
The condition for obtaining secondary maxima in the diffraction pattern due to single slit is:
a) $a\sin \theta =n\lambda $
b) $a\sin \theta =(2n-1)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
c) $a\sin \theta =(2n-1)\lambda $
d) $a\sin \theta =\dfrac{n\lambda }{2}$
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: Single slit experiment forms a series of light and dark patterns on the wall. The Illuminated portion is linked with the maxima and the dark ones with the minima. There is a unique relation between the wavelength and the slit width for each of the maxima as well as minima.
Complete answer:
We generally believed that light travels in a straight line. But we later came to know that the light can also bend. We can do this bending of light as diffraction.
Diffraction is nothing but the bending of light around the corners and edges. It lights the part of the surface which otherwise would have remained dark.
There are different experiments to study this bending of light or diffraction. One amongst them is the Young’s single slit experiment. In this experiment, light is allowed to pass through a narrow split or opening which causes the light to bend. We study the angle of this bend through the intensity of light at the surface illuminated by the diffracted light.
This can be depicted in the diagram as:
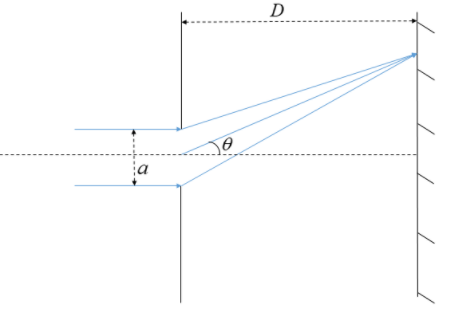
Here, the light comes and incidences on the narrow slit of width $a$. After suffering diffraction at the edges of the slit, light bends and creates a series of lighted and dark patterns on the wall.
The lighted portion on the wall is termed as the part where the maxima of the diffracted light incidences. While the part where there is dark, is said to be the part where the minima of the diffracted light falls.
There is a unique formula that relates the wavelength of the light with the distance of incidence of the light with diffraction. The portion where maxima falls has a different relation as compared to the part where minima of the diffracted light falls.
The condition to obtain secondary maxima in the diffraction pattern due to single slit is given by the formula:
$a\sin \theta =(2n-1)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
Where, $a$ is the width of the slit, $n$ is the order of maxima and $\lambda $ is the wavelength of the incident light.
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Note:
Do not get confused between $a$ and $D$ while putting the value in the formula. $a$ is the width of the narrow slit through which the light diffracts. It is not the distance between the slit and the wall. The distance between the slit and the wall is denoted by $D$.
Complete answer:
We generally believed that light travels in a straight line. But we later came to know that the light can also bend. We can do this bending of light as diffraction.
Diffraction is nothing but the bending of light around the corners and edges. It lights the part of the surface which otherwise would have remained dark.
There are different experiments to study this bending of light or diffraction. One amongst them is the Young’s single slit experiment. In this experiment, light is allowed to pass through a narrow split or opening which causes the light to bend. We study the angle of this bend through the intensity of light at the surface illuminated by the diffracted light.
This can be depicted in the diagram as:

Here, the light comes and incidences on the narrow slit of width $a$. After suffering diffraction at the edges of the slit, light bends and creates a series of lighted and dark patterns on the wall.
The lighted portion on the wall is termed as the part where the maxima of the diffracted light incidences. While the part where there is dark, is said to be the part where the minima of the diffracted light falls.
There is a unique formula that relates the wavelength of the light with the distance of incidence of the light with diffraction. The portion where maxima falls has a different relation as compared to the part where minima of the diffracted light falls.
The condition to obtain secondary maxima in the diffraction pattern due to single slit is given by the formula:
$a\sin \theta =(2n-1)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
Where, $a$ is the width of the slit, $n$ is the order of maxima and $\lambda $ is the wavelength of the incident light.
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Note:
Do not get confused between $a$ and $D$ while putting the value in the formula. $a$ is the width of the narrow slit through which the light diffracts. It is not the distance between the slit and the wall. The distance between the slit and the wall is denoted by $D$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




