
The complex $ \left[ {Ni{{\left( {dmg} \right)}_2}} \right] $ , (where $ dmg $ is dimethylglyoxime):
(A) Has a square planar geometry and is paramagnetic in nature
(B) Has a square planar geometry and is diamagnetic in nature
(C) Has a tetrahedral geometry and is paramagnetic in nature
(D) Has a tetrahedral geometry and is diamagnetic in nature
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: to determine the shape of the complex we have to first look at the ligand. If the given ligand is strong then it will pair the unpaired electrons of the element whereas if the given ligand is weak there will be no change in the electrons of the element.
Complete answer:
To answer this question we have to write the electronic configuration of nickel then we will write the electronic configuration of nickel $ \left( {II} \right) $ ion then we will write the electronic configuration of $ \left[ {Ni{{\left( {dmg} \right)}_2}} \right] $ which are as follows:
$ Ni = \;3{d^8}\;4{s^2} $
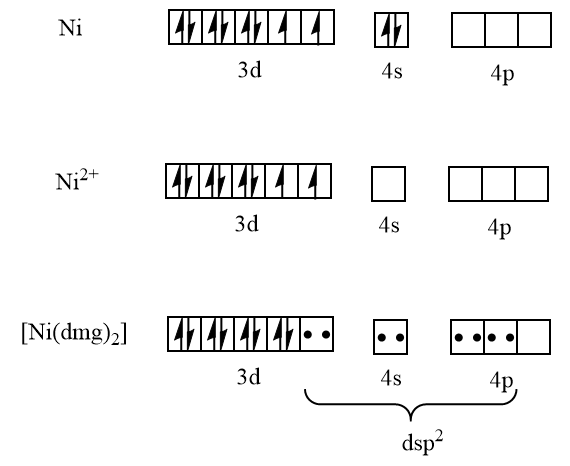
Here the coordination number is four and it has $ ds{p^2} $ hybridization. From the diagram it is clear that all electrons here are paired thus it is diamagnetic in nature. And nickel with coordination number four and $ ds{p^2} $ hybridization has the square planar geometry which is:
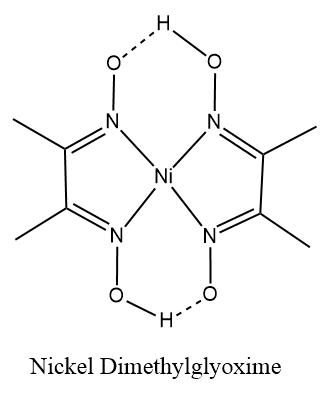
Thus, the complex $ \left[ {Ni{{\left( {dmg} \right)}_2}} \right] $ has square planar geometry and is diamagnetic in nature.
Therefore, option $ \left( b \right) $ is correct.
Note:
Here the $ dmg $ which is dimethylglyoxime, is a polydentate ligand. The polydentate ligands are those in which the numbers of donor atoms are two or more than two atoms. They form bonds to a central metal atom or ion. In other words they are the ligands which are attached with the central metal ion or atom by bonds from two or more donor atoms.
Complete answer:
To answer this question we have to write the electronic configuration of nickel then we will write the electronic configuration of nickel $ \left( {II} \right) $ ion then we will write the electronic configuration of $ \left[ {Ni{{\left( {dmg} \right)}_2}} \right] $ which are as follows:
$ Ni = \;3{d^8}\;4{s^2} $

Here the coordination number is four and it has $ ds{p^2} $ hybridization. From the diagram it is clear that all electrons here are paired thus it is diamagnetic in nature. And nickel with coordination number four and $ ds{p^2} $ hybridization has the square planar geometry which is:

Thus, the complex $ \left[ {Ni{{\left( {dmg} \right)}_2}} \right] $ has square planar geometry and is diamagnetic in nature.
Therefore, option $ \left( b \right) $ is correct.
Note:
Here the $ dmg $ which is dimethylglyoxime, is a polydentate ligand. The polydentate ligands are those in which the numbers of donor atoms are two or more than two atoms. They form bonds to a central metal atom or ion. In other words they are the ligands which are attached with the central metal ion or atom by bonds from two or more donor atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




