
The dihalides in which halogen atoms are attached to adjacent carbon atom are termed:
(a)- Vicinal dihalides
(b)- Geminal dihalides
(c)- Both A and B
(d)- None of the above
Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: By the position of the halogens on the carbon atom we can classify them into vicinal and geminal, and both are different. Both the terms are used when the number of halogens in the carbon chain is 2.
Complete answer:
We know that in a carbon chain there are many types of substituents by which we can name the compound. And with these substituents, we can also classify the compound. For example when different functional groups are present, then we can classify them into different compounds.
So, when the carbon chain contains two halogen atoms then by the position of the halogen toms we can classify them into two, i.e., vicinal dihalides and geminal dihalides.
If the same carbon atom has both halogen atoms then it is classified as geminal halides. For example, 1,1-Dibromoethane. Its structure is given below:
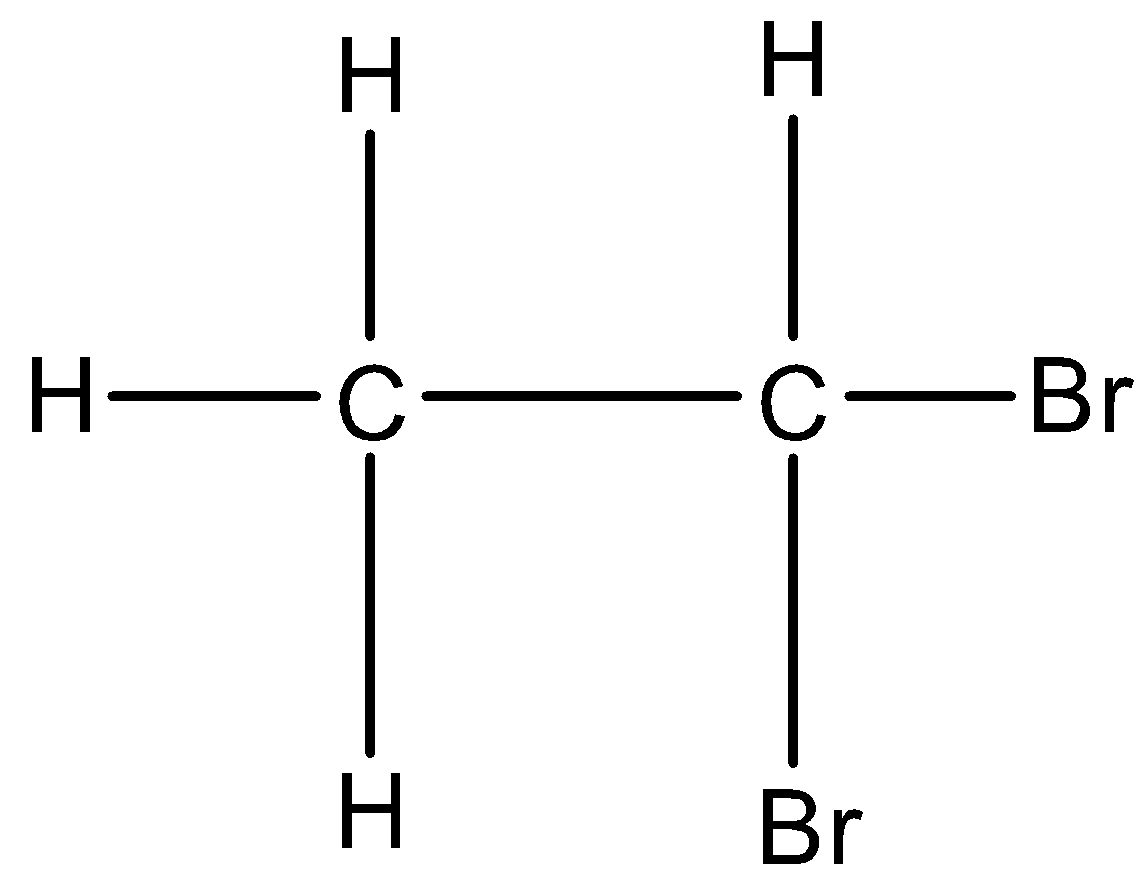
In this the same carbon atom has both the bromine atoms, hence it is geminal dihalides.
And if the halogen atoms are placed on the adjacent carbon atoms then it is classified as vicinal dihalides. For example, 1,2-Dibromoethane. Its structure is given below:
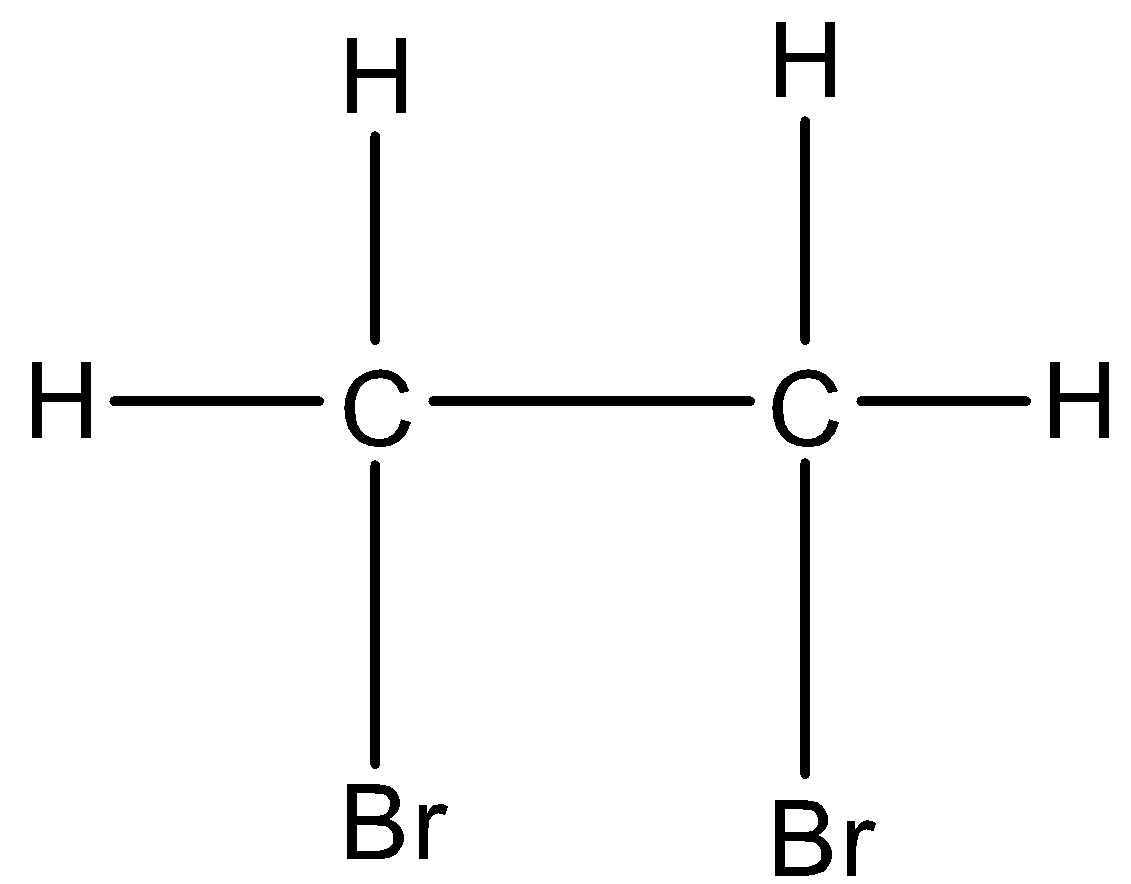
In this two different carbon atoms are having the bromine atom and both are at an adjacent position.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (a)- Vicinal dihalides.
Note:
If there is a gap of carbon atoms between the two carbon atoms having the halogen atoms then it is classified as isolated dihalides, even if there is only one carbon in-between the dihalides. For example, 1,3-Dibromopropane, 1,4-Dibromohexane, etc.
Complete answer:
We know that in a carbon chain there are many types of substituents by which we can name the compound. And with these substituents, we can also classify the compound. For example when different functional groups are present, then we can classify them into different compounds.
So, when the carbon chain contains two halogen atoms then by the position of the halogen toms we can classify them into two, i.e., vicinal dihalides and geminal dihalides.
If the same carbon atom has both halogen atoms then it is classified as geminal halides. For example, 1,1-Dibromoethane. Its structure is given below:

In this the same carbon atom has both the bromine atoms, hence it is geminal dihalides.
And if the halogen atoms are placed on the adjacent carbon atoms then it is classified as vicinal dihalides. For example, 1,2-Dibromoethane. Its structure is given below:

In this two different carbon atoms are having the bromine atom and both are at an adjacent position.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (a)- Vicinal dihalides.
Note:
If there is a gap of carbon atoms between the two carbon atoms having the halogen atoms then it is classified as isolated dihalides, even if there is only one carbon in-between the dihalides. For example, 1,3-Dibromopropane, 1,4-Dibromohexane, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




