
The common method of reproduction in yeast is
a) Fission
b) Binary fission
c) Budding
d) Sexual reproduction
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom.
The most common yeast known is Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is used in the baking- and brewing industry.
Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parents".
Yeast reproduce mainly through budding. A small outgrowth is developed on the parent plant. The outgrowth has the structure like bud thus the process called budding. The outgrowth then develop and after developing they detach from parent plants and act as a complete individual. This is a type of asexual reproduction.
Complete answer:
FISSION:- It is the division of a single entity into two or more parts and the regeneration of those parts to separate entities resembling the original. It is of two types BINARY FISSION AND MULTIPLE FISSION. Fission usually occurs in amoeba , paramecium . So, this option is not correct
BINARY FISSION :- Binary fission is a kind of asexual reproduction. It is a common type of reproduction found in bacteria and protists like Amoeba in which the fully grown parent cell splits into two halves, producing two new cells. Hence , this option is also incorrect.
BUDDING :- The process in which an outgrowth is developed as bud . The bud grows and detaches from the parent body. It is a common process in yeast. So, this option is correct.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION :- The reproduction in which male gamete and female gamete fuses to form a new individual. This is a common process in humans. So , this option is also not correct.
Our correct option c that is budding.
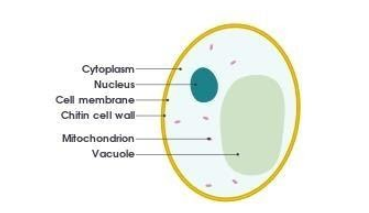
Note: Other example of homologous organs is :-
The most common mode of vegetative growth in yeast is asexual reproduction by budding, where a small bud (also known as a bleb or daughter cell) is formed on the parent cell. The nucleus of the parent cell splits into a daughter nucleus and migrates into the daughter cell.
First it produces a small protuberance on the parent cell that grows to a full size and forms a bud.
The nucleus of the parent cell splits into a daughter nucleus and migrates into the daughter cell.
The most common yeast known is Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is used in the baking- and brewing industry.
Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parents".
Yeast reproduce mainly through budding. A small outgrowth is developed on the parent plant. The outgrowth has the structure like bud thus the process called budding. The outgrowth then develop and after developing they detach from parent plants and act as a complete individual. This is a type of asexual reproduction.
Complete answer:
FISSION:- It is the division of a single entity into two or more parts and the regeneration of those parts to separate entities resembling the original. It is of two types BINARY FISSION AND MULTIPLE FISSION. Fission usually occurs in amoeba , paramecium . So, this option is not correct
BINARY FISSION :- Binary fission is a kind of asexual reproduction. It is a common type of reproduction found in bacteria and protists like Amoeba in which the fully grown parent cell splits into two halves, producing two new cells. Hence , this option is also incorrect.
BUDDING :- The process in which an outgrowth is developed as bud . The bud grows and detaches from the parent body. It is a common process in yeast. So, this option is correct.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION :- The reproduction in which male gamete and female gamete fuses to form a new individual. This is a common process in humans. So , this option is also not correct.
Our correct option c that is budding.

Note: Other example of homologous organs is :-
The most common mode of vegetative growth in yeast is asexual reproduction by budding, where a small bud (also known as a bleb or daughter cell) is formed on the parent cell. The nucleus of the parent cell splits into a daughter nucleus and migrates into the daughter cell.
First it produces a small protuberance on the parent cell that grows to a full size and forms a bud.
The nucleus of the parent cell splits into a daughter nucleus and migrates into the daughter cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




