
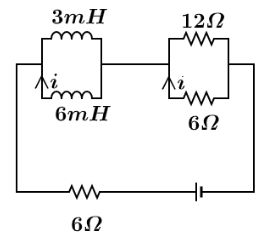
The circuit shown here is in its steady state. Time constant of the circuit is
A. $0.1\,ms$
B. $0.2\,ms$
C. $0.3\,ms$
D. Information is insufficient to find time constant.

Answer
516k+ views
Hint: In electrical LR circuits which consists of inductor and resistors, the time taken by the current to reach its maximum value called time constant and in LR circuits mathematically, its denoted by $\tau = \dfrac{{{L_{net}}}}{{{R_{net}}}}$ which is the ratio of net inductance of the circuit to the net resistance. We will find net resistance and inductance of the circuit then using the above formula we will find the time constant of the circuit.
Formula used:
If two inductors of inductance say ${L_1}(and){L_2}$ are connected in parallel to each other then, net inductance can be found mathematically as,
$\dfrac{1}{{{L_{net}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{L_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{L_2}}}$
And if two resistances connected in parallel to each other the mathematical formula of net resistance is given a $\dfrac{1}{{{R_{parallel}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$ while when resistance connected in series it’s given by ${R_{series}} = {R_1} + {R_2}$ .
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first find net inductance of two inductors having inductance of ${L_1} = 3mH$ and ${L_2} = 6mH$ which are connected in parallel combination, so
$\dfrac{1}{{{L_{net}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{L_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{L_2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{L_{net}}}} = \dfrac{1}{3} + \dfrac{1}{6}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{L_{net}}}} = \dfrac{9}{{18}}$
$\Rightarrow {L_{net}} = 2mH \to (i)$
Now, as we see from the circuit the resistances $6\Omega $ and $12\Omega $ are in parallel combination so,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{parallel}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{parallel}}}} = \dfrac{1}{6} + \dfrac{1}{{12}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{parallel}}}} = \dfrac{{18}}{{72}}$
$\Rightarrow {R_{parallel}} = 4\Omega $
Now, this net resistance of ${R_{parallel}} = 4\Omega $ is in series combination of remaining $6\Omega $ resistance, so
$\Rightarrow {R_{net}} = {R_{parallel}} + {R_{6\Omega }}$
$\Rightarrow {R_{net}} = 4 + 6$
$\Rightarrow {R_{net}} = 10\Omega \to (ii)$
Now, from using equation $(i)and(ii)$ put this value on time constant formula as
$\tau = \dfrac{{{L_{net}}}}{{{R_{net}}}}$
$\Rightarrow \tau = \dfrac{{2mH}}{{4\Omega }}$
$\therefore \tau = 0.2\,ms$
So, the time constant has a value of $\tau = 0.2\,ms$
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: It should be remembered that, a steady state is one when the inductor gets fully charged and no more current flows across the inductor. And if two inductors are connected in series with each other then their net inductance is calculated as ${L_{net}} = {L_1} + {L_2}$ . The $ms$ in the $\tau = 0.2ms$ stands for micro seconds where $1micro\sec = {10^{ - 6}}\sec $.
Formula used:
If two inductors of inductance say ${L_1}(and){L_2}$ are connected in parallel to each other then, net inductance can be found mathematically as,
$\dfrac{1}{{{L_{net}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{L_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{L_2}}}$
And if two resistances connected in parallel to each other the mathematical formula of net resistance is given a $\dfrac{1}{{{R_{parallel}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$ while when resistance connected in series it’s given by ${R_{series}} = {R_1} + {R_2}$ .
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first find net inductance of two inductors having inductance of ${L_1} = 3mH$ and ${L_2} = 6mH$ which are connected in parallel combination, so
$\dfrac{1}{{{L_{net}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{L_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{L_2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{L_{net}}}} = \dfrac{1}{3} + \dfrac{1}{6}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{L_{net}}}} = \dfrac{9}{{18}}$
$\Rightarrow {L_{net}} = 2mH \to (i)$
Now, as we see from the circuit the resistances $6\Omega $ and $12\Omega $ are in parallel combination so,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{parallel}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{parallel}}}} = \dfrac{1}{6} + \dfrac{1}{{12}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{parallel}}}} = \dfrac{{18}}{{72}}$
$\Rightarrow {R_{parallel}} = 4\Omega $
Now, this net resistance of ${R_{parallel}} = 4\Omega $ is in series combination of remaining $6\Omega $ resistance, so
$\Rightarrow {R_{net}} = {R_{parallel}} + {R_{6\Omega }}$
$\Rightarrow {R_{net}} = 4 + 6$
$\Rightarrow {R_{net}} = 10\Omega \to (ii)$
Now, from using equation $(i)and(ii)$ put this value on time constant formula as
$\tau = \dfrac{{{L_{net}}}}{{{R_{net}}}}$
$\Rightarrow \tau = \dfrac{{2mH}}{{4\Omega }}$
$\therefore \tau = 0.2\,ms$
So, the time constant has a value of $\tau = 0.2\,ms$
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: It should be remembered that, a steady state is one when the inductor gets fully charged and no more current flows across the inductor. And if two inductors are connected in series with each other then their net inductance is calculated as ${L_{net}} = {L_1} + {L_2}$ . The $ms$ in the $\tau = 0.2ms$ stands for micro seconds where $1micro\sec = {10^{ - 6}}\sec $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




