
The compound ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}$shows optical isomerism. Draw the structural formula of the compound and name it.
Answer
589.5k+ views
HINT: Dissymmetric molecules show optical activity. The compounds which change the direction of light when a plane of polarised light is passed through them are optically active. They are named according to the direction towards which they change the light.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: As we know, optical isomers are compounds having the same atoms and bonds but in different spatial arrangements and will have non-superimposable mirror images. These non-superimposable mirror images are called enantiomers.
Optical activity of a molecule does not depend on its chirality. If the molecule is dissymmetric and has at least one non superimposable mirror image, it exhibits optical activity.
Chiral centre is an atom to which 4 different groups or atoms are bonded so that they can form a non-superimposable mirror image.
Over here, we have ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}$which shows optical isomerism which means it has a dissymmetric structure i.e. it cannot be a straight six membered chain also, if it is a six membered straight chain, the hydrogen count would increase-
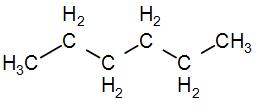
Therefore, this cannot be the structure.
As we can understand from the above example, in order to make an optically active compound from${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}$, we have to make a five membered alkene structure to which one methyl group is added to a C-atom. Therefore, we can draw the structure as-
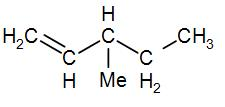
The name of the above compound will be- 3-methylpent-1-ene as the methyl group is at the third carbon and the double bond at the first carbon.
The above centre has a chiral centre, passing through C-3. We can draw its mirror image as-
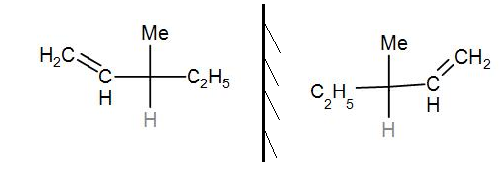
As it has a non-superimposable mirror image, it is optically active.
Therefore, the name of the optically active${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}$compound is 3-methylpent-1-ene and its structure is-
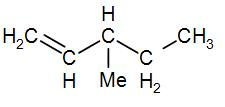
NOTE: It is important to remember here that optical activity does not depend on the chirality of a molecule. It is also important to remember the IUPAC naming norms in order to name the compound.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: As we know, optical isomers are compounds having the same atoms and bonds but in different spatial arrangements and will have non-superimposable mirror images. These non-superimposable mirror images are called enantiomers.
Optical activity of a molecule does not depend on its chirality. If the molecule is dissymmetric and has at least one non superimposable mirror image, it exhibits optical activity.
Chiral centre is an atom to which 4 different groups or atoms are bonded so that they can form a non-superimposable mirror image.
Over here, we have ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}$which shows optical isomerism which means it has a dissymmetric structure i.e. it cannot be a straight six membered chain also, if it is a six membered straight chain, the hydrogen count would increase-

Therefore, this cannot be the structure.
As we can understand from the above example, in order to make an optically active compound from${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}$, we have to make a five membered alkene structure to which one methyl group is added to a C-atom. Therefore, we can draw the structure as-

The name of the above compound will be- 3-methylpent-1-ene as the methyl group is at the third carbon and the double bond at the first carbon.
The above centre has a chiral centre, passing through C-3. We can draw its mirror image as-

As it has a non-superimposable mirror image, it is optically active.
Therefore, the name of the optically active${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}$compound is 3-methylpent-1-ene and its structure is-

NOTE: It is important to remember here that optical activity does not depend on the chirality of a molecule. It is also important to remember the IUPAC naming norms in order to name the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




