
The commercial motor use
(A) An electromagnet in place of permanent magnet
(B) Large number of turns of the conducting wire in the current carrying coil
(C) A soft iron core on which the coil is wound
(D) All
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: The commercial motor works on the same principle as that of a moving coil galvanometer. When a current is passed through a coil placed in a magnetic field, the coil experiences a torque in a direction given by Fleming’s left-hand rule. This torque gives a continuous rotatory motion to the coil in the magnetic field.
Complete step by step solution
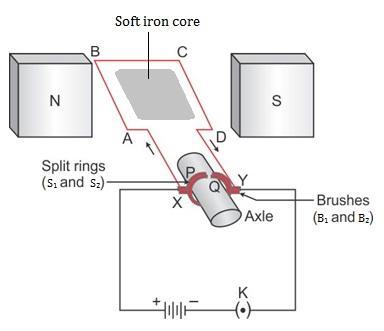
Construction: The main parts of a commercial electric motor are the electromagnets, armature, split ring commutators, and brushes. The armature coil ABCD consists of a rectangular coil made of insulated copper wire wound on a laminated soft iron core. The coil is mounted on an axle and is placed between the cylindrical concave poles of an electromagnet. The commutator is a copper ring split into two parts P and Q as shown in the figure above. The commutators are used to reverse the direction of the flow of the current. The split rings are insulated from each other and are mounted on the axle of the motor. The segment P and Q of the commutator come alternately in contact with the carbon brushes X and Y during the rotation of the armature. The power source is connected across the brushes X and Y.
Working of the Electric motor: When the power source is turned on, a current flow around the armature coil in the direction ABCD. Suppose, initially the coil is horizontal and the segments P and Q are in contact with the brushes X and Y respectively as shown in the figure. According to Fleming’s left-hand rule, a downward force acts on the arm AB of the armature and an equal and opposite force acts on the arm CD. These forces form a couple which rotates the coil in the anticlockwise direction. The couple vanishes when the coil is vertical but the momentum on the coil carries it past the vertical. The two segments P and Q make contact with the carbon brushes at Y and X respectively. The current in the coil is thereby reversed with the result that the couple due to the forces on the two arms of the coil is still in the same direction and the coil continues to rotate in an anticlockwise direction. The same process is repeated again and again and thus the coil rotates continuously. The rotation of the coil is jerky. To obtain steady rotation the number of turns of the coils is increased.
Thus, the answer to this question is option D.
Note: The difference between a simple motor and a commercial motor is that a commercial motor requires a strong magnetic field so the permanent magnet is replaced by an electromagnet.
Complete step by step solution

Construction: The main parts of a commercial electric motor are the electromagnets, armature, split ring commutators, and brushes. The armature coil ABCD consists of a rectangular coil made of insulated copper wire wound on a laminated soft iron core. The coil is mounted on an axle and is placed between the cylindrical concave poles of an electromagnet. The commutator is a copper ring split into two parts P and Q as shown in the figure above. The commutators are used to reverse the direction of the flow of the current. The split rings are insulated from each other and are mounted on the axle of the motor. The segment P and Q of the commutator come alternately in contact with the carbon brushes X and Y during the rotation of the armature. The power source is connected across the brushes X and Y.
Working of the Electric motor: When the power source is turned on, a current flow around the armature coil in the direction ABCD. Suppose, initially the coil is horizontal and the segments P and Q are in contact with the brushes X and Y respectively as shown in the figure. According to Fleming’s left-hand rule, a downward force acts on the arm AB of the armature and an equal and opposite force acts on the arm CD. These forces form a couple which rotates the coil in the anticlockwise direction. The couple vanishes when the coil is vertical but the momentum on the coil carries it past the vertical. The two segments P and Q make contact with the carbon brushes at Y and X respectively. The current in the coil is thereby reversed with the result that the couple due to the forces on the two arms of the coil is still in the same direction and the coil continues to rotate in an anticlockwise direction. The same process is repeated again and again and thus the coil rotates continuously. The rotation of the coil is jerky. To obtain steady rotation the number of turns of the coils is increased.
Thus, the answer to this question is option D.
Note: The difference between a simple motor and a commercial motor is that a commercial motor requires a strong magnetic field so the permanent magnet is replaced by an electromagnet.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




