
The electric charges are distributed in a small volume. The flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of a radius of $10cm$ surrounding the total charge is $20Vm$. The flux over a concentric sphere of radius $20cm$ will be
A. $20Vm$
B. $25Vm$
C. $40Vm$
D. $200Vm$
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: In this question, we use gauss law. It states that total electric flux $\left( \phi \right)$ through any closed in free space is equal to $1/{ \in _o}$ times the total electric charge $\left( q \right)$ enclosed by the surface. Here electric flux means the total number of electric field lines passing through that surface.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question we have,
Radius of spherical surface (r)$ = 10\;cm$
Total charge (q) =$20\; Vm$
Radius of second spherical surface (R) $ = 20\;cm$
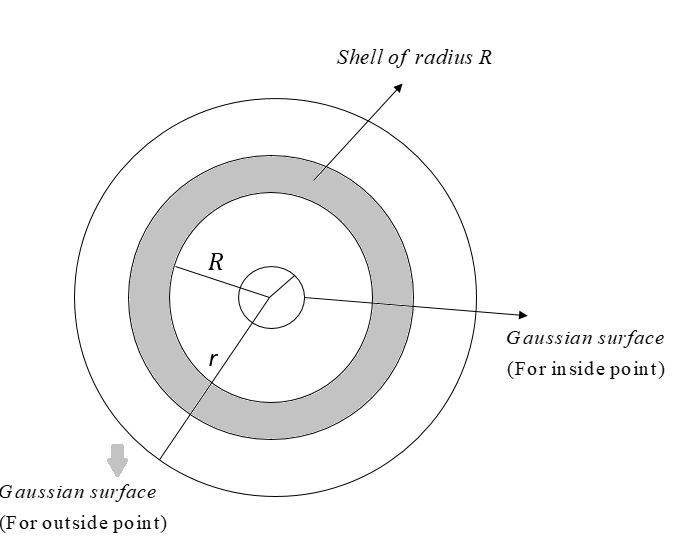
Consider two concentric spheres having different radii (r and R), but the total charge is the same for both the spheres.
Now by using Gauss' law, Flux for sphere having radius r ${\phi _{10}} = \dfrac{{{{\rm{q}}_{10}}}}{{{ \in _0}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\rm{q}}_{10}} = 20{ \in _0}$
Again Flux for second shere R ${\phi _{20}} = \dfrac{{{{\rm{q}}_{20}}}}{{{ \in _0}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\rm{q}}_{20}} = 20{ \in _0}$
Since the electric flux through a surface is independent of shape and size, it only depends upon the charge enclosed inside the volume. Thus charge enclosed by the sphere of radii 10cm and 20cm. So the flux remains the same for both spheres, i.e., $20{\rm{Vm}}$. Hence option (A) is correct.
Note:
The gaussian surface is in the form of a sphere at radius r > R, the electric field has the same magnitude at every point of the surface and is directed outward. The electric flux is then just the electric field times the area of the spherical surface. Here the Gaussian surface means an imaginary surface.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question we have,
Radius of spherical surface (r)$ = 10\;cm$
Total charge (q) =$20\; Vm$
Radius of second spherical surface (R) $ = 20\;cm$

Consider two concentric spheres having different radii (r and R), but the total charge is the same for both the spheres.
Now by using Gauss' law, Flux for sphere having radius r ${\phi _{10}} = \dfrac{{{{\rm{q}}_{10}}}}{{{ \in _0}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\rm{q}}_{10}} = 20{ \in _0}$
Again Flux for second shere R ${\phi _{20}} = \dfrac{{{{\rm{q}}_{20}}}}{{{ \in _0}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\rm{q}}_{20}} = 20{ \in _0}$
Since the electric flux through a surface is independent of shape and size, it only depends upon the charge enclosed inside the volume. Thus charge enclosed by the sphere of radii 10cm and 20cm. So the flux remains the same for both spheres, i.e., $20{\rm{Vm}}$. Hence option (A) is correct.
Note:
The gaussian surface is in the form of a sphere at radius r > R, the electric field has the same magnitude at every point of the surface and is directed outward. The electric flux is then just the electric field times the area of the spherical surface. Here the Gaussian surface means an imaginary surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




