q along the rod, we need to know the forces acting on charge Q. Let the charge Q be at a distance $x$ from the charge 3q and $\left( d-x \right)$ distance from the charge q.
The electrostatic force acting on charge Q due to charge 3q is, the field will be along the rod from left to right.
${{F}_{1}}=k\dfrac{3qQ}{{{x}^{2}}}$ … equation (1)
Where k is a proportionality constant whose value is $9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$
The electrostatic force acting on charge Q due to charge q is, the field will be along the rod from right to left.
${{F}_{2}}=k\dfrac{qQ}{{{\left( d-x \right)}^{2}}}$ …. equation (2)
The charge Q will be in equilibrium when the sum of the forces acting on it is zero, so we can write, $\sum{{{F}_{i}}=0}$
Substituting the forces in equation (1) and (2) in the above equations, we get,
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{1}}-{{F}_{2}}=0$
The minus sign is due to the direction of these fields which are opposite to each other.
$k\dfrac{3qQ}{{{x}^{2}}}-k\dfrac{qQ}{{{\left( d-x \right)}^{2}}}=0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{{{x}^{2}}}-\dfrac{1}{{{\left( d-x \right)}^{2}}}=0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{x}=\dfrac{1}{d-x}$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}d=\left( 1+\sqrt{3} \right)x$
$\therefore x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}d}{\left( 1+\sqrt{3} \right)}$
So, the equilibrium will be at a distance of $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}d}{\left( 1+\sqrt{3} \right)}$ from the charge +3q.
The charge Q is in a stable equilibrium position.
So, the answer to the question is option (A).
Note: The electric field produced by a charge q at a distance r from the charge is given by,
$\overrightarrow{E}=k\dfrac{q}{{{r}^{2}}}\hat{r}$
Where
k is a proportionality constant whose value is $9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$
$\hat{r}$ is the unit vector along the distance r.
The proportional k can be written as,
$k=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
Where ${{\varepsilon }_{0}}$ is known as the permittivity of free space, whose value is $8.85\times {{10}^{-12}}Farad/metre$.
The electric field produced by a positive charge is always directed outwards of the positive charge, while the electric produced by a negative charge is always directed inwards to the negative charge.
Formula Used:
According Coulomb’s law the force of attraction or repulsion between two charges ${{q}_{1\text{ }}}and\text{ }{{\text{q}}_{2}}$ separated by a distance r is given as,
$\overrightarrow{F}=k\dfrac{{{q}_{1}}{{q}_{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}\widehat{r}$
Where
k is a proportionality constant whose value is $9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$
$\hat{r}$ is the unit vector along the distance r.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question we have a long horizontal, insulating rod which has charges $\text{3q and q}$ fixed at its end, a charge Q is placed on the rod, which can slide along the rod. So in order to find the equilibrium position of the charge Q along the rod, we need to know the forces acting on charge Q. Let the charge Q be at a distance $x$ from the charge 3q and $\left( d-x \right)$ distance from the charge q.
The electrostatic force acting on charge Q due to charge 3q is, the field will be along the rod from left to right.
${{F}_{1}}=k\dfrac{3qQ}{{{x}^{2}}}$ … equation (1)
Where k is a proportionality constant whose value is $9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$
The electrostatic force acting on charge Q due to charge q is, the field will be along the rod from right to left.
${{F}_{2}}=k\dfrac{qQ}{{{\left( d-x \right)}^{2}}}$ …. equation (2)
The charge Q will be in equilibrium when the sum of the forces acting on it is zero, so we can write, $\sum{{{F}_{i}}=0}$
Substituting the forces in equation (1) and (2) in the above equations, we get,
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{1}}-{{F}_{2}}=0$
The minus sign is due to the direction of these fields which are opposite to each other.
$k\dfrac{3qQ}{{{x}^{2}}}-k\dfrac{qQ}{{{\left( d-x \right)}^{2}}}=0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{{{x}^{2}}}-\dfrac{1}{{{\left( d-x \right)}^{2}}}=0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{x}=\dfrac{1}{d-x}$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}d=\left( 1+\sqrt{3} \right)x$
$\therefore x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}d}{\left( 1+\sqrt{3} \right)}$
So, the equilibrium will be at a distance of $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}d}{\left( 1+\sqrt{3} \right)}$ from the charge +3q.
The charge Q is in a stable equilibrium position.
So, the answer to the question is option (A).
Note: The electric field produced by a charge q at a distance r from the charge is given by,
$\overrightarrow{E}=k\dfrac{q}{{{r}^{2}}}\hat{r}$
Where
k is a proportionality constant whose value is $9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$
$\hat{r}$ is the unit vector along the distance r.
The proportional k can be written as,
$k=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
Where ${{\varepsilon }_{0}}$ is known as the permittivity of free space, whose value is $8.85\times {{10}^{-12}}Farad/metre$.
The electric field produced by a positive charge is always directed outwards of the positive charge, while the electric produced by a negative charge is always directed inwards to the negative charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




