
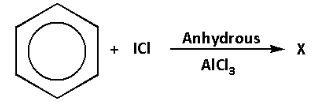
The compound ‘X’ in the reaction is:
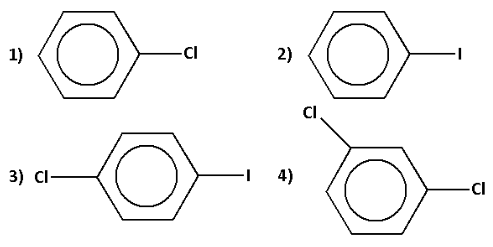


Answer
567k+ views
Hint: We are given a reaction in which benzene reacts with iodine chloride in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride. Anhydrous aluminium chloride is a Lewis acid and reacts with iodine chloride to produce iodonium ion.
Complete step-by-step answer :We are given a reaction in which benzene reacts with iodine chloride in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride.
The anhydrous aluminium chloride needs two electrons to complete its octet. Thus, anhydrous aluminium chloride acts as a Lewis acid. The main function of anhydrous aluminium chloride is to produce an electrophile.
Anhydrous aluminium chloride reacts with iodine chloride and produces iodonium ion $\left( {{{\text{I}}^ + }} \right)$. This is because the electronegativity of iodine is less than that of chlorine. The iodonium ion acts as an electrophile.
We know that benzene is a planar molecule and has a cloud of delocalised electrons above the plane of the ring. Thus, benzene is rich in electrons. As a result, benzene is highly attractive towards the species that are electron deficient i.e. electrophiles.
Thus, the iodonium ion which is an electrophile attacks the benzene ring and iodobenzene is formed as the product. One hydrogen atom of the benzene ring is substituted by iodonium ion. Thus, it is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
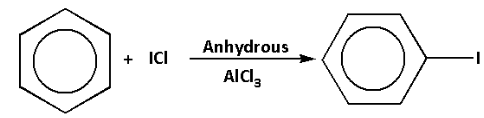
The reaction of benzene with iodine chloride in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride is as follows:
Thus, the correct option is 2).
Note:Remember that benzene is a planar molecule and has a cloud of delocalised electrons above the plane of the ring. Thus, benzene is rich in electrons. As a result, benzene is highly attractive towards the species that are electron deficient i.e. electrophiles. Thus, benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions.
Complete step-by-step answer :We are given a reaction in which benzene reacts with iodine chloride in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride.
The anhydrous aluminium chloride needs two electrons to complete its octet. Thus, anhydrous aluminium chloride acts as a Lewis acid. The main function of anhydrous aluminium chloride is to produce an electrophile.
Anhydrous aluminium chloride reacts with iodine chloride and produces iodonium ion $\left( {{{\text{I}}^ + }} \right)$. This is because the electronegativity of iodine is less than that of chlorine. The iodonium ion acts as an electrophile.
We know that benzene is a planar molecule and has a cloud of delocalised electrons above the plane of the ring. Thus, benzene is rich in electrons. As a result, benzene is highly attractive towards the species that are electron deficient i.e. electrophiles.
Thus, the iodonium ion which is an electrophile attacks the benzene ring and iodobenzene is formed as the product. One hydrogen atom of the benzene ring is substituted by iodonium ion. Thus, it is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
The reaction of benzene with iodine chloride in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride is as follows:

Thus, the correct option is 2).
Note:Remember that benzene is a planar molecule and has a cloud of delocalised electrons above the plane of the ring. Thus, benzene is rich in electrons. As a result, benzene is highly attractive towards the species that are electron deficient i.e. electrophiles. Thus, benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




