
The drift current in p-n junction is
A. from the n- side to the p- side
B. from the p- side to the n- side
C. from the n- side to the p-side if the junction is forward- biased and in the opposite direction if it is reverse biased
D. from the p- side to the n-side if the junction is forward- biased and in the opposite direction if it is reverse biased
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: In p- n junction, holes from p side and electrons from n side start moving to the opposite side. The movement of electron and holes gives rise to a potential difference, which set up barrier field and starts pushing electrons towards n- side and holes towards p- side
Complete answer:
When the p- n junction is created, the p- side of the junction has higher concentration of holes whereas n- side has higher concentration of electrons. Because of this concentration difference, the electrons begin to move from n- side to p- side whereas holes begin to move from p- side to n – side. This results in the depletion region and this forms an electric field close to the junction from the n- p side.
The formation of the p- n junction is shown in the figure below:
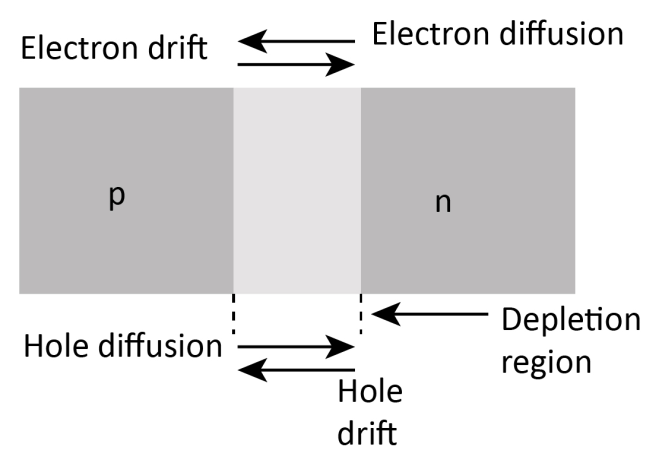
Any electron is pushed by this electric field to the p- side and any hole is pushed by the electric field to the n –side. This results in a potential difference across the junction also known as the potential barrier.
The barrier potential develops a barrier field in the direction n to p side. This barrier field immediately pushes the electron towards the n- side and holes towards the p- side, and then a current is set up by the barrier field from n to p side. This current is known as drift current.
Note:
The movement of majority charge carriers across the junction results in an electric current from p to n side and this current is called diffusion current.
The drift and diffusion current directions are opposite.
The electrons begin to move from n- side to p- side whereas holes begin to move from p- side to n – side.
Complete answer:
When the p- n junction is created, the p- side of the junction has higher concentration of holes whereas n- side has higher concentration of electrons. Because of this concentration difference, the electrons begin to move from n- side to p- side whereas holes begin to move from p- side to n – side. This results in the depletion region and this forms an electric field close to the junction from the n- p side.
The formation of the p- n junction is shown in the figure below:

Any electron is pushed by this electric field to the p- side and any hole is pushed by the electric field to the n –side. This results in a potential difference across the junction also known as the potential barrier.
The barrier potential develops a barrier field in the direction n to p side. This barrier field immediately pushes the electron towards the n- side and holes towards the p- side, and then a current is set up by the barrier field from n to p side. This current is known as drift current.
Note:
The movement of majority charge carriers across the junction results in an electric current from p to n side and this current is called diffusion current.
The drift and diffusion current directions are opposite.
The electrons begin to move from n- side to p- side whereas holes begin to move from p- side to n – side.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




