
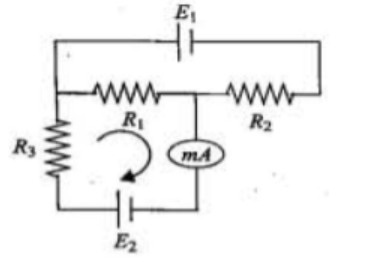
The circuit contains three resistors ${R_1} = 100\Omega ,{R_2} = 50\Omega $ and ${R_3} = 20\Omega $ and cells of emf ${E_1} = 2V$ and${E_2}$. The ammeter indicates a current of 50 mA. Determine the currents in the resistors and the emf of the second cell. The internal resistance of the ammeter and of the cells should be neglected.

Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: In this question we will firstly learn what a resistor is by going through its definition and the concept behind it. Then we will solve the given problem by using our knowledge and the formulas required. We will be solving our query with a good and easy technique so that we can easily approach our solution.
Step-By-Step answer:
An electrical component which is used for controlling voltage and temperature is known as a resistor. Current’s flow is reduced by the use or help of a resistor, it is its main purpose and also to lower down the voltage in any particular portion of the surface. Copper wires are used to make a resistor which is coiled around a rod made of ceramic. Resistor’s outer part is coated with the insulating paint. The unit of resistor is $\Omega $ (read as ohm). Every resistor has 2 terminals and 1 connection. Resistors have different shapes as well as different sizes.
There are two types of resistors: - Linear resistor and non-linear resistor.
Now, it is given,
\[{E_1} = 2V\]
${R_1} = 100\Omega $
${R_2} = 50\Omega $
${R_3} = 20\Omega $
According to Kirchhoff’s law in loop ABCDA:
$
- {E_1} + \left( {I + 0.5} \right){R_1} + I{R_2} = 0 \\
\therefore - 2 + \left( {I + 0.5} \right)\left( {100} \right) + I\left( {50} \right) = 0 \\
$
According to Kirchhoff loop law in BGE FB:
$
- {E_2} + \left( {0.05} \right){R_3} + \left( {I + 0.05} \right){R_1} = 0 \\
\therefore - {E_2} + \left( {0.05} \right)\left( {20} \right) + \left( { - 0.02 + 0.05} \right)\left( {100} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {E_2} = 4V \\
$
Hence, current flowing through -
${R_{1,}}{I_1} = 0.05 - 0.02 = 0.03A = 30mA$ Towards right.
NOTE: Resistors like surface mount and through-hole are available in common types. Resistors can be static, special, standard resistor or pack of variable resistor. Resistance can be calculated through the resistor’s color pattern but the value of resistor may not be displayed outside. Resistors are also used in transmitters, modulators and demodulators, amplifiers, oscillators etc.
Step-By-Step answer:
An electrical component which is used for controlling voltage and temperature is known as a resistor. Current’s flow is reduced by the use or help of a resistor, it is its main purpose and also to lower down the voltage in any particular portion of the surface. Copper wires are used to make a resistor which is coiled around a rod made of ceramic. Resistor’s outer part is coated with the insulating paint. The unit of resistor is $\Omega $ (read as ohm). Every resistor has 2 terminals and 1 connection. Resistors have different shapes as well as different sizes.
There are two types of resistors: - Linear resistor and non-linear resistor.
Now, it is given,
\[{E_1} = 2V\]
${R_1} = 100\Omega $
${R_2} = 50\Omega $
${R_3} = 20\Omega $
According to Kirchhoff’s law in loop ABCDA:
$
- {E_1} + \left( {I + 0.5} \right){R_1} + I{R_2} = 0 \\
\therefore - 2 + \left( {I + 0.5} \right)\left( {100} \right) + I\left( {50} \right) = 0 \\
$
According to Kirchhoff loop law in BGE FB:
$
- {E_2} + \left( {0.05} \right){R_3} + \left( {I + 0.05} \right){R_1} = 0 \\
\therefore - {E_2} + \left( {0.05} \right)\left( {20} \right) + \left( { - 0.02 + 0.05} \right)\left( {100} \right) = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {E_2} = 4V \\
$
Hence, current flowing through -
${R_{1,}}{I_1} = 0.05 - 0.02 = 0.03A = 30mA$ Towards right.
NOTE: Resistors like surface mount and through-hole are available in common types. Resistors can be static, special, standard resistor or pack of variable resistor. Resistance can be calculated through the resistor’s color pattern but the value of resistor may not be displayed outside. Resistors are also used in transmitters, modulators and demodulators, amplifiers, oscillators etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




