
The correct statement of $\alpha $ elimination is?
A) It forms cyclic compounds.
B) It forms carbene or substituted carbene.
C) Two atoms are removed from $\alpha $ and $\beta $ positions.
D) In \[CHC{l_3}\],$\alpha $ elimination is not possible.
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: Alpha$(\alpha )$elimination is the elimination in which both the proton and the leaving group are located on the same atom ($\alpha $atom). The proton is eliminated first followed by the elimination of the leaving group.
Complete answer:
Elimination reactions are the type of chemical reactions in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one-step or a two-step mechanism. Alpha elimination is a category of elimination reactions in which the proton and the leaving group both are eliminated from the same$(\alpha )$ atom. A good example of alpha elimination is the reaction of chloroform (\[CHC{l_3}\]) with a base like hydroxide ion. The mechanism for the following reaction is:
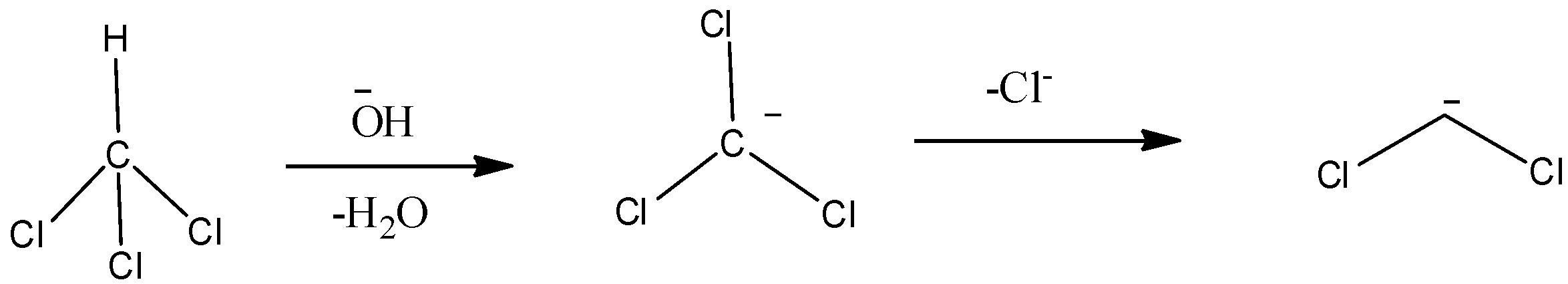
The base (\[O{H^ - }\] in this case) firstly removes the hydrogen as a proton (\[{H^ + }\]) to form a water molecule and \[CC{l_3}^ - \]. Then \[CC{l_3}^ - \] eliminates a chlorine ion which then forms a reactive intermediate known as a carbene. The carbon atom has only three lone pairs of electrons around it (Two pairs in the C-Cl bond and other two electrons). There are two possibilities for how the two nonbonding electrons are distributed and thus two types of carbenes-
Triplet carbene- It has two unpaired electrons, one in an ‘\[s{p^2}\]’ orbital and the other in a ‘p’ orbital.
Singlet carbene: It has a lone pair of electrons in a nonbonding ‘\[s{p^2}\]’ orbital, a vacant ‘p’ orbital.
Hence, the correct answer is (B).
Note:
Remember that carbenes are very reactive and generally react with other compounds to form a cyclic compound. The reactions of singlet carbene are stereospecific whereas those of triplet carbene are stereoselective.
Complete answer:
Elimination reactions are the type of chemical reactions in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one-step or a two-step mechanism. Alpha elimination is a category of elimination reactions in which the proton and the leaving group both are eliminated from the same$(\alpha )$ atom. A good example of alpha elimination is the reaction of chloroform (\[CHC{l_3}\]) with a base like hydroxide ion. The mechanism for the following reaction is:

The base (\[O{H^ - }\] in this case) firstly removes the hydrogen as a proton (\[{H^ + }\]) to form a water molecule and \[CC{l_3}^ - \]. Then \[CC{l_3}^ - \] eliminates a chlorine ion which then forms a reactive intermediate known as a carbene. The carbon atom has only three lone pairs of electrons around it (Two pairs in the C-Cl bond and other two electrons). There are two possibilities for how the two nonbonding electrons are distributed and thus two types of carbenes-
Triplet carbene- It has two unpaired electrons, one in an ‘\[s{p^2}\]’ orbital and the other in a ‘p’ orbital.
Singlet carbene: It has a lone pair of electrons in a nonbonding ‘\[s{p^2}\]’ orbital, a vacant ‘p’ orbital.
Hence, the correct answer is (B).
Note:
Remember that carbenes are very reactive and generally react with other compounds to form a cyclic compound. The reactions of singlet carbene are stereospecific whereas those of triplet carbene are stereoselective.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




