
The distance of the point $P\left( 3,8,2 \right)$ from the line $\dfrac{x-1}{2}=\dfrac{y-3}{4}=\dfrac{z-2}{3}$ measured parallel to the plane $3x+2y-2z+15=0$ is
A. 7
B. 9
C. $\sqrt{7}$
D. 49
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: We are asked to find the distance from a point to the line measured parallel to a plane. To do this kind of problem in 3D, we should construct a plane parallel to the given plane $3x+2y-2z+15=0$ and pass through $P\left( 3,8,2 \right)$. The plane parallel to $3x+2y-2z+15=0$ is given by $3x+2y-2z+d=0$. By substituting P, we can get the required plane. To find the required distance, we should find the point of intersection of the new plane and the line $\dfrac{x-1}{2}=\dfrac{y-3}{4}=\dfrac{z-2}{3}$. By assuming $\dfrac{x-1}{2}=\dfrac{y-3}{4}=\dfrac{z-2}{3}=\beta $ and substituting the values of x, y, z in the new plane, we get the point of intersection B. The required distance is the distance between the point of intersection B and the given point $P\left( 3,8,2 \right)$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
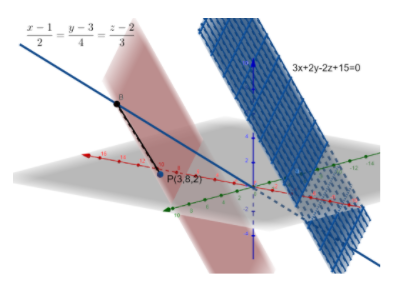
The equation of a plane parallel to $ax+by+cz+d=0$ is $ax+by+cz+{{d}_{1}}=0$.
Here, the equation of the plane is $3x+2y-2z+15=0$. In the above diagram, it is denoted by the blue surface.
Let us assume the equation of the plane parallel to the plane as $3x+2y-2z+d=0$.
We know that the point $P\left( 3,8,2 \right)$ lies on the plane $3x+2y-2z+d=0$. Let us substitute the point in the equation of the plane.
$\begin{align}
& 3\times 3+2\times 8-2\times 2+d=0 \\
& 21+d=0 \\
& d=-21 \\
\end{align}$
The equation of the required plane is $3x+2y-2z-21=0$. In the diagram, it is denoted by the light cream coloured surface.
The required distance along the plane is given by the distance between the point P and the point of intersection of the line $\dfrac{x-1}{2}=\dfrac{y-3}{4}=\dfrac{z-2}{3}=\beta $ and the plane $3x+2y-2z-21=0$. It is denoted by B.
Using this equation, $\dfrac{x-1}{2}=\dfrac{y-3}{4}=\dfrac{z-2}{3}=\beta $
$\begin{align}
& x=2\beta +1 \\
& y=4\beta +3 \\
& z=3\beta +2 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the values in the plane $3x+2y-2z-21=0$.
$\begin{align}
& 3\left( 2\beta +1 \right)+2\left( 4\beta +3 \right)-2\left( 3\beta +2 \right)-21=0 \\
& 6\beta +3+8\beta +6-6\beta -4-21=0 \\
& 8\beta =16 \\
& \beta =2 \\
\end{align}$
The point B is $\left( 2\times 2+1,4\times 2+3,3\times 2+2 \right)=\left( 5,11,8 \right)$
The distance between the two points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}},{{z}_{1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}},{{z}_{2}} \right)$ is given by
\[\text{distance}=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{z}_{2}}-{{z}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
Distance between the points P and B is
\[\text{distance}=\sqrt{{{\left( 5-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 11-8 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 8-2 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{4+9+36}=\sqrt{49}=7\]
$\therefore $ The required distance is equal to 7 units. The answer is option-A.
Note: An alternative way is to take a parametric form of the point B. The parametric form of the point B is $\left( 2\beta +1,4\beta +3,3\beta +2 \right)$. The line PB is perpendicular to the normal of the plane $3x+2y-2z+15=0$. The directional ratios of PB are $\begin{align}
& 2\beta +1-3,4\beta +3-8,3\beta +2-2 \\
& 2\beta -2,4\beta -5,3\beta \\
\end{align}$
Applying the perpendicular condition, we get
$\begin{align}
& \left( 2\beta -2 \right)\times 3+\left( 4\beta -5 \right)\times 2+\left( 3\beta \right)\times \left( -2 \right)=0 \\
& 6\beta -6+8\beta -10-6\beta =0 \\
& 8\beta =16 \\
& \beta =2 \\
\end{align}$
Using this and by calculating the perpendicular distance, we get the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:

The equation of a plane parallel to $ax+by+cz+d=0$ is $ax+by+cz+{{d}_{1}}=0$.
Here, the equation of the plane is $3x+2y-2z+15=0$. In the above diagram, it is denoted by the blue surface.
Let us assume the equation of the plane parallel to the plane as $3x+2y-2z+d=0$.
We know that the point $P\left( 3,8,2 \right)$ lies on the plane $3x+2y-2z+d=0$. Let us substitute the point in the equation of the plane.
$\begin{align}
& 3\times 3+2\times 8-2\times 2+d=0 \\
& 21+d=0 \\
& d=-21 \\
\end{align}$
The equation of the required plane is $3x+2y-2z-21=0$. In the diagram, it is denoted by the light cream coloured surface.
The required distance along the plane is given by the distance between the point P and the point of intersection of the line $\dfrac{x-1}{2}=\dfrac{y-3}{4}=\dfrac{z-2}{3}=\beta $ and the plane $3x+2y-2z-21=0$. It is denoted by B.
Using this equation, $\dfrac{x-1}{2}=\dfrac{y-3}{4}=\dfrac{z-2}{3}=\beta $
$\begin{align}
& x=2\beta +1 \\
& y=4\beta +3 \\
& z=3\beta +2 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the values in the plane $3x+2y-2z-21=0$.
$\begin{align}
& 3\left( 2\beta +1 \right)+2\left( 4\beta +3 \right)-2\left( 3\beta +2 \right)-21=0 \\
& 6\beta +3+8\beta +6-6\beta -4-21=0 \\
& 8\beta =16 \\
& \beta =2 \\
\end{align}$
The point B is $\left( 2\times 2+1,4\times 2+3,3\times 2+2 \right)=\left( 5,11,8 \right)$
The distance between the two points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}},{{z}_{1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}},{{z}_{2}} \right)$ is given by
\[\text{distance}=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{z}_{2}}-{{z}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
Distance between the points P and B is
\[\text{distance}=\sqrt{{{\left( 5-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 11-8 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 8-2 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{4+9+36}=\sqrt{49}=7\]
$\therefore $ The required distance is equal to 7 units. The answer is option-A.
Note: An alternative way is to take a parametric form of the point B. The parametric form of the point B is $\left( 2\beta +1,4\beta +3,3\beta +2 \right)$. The line PB is perpendicular to the normal of the plane $3x+2y-2z+15=0$. The directional ratios of PB are $\begin{align}
& 2\beta +1-3,4\beta +3-8,3\beta +2-2 \\
& 2\beta -2,4\beta -5,3\beta \\
\end{align}$
Applying the perpendicular condition, we get
$\begin{align}
& \left( 2\beta -2 \right)\times 3+\left( 4\beta -5 \right)\times 2+\left( 3\beta \right)\times \left( -2 \right)=0 \\
& 6\beta -6+8\beta -10-6\beta =0 \\
& 8\beta =16 \\
& \beta =2 \\
\end{align}$
Using this and by calculating the perpendicular distance, we get the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




