
The correct statement about the following disaccharide is :
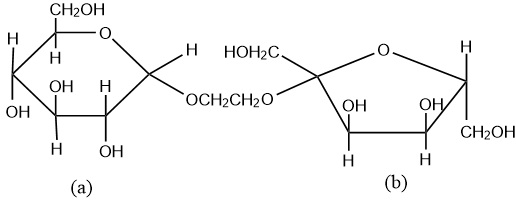
(A) Ring (a) is pyranose with $\alpha $- glycosidic link
(B) Ring (a) is furanose with $\alpha $- glycosidic link
(C) Ring (b) is furanose with $\alpha $- glycosidic link
(D) Ring (b) is pyranose with $\beta $- glycosidic link

Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: A disaccharide is the sugar formed when two monosaccharides are joined by glycosidic linkage. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides are soluble in water. A glycosidic linkage or bond is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
Complete step by step answer:
1,4 glycosidic bonds are formed due to condensation reactions between a hydroxyl oxygen atom on carbon-4 on one sugar and the $\alpha $-anomeric form of C-1 on the other.There are two types of glycosidic bond- 1,4 $\alpha $ glycosidic bonds and 1,4 beta glycosidic bonds.
1,4 $\alpha $ glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH on the carbon-1 is below the glucose ring ; while 1,4 beta glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH is above the plane.
The ring (i) is pyranose with $\alpha $ glycosidic linkage. The six membered cyclic structure of glucose is called pyranose structure, in analogy with pyran which is a cyclic organic compound with one oxygen and five carbon atoms in the ring. The ring (i) is pyranose with $\alpha $ glycosidic linkage which means the oxide linkage which connects the monosaccharide units in polysaccharide below the plane.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: A glycosidic linkage is formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group of a saccharide and the hydroxyl group of some compound such as an alcohol. The five membered cyclic structure of carbohydrates is called pyranose structure.
Complete step by step answer:
1,4 glycosidic bonds are formed due to condensation reactions between a hydroxyl oxygen atom on carbon-4 on one sugar and the $\alpha $-anomeric form of C-1 on the other.There are two types of glycosidic bond- 1,4 $\alpha $ glycosidic bonds and 1,4 beta glycosidic bonds.
1,4 $\alpha $ glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH on the carbon-1 is below the glucose ring ; while 1,4 beta glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH is above the plane.
The ring (i) is pyranose with $\alpha $ glycosidic linkage. The six membered cyclic structure of glucose is called pyranose structure, in analogy with pyran which is a cyclic organic compound with one oxygen and five carbon atoms in the ring. The ring (i) is pyranose with $\alpha $ glycosidic linkage which means the oxide linkage which connects the monosaccharide units in polysaccharide below the plane.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: A glycosidic linkage is formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group of a saccharide and the hydroxyl group of some compound such as an alcohol. The five membered cyclic structure of carbohydrates is called pyranose structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




