
The complex ion $ {[Cu{(N{H_3})_4}]^{2 + }} $ is:
(A) Tetrahedral and paramagnetic
(B) Tetrahedral and diamagnetic
(C) Square planar and paramagnetic
(D) Square planar and diamagnetic
Answer
541.2k+ views
Hint :We will use the concept of Crystal field theory which states that the breaking of orbital degeneracy in transition metal complexes happens due to the presence of Ligands. On the basis of hybridization, we will explain the geometry of $ {[Cu{(N{H_3})_4}]^{2 + }} $ and also by determining the nature of the ligand according to its position in spectrochemical series i.e. whether it is a strong ligand or a weak ligand.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As we know the atomic number of $ Cu $ is $ 29 $ so the electronic configuration will be:- $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}3{s^2}3{p^6}4{s^2}3{d^9} $
But here $ Cu $ exists in $ C{u^{ + 2}} $ oxidation state so two electrons will be eliminated from the $ 4s $ orbital so the electronic configuration of $ C{u^{ + 2}} $ will be:- $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}3{s^2}3{p^6}3{d^9}4{s^0} $
We will now draw the orbitals of $ 3d,4s\& 4p $ to determine the hybridization: -
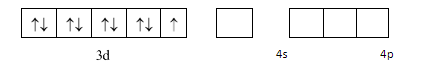
As $ N{H_3} $ is a strong ligand so pairing should take place but here we see that an electron is transferred from $ 3d $ orbital to $ 4p $ orbital . This happens according to the concept of transference which states that an electron can be transferred from a lower energy orbital to a higher energy orbital if strong ligands are present and if there is a possibility of formation of a lower orbital complex. We depict it as: -
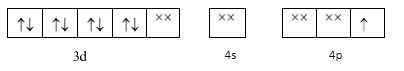
Now these $ ds{p^2} $ hybrid orbitals will accept the electron pair from the four $ N{H_3} $ ligands individually and thus will form a $ ds{p^2} $ hybridization and a square planar geometry.
As the compound contains 1 unpaired electron so the magnetic nature would be paramagnetic.
So, the correct option is Option c i.e. Square planar and paramagnetic.
Note :
Practically $ {[Cu{(N{H_3})_4}]^{2 + }} $ should form $ s{p^3} $ hybridization with tetrahedral geometry but this does not happen because $ 3d $ orbital contains only one unpaired electron, so the unpaired electron is shifted to 4p orbital for more stability. This cause of transference and the source of energy required for transfer of electrons could not be explained by the Valence Bond Theory.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
As we know the atomic number of $ Cu $ is $ 29 $ so the electronic configuration will be:- $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}3{s^2}3{p^6}4{s^2}3{d^9} $
But here $ Cu $ exists in $ C{u^{ + 2}} $ oxidation state so two electrons will be eliminated from the $ 4s $ orbital so the electronic configuration of $ C{u^{ + 2}} $ will be:- $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}3{s^2}3{p^6}3{d^9}4{s^0} $
We will now draw the orbitals of $ 3d,4s\& 4p $ to determine the hybridization: -

As $ N{H_3} $ is a strong ligand so pairing should take place but here we see that an electron is transferred from $ 3d $ orbital to $ 4p $ orbital . This happens according to the concept of transference which states that an electron can be transferred from a lower energy orbital to a higher energy orbital if strong ligands are present and if there is a possibility of formation of a lower orbital complex. We depict it as: -

Now these $ ds{p^2} $ hybrid orbitals will accept the electron pair from the four $ N{H_3} $ ligands individually and thus will form a $ ds{p^2} $ hybridization and a square planar geometry.
As the compound contains 1 unpaired electron so the magnetic nature would be paramagnetic.
So, the correct option is Option c i.e. Square planar and paramagnetic.
Note :
Practically $ {[Cu{(N{H_3})_4}]^{2 + }} $ should form $ s{p^3} $ hybridization with tetrahedral geometry but this does not happen because $ 3d $ orbital contains only one unpaired electron, so the unpaired electron is shifted to 4p orbital for more stability. This cause of transference and the source of energy required for transfer of electrons could not be explained by the Valence Bond Theory.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




