
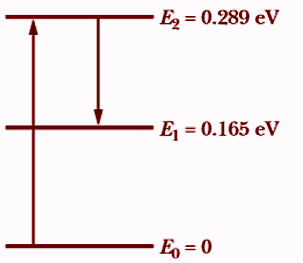
The \[C{O_2}\] laser where sunlight shines on the atmosphere of Mars, carbon dioxide molecules at an altitude of about 75km undergo natural laser action. The energy levels involved in the action are shown in the above figure; population inversion occurs between energy levels \[{E_2}\] and \[{E_1}\].
(a) What wavelength of sunlight excites the molecules in the lasing action?
(b) At what wave-length does aliasing occur?
(c) In what region of the electromagnetic spectrum do the excitation and lasing wavelengths lie?

Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint:One of the first gas lasers to be developed was the carbon dioxide laser. Kumar Patel of Bell Labs invented it in 1964, and it is now one of the most useful forms of laser. Carbon dioxide lasers are now the most powerful continuous wave lasers available. They're also very efficient: the output power to pump power ratio can be as high as 20%. The \[C{O_2}\] laser generates an infrared light beam with wavelength bands centred on 9.6 and 10.6 micrometres (μm).
Complete step by step answer:
(a) As the electron jumps from the peak energy level \[{E_2}\] to the lowest level \[{E_1}\], the laser operation occurs. As a result, the wavelength that corresponds will satisfy.Change in electron energy is given as,
\[\Delta E = {E_2} - {E_1}\]
\[\Rightarrow \Delta E = {E_2} - {E_1} = \dfrac{{hc}}{\lambda }\]
This can be rewritten as
\[{\lambda ^\prime } = \dfrac{{hc}}{{{E_2} - {E_1}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {\lambda ^\prime } = \dfrac{{1240{\rm{eV}} \cdot n\;{\rm{m}}}}{{0.289{\rm{eV}} - 0.165\;e{\rm{V}}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {\lambda ^\prime } = 1.00 \times {10^4}\;{\rm{nm}}\]
\[\therefore {\lambda ^\prime } = 10.0\;\mu {\rm{m}}\]
(b) At the wavelength of 0.4 & 0.8 micrometer aliasing will occur.
(c) So, the wavelength lies in the visible region.
Note:The visible light continuum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be seen by the naked eye. This spectrum of wavelengths is referred to as visible light.The human eye can sense wavelengths ranging from 380 to 700 nanometers in most cases.Visible light has wavelengths ranging from 400 to 750 nanometers (0.4 to 0.75 micrometres).Human eyes are only open to this part of the continuum. In the visible part of the spectrum, the Sun emits the most radiation.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) As the electron jumps from the peak energy level \[{E_2}\] to the lowest level \[{E_1}\], the laser operation occurs. As a result, the wavelength that corresponds will satisfy.Change in electron energy is given as,
\[\Delta E = {E_2} - {E_1}\]
\[\Rightarrow \Delta E = {E_2} - {E_1} = \dfrac{{hc}}{\lambda }\]
This can be rewritten as
\[{\lambda ^\prime } = \dfrac{{hc}}{{{E_2} - {E_1}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {\lambda ^\prime } = \dfrac{{1240{\rm{eV}} \cdot n\;{\rm{m}}}}{{0.289{\rm{eV}} - 0.165\;e{\rm{V}}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {\lambda ^\prime } = 1.00 \times {10^4}\;{\rm{nm}}\]
\[\therefore {\lambda ^\prime } = 10.0\;\mu {\rm{m}}\]
(b) At the wavelength of 0.4 & 0.8 micrometer aliasing will occur.
(c) So, the wavelength lies in the visible region.
Note:The visible light continuum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be seen by the naked eye. This spectrum of wavelengths is referred to as visible light.The human eye can sense wavelengths ranging from 380 to 700 nanometers in most cases.Visible light has wavelengths ranging from 400 to 750 nanometers (0.4 to 0.75 micrometres).Human eyes are only open to this part of the continuum. In the visible part of the spectrum, the Sun emits the most radiation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




