
The correct IUPAC name of
is,
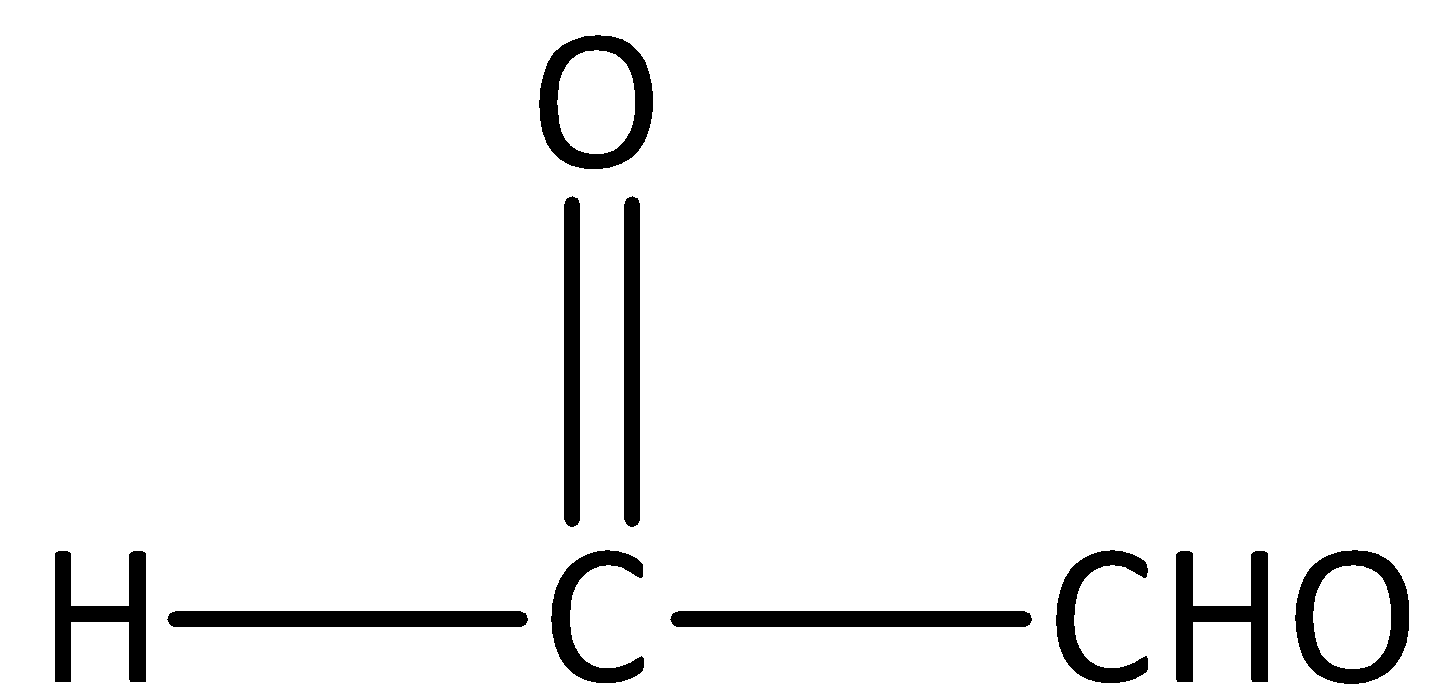
A.Formyl methanal
B.1,2-Ethanedione
C.2-Oxobutanal
D.Ethanedial

Answer
561k+ views
Hint:We know aldehydes are organic compounds that contain carbonyl groups. We can write the general formula of aldehydes as \[R - CHO\] , here R is the alkyl group. Aldehydes are used in the preparation of plasticizers and polyols, they can be reduced to alcohols.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that Aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl group.
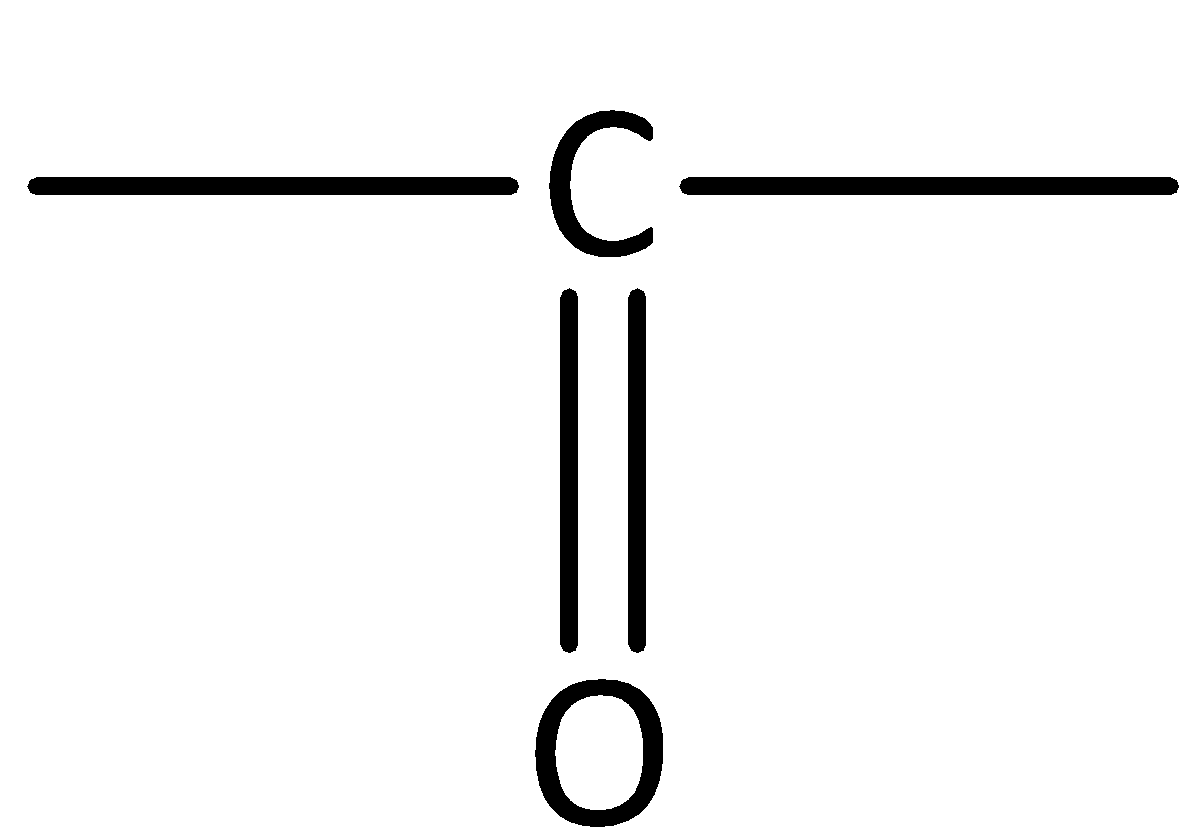
In aldehydes, the carbonyl group is attached at the end of the hydrocarbon chain. The carbonyl carbon is bonded to at least one hydrogen.
Aldehydes have a general formula of $R - CHO$ . The general structure of an aldehyde is,
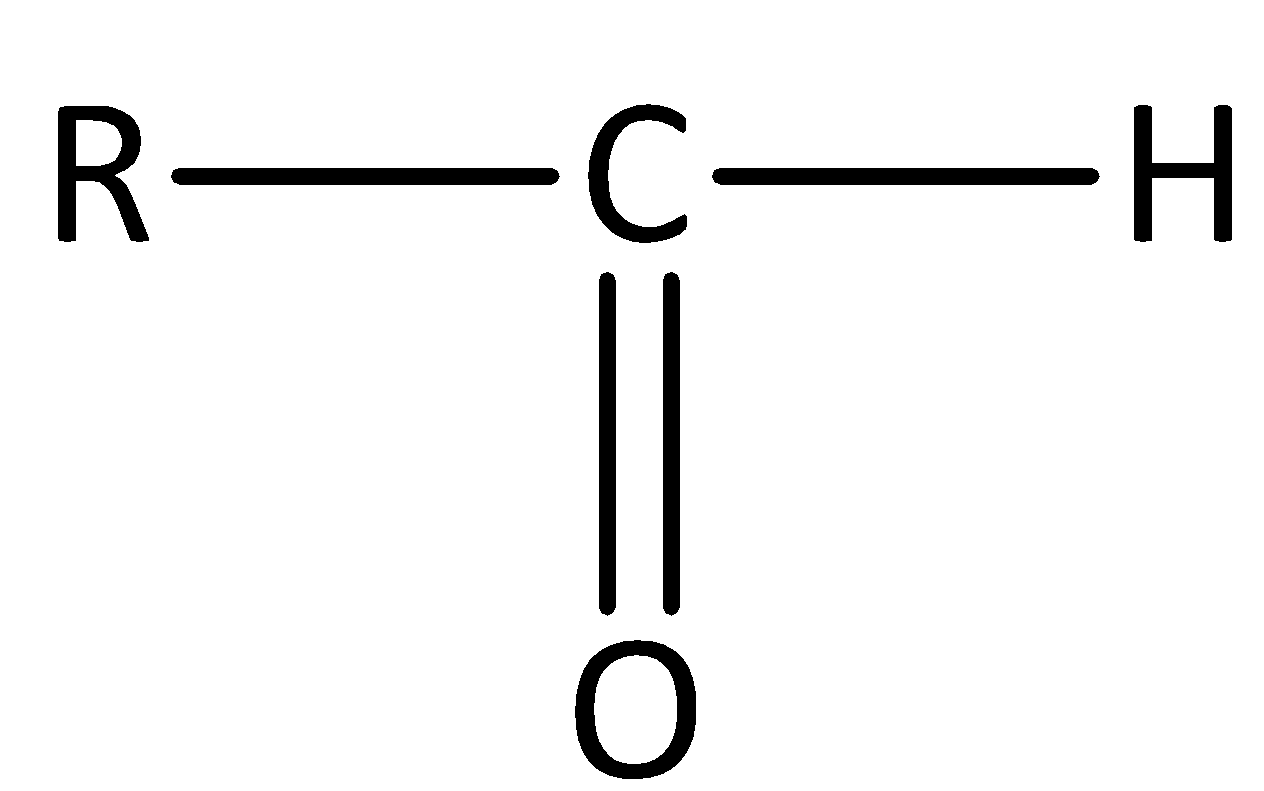
Here R is the alkyl group.
We can give the IUPAC Nomenclature for naming aldehydes as follows,
-The parent compound; that is the longest continuous carbon chain containing the carbonyl group has to be determined.
-Replace the final –e of the parent alkane with –al.
-The chain beginning with the carbonyl carbon is named as carbon${\text{ - 1}}{\text{.}}$
-All the substituents are named and numbered.
-No number is used for the position of carbonyl group because it is always at the end of the parent chain. Therefore, it must be carbon${\text{ - 1}}{\text{.}}$
We can give the common name system for naming aldehydes as follows,
The common names of the aldehydes are derived from the Latin roots.
Example, the common name of methanal is formaldehyde.
Common name of substituted aldehydes can be given as follows,
-The common names of substituted aldehydes are named as derivatives of straight-chain parent compounds.
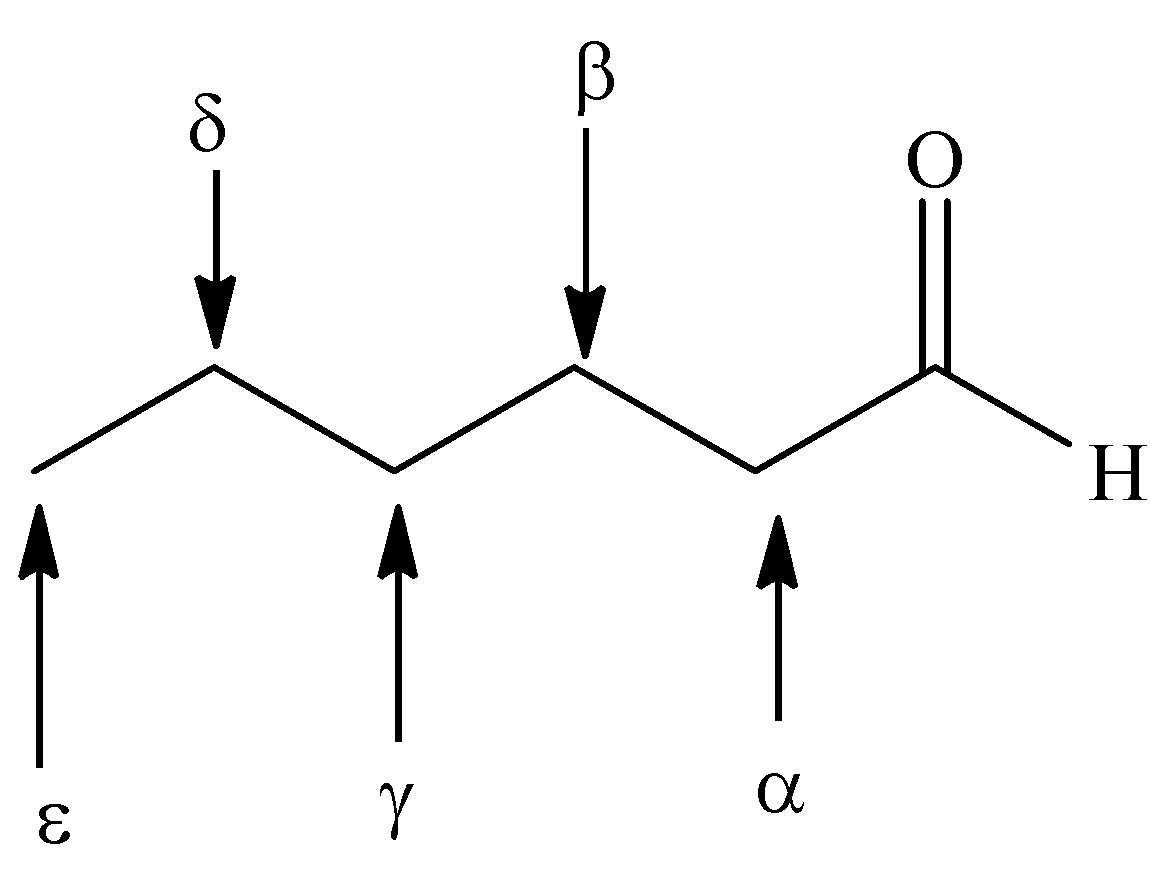
-Greek letters designate the carbon atoms near the carbonyl group.
-The carbon atom bonded to the carbonyl group is alpha, the next removed is beta and so on.
The given structure is,
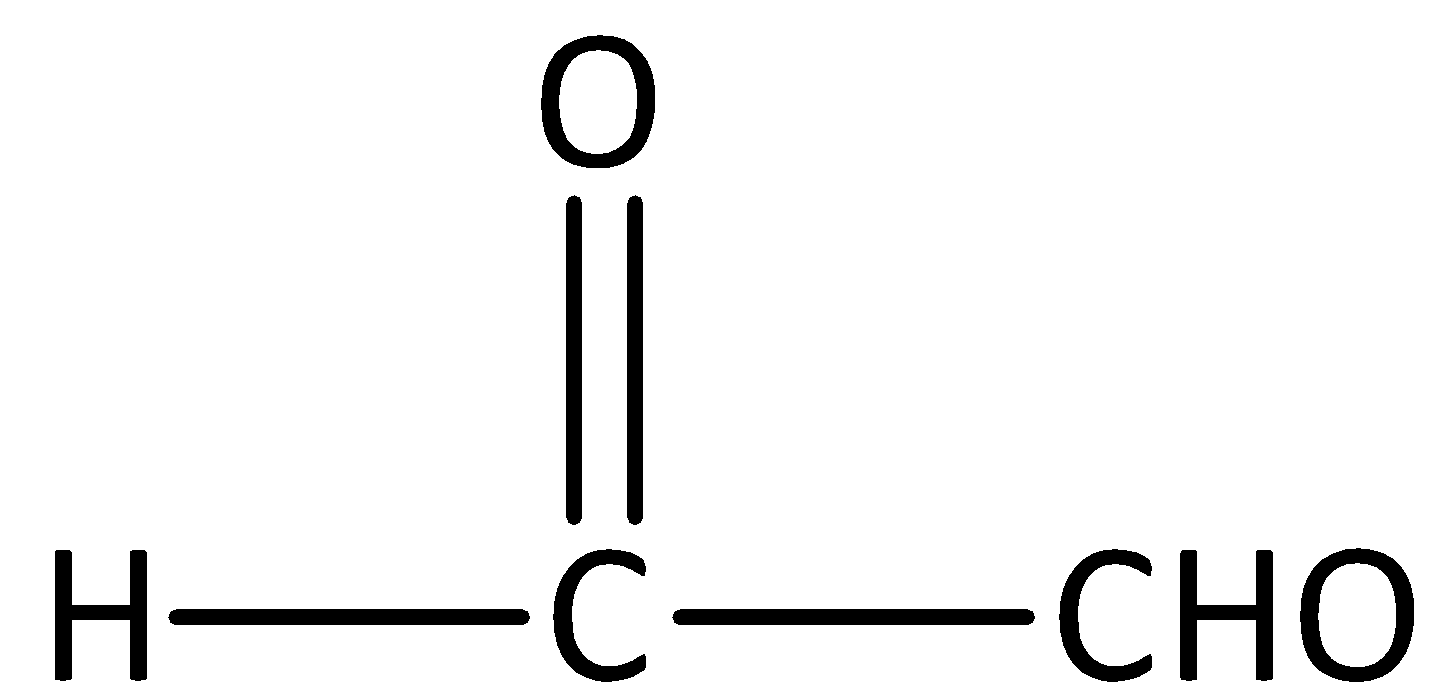
We can observe from the structure that there are two carbons present in the compound, hence the parent carbon chain would be ethane.
We can expand the given structure as,
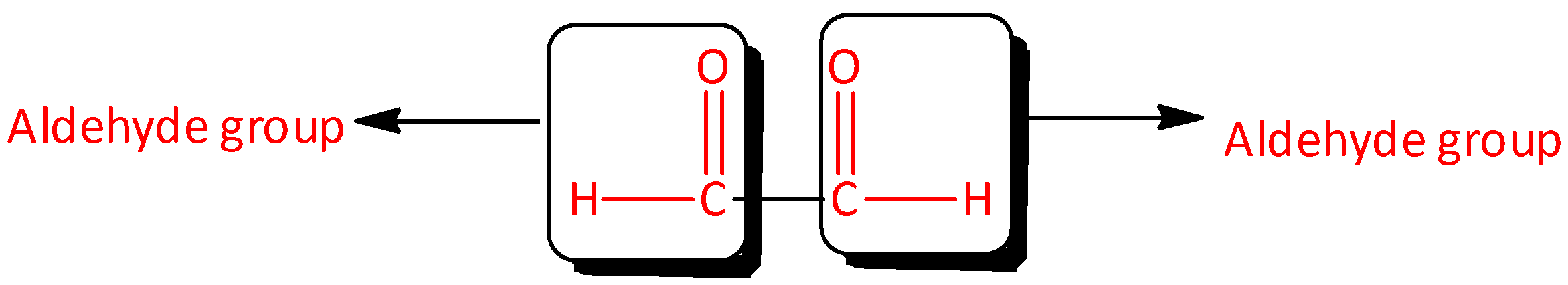
We can also note that there are two aldehyde groups present in the compound. So, we have attached the suffix “-dial” to the parent name.
The IUPAC name of the compound would be Ethanedial.
$\therefore $ Option (D) is correct.
The other common names of Ethanedial are glyoxal, oxalaldehyde, oxaldehyde. It is the smallest of the dialdehyde family, which has two aldehyde groups.
Note:
We can prepare carboxylic acids by oxidizing aldehydes. Alcohols can be prepared by reducing aldehydes. Smaller aldehydes are sparingly water soluble, higher aldehydes are insoluble in water. Aldehydes are used in organic reactions such as,
-Wolf-Kishner reduction
-Pinacol coupling reaction
-Oxo-Diels-Alder reaction
-Decarboxylation
Complete step by step answer:
We know that Aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl group.

In aldehydes, the carbonyl group is attached at the end of the hydrocarbon chain. The carbonyl carbon is bonded to at least one hydrogen.
Aldehydes have a general formula of $R - CHO$ . The general structure of an aldehyde is,

Here R is the alkyl group.
We can give the IUPAC Nomenclature for naming aldehydes as follows,
-The parent compound; that is the longest continuous carbon chain containing the carbonyl group has to be determined.
-Replace the final –e of the parent alkane with –al.
-The chain beginning with the carbonyl carbon is named as carbon${\text{ - 1}}{\text{.}}$
-All the substituents are named and numbered.
-No number is used for the position of carbonyl group because it is always at the end of the parent chain. Therefore, it must be carbon${\text{ - 1}}{\text{.}}$
We can give the common name system for naming aldehydes as follows,
The common names of the aldehydes are derived from the Latin roots.
Example, the common name of methanal is formaldehyde.
Common name of substituted aldehydes can be given as follows,
-The common names of substituted aldehydes are named as derivatives of straight-chain parent compounds.
-Greek letters designate the carbon atoms near the carbonyl group.
-The carbon atom bonded to the carbonyl group is alpha, the next removed is beta and so on.

The given structure is,

We can observe from the structure that there are two carbons present in the compound, hence the parent carbon chain would be ethane.
We can expand the given structure as,

We can also note that there are two aldehyde groups present in the compound. So, we have attached the suffix “-dial” to the parent name.
The IUPAC name of the compound would be Ethanedial.
$\therefore $ Option (D) is correct.
The other common names of Ethanedial are glyoxal, oxalaldehyde, oxaldehyde. It is the smallest of the dialdehyde family, which has two aldehyde groups.
Note:
We can prepare carboxylic acids by oxidizing aldehydes. Alcohols can be prepared by reducing aldehydes. Smaller aldehydes are sparingly water soluble, higher aldehydes are insoluble in water. Aldehydes are used in organic reactions such as,
-Wolf-Kishner reduction
-Pinacol coupling reaction
-Oxo-Diels-Alder reaction
-Decarboxylation
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




