
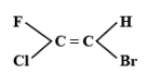
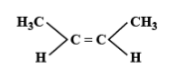
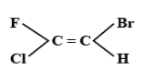
The E-isomer is shown by:
A.
B.
C.
D.
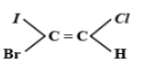



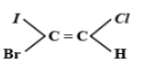
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, recall the concept of geometrical isomerism. Geometrical isomerism is defined as the type of stereoisomerism having the same molecular formula and same structure but differ in the relative arrangement of atoms. E isomer is analogous to the trans isomer and Z isomer is analogous to cis isomer.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that isomers are defined as the molecules with the same molecular formula but possess a different arrangement of the atoms in space or different connectivity of atoms. The phenomenon in which the molecules that form the isomers are connected differently is known as structural isomerism. The phenomenon in which the connectivity of atoms is the same in isomers but a different spatial arrangement is a stereoisomerism.
The E-Z isomerism is a type of geometrical isomerism when all the four groups attached are different. In case the two groups with the higher priorities i.e. higher atomic number are on the same side of the double bond, then that molecule is termed as Z- isomer. So, the IUPAC name of that compound will be (Z)-name of the compound. The symbol Z denotes together and is derived from the German word zusammen. In the second case if the two groups with the higher priorities i.e. higher atomic number are attached on opposite sides of the double bond, then this isomer is called (E)- isomer. E means opposite and is derived from the German word entgegen.
We can write the isomers for the given compounds as:
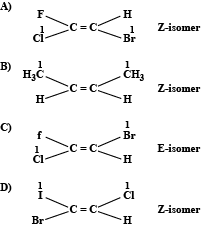
Hence option C is correct.
Note:
Geometric isomerism is one of the forms of stereoisomerism. The key point in geometrical isomers is the restricted rotation of a bond present somewhere in a molecule. At the most basic level of organic chemistry, carbon-carbon double bond is one of the examples leading to a restricted rotation.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that isomers are defined as the molecules with the same molecular formula but possess a different arrangement of the atoms in space or different connectivity of atoms. The phenomenon in which the molecules that form the isomers are connected differently is known as structural isomerism. The phenomenon in which the connectivity of atoms is the same in isomers but a different spatial arrangement is a stereoisomerism.
The E-Z isomerism is a type of geometrical isomerism when all the four groups attached are different. In case the two groups with the higher priorities i.e. higher atomic number are on the same side of the double bond, then that molecule is termed as Z- isomer. So, the IUPAC name of that compound will be (Z)-name of the compound. The symbol Z denotes together and is derived from the German word zusammen. In the second case if the two groups with the higher priorities i.e. higher atomic number are attached on opposite sides of the double bond, then this isomer is called (E)- isomer. E means opposite and is derived from the German word entgegen.
We can write the isomers for the given compounds as:

Hence option C is correct.
Note:
Geometric isomerism is one of the forms of stereoisomerism. The key point in geometrical isomers is the restricted rotation of a bond present somewhere in a molecule. At the most basic level of organic chemistry, carbon-carbon double bond is one of the examples leading to a restricted rotation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




