
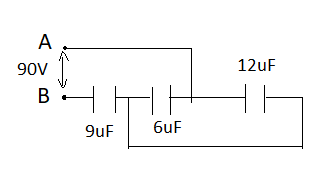
The charge on the $6\mu F$ capacitor in the circuit shown is

Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint:
To solve the above circuit we can see that capacitors $12\mu F$ and $6\mu F$ are in parallel so we just need to calculate C effectively from a given circuit and, according to parallel or series combination we can distribute charges and voltage on each capacitor.
Formula used:
For parallel combination of capacitors, its equivalent capacitor is${{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{2}}$
For series combination, its equivalent capacitor is $\dfrac{1}{C}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}$
Complete Step by step solution:
Capacitor $12\mu F$ and $6\mu F$ are in parallel so effective capacitance between them is given by,
${{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{2}}$, which is equivalent to 12+6 =$18\mu F$.
Now, capacitors of capacitance $18\mu F$and $9\mu F$ are in series so, the effective capacitance C in series is given by,
$\dfrac{1}{C}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{C2}=\dfrac{1}{18}+\dfrac{1}{9}=\dfrac{3}{18}$
So,$C=\dfrac{18}{3}=6\mu F$
Now, the effective capacitance between A and B is $6\mu F$so,
Total charge $Q$on circuit will be given by, $Q=CV$
Here, $Q$(total charge), $C$(effective capacitance between two point) and $V$(total voltage)
So,$Q=6\times 90=540$micro coulomb.
$\therefore $When capacitors in series charges remains same on capacitors and for in parallel voltage remains same.
Capacitors $18\mu F$ and $9\mu F$ are in series so charges remain the same, but potential varies from one capacitor to other so.
We know that, $V=Q/C$, so for $18\mu F$ voltage will be $V=\dfrac{540}{18}=30V$ since charge 540micro coulomb is the same for both capacitors.
Now, when we look in further circuit our $6\mu F$ and $12\mu F$ are in parallel so voltage will remains same which is equal to $30V$ and we need to calculate charge on $6\mu F$ capacitor,
$Q=CV=6\times 30=180$micro coulomb
So,$Q=180\mu C$ option (3) is correct.
Note:
When we need to find charge or potential on a capacitor in any circuit first we need to simplify the circuit to the extent till when we can calculate effective charge charge Q between point A and B and then by applying distributive properties of charge and voltage in series as well as parallel combinations of capacitors.
To solve the above circuit we can see that capacitors $12\mu F$ and $6\mu F$ are in parallel so we just need to calculate C effectively from a given circuit and, according to parallel or series combination we can distribute charges and voltage on each capacitor.
Formula used:
For parallel combination of capacitors, its equivalent capacitor is${{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{2}}$
For series combination, its equivalent capacitor is $\dfrac{1}{C}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}$
Complete Step by step solution:
Capacitor $12\mu F$ and $6\mu F$ are in parallel so effective capacitance between them is given by,
${{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{2}}$, which is equivalent to 12+6 =$18\mu F$.
Now, capacitors of capacitance $18\mu F$and $9\mu F$ are in series so, the effective capacitance C in series is given by,
$\dfrac{1}{C}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{C2}=\dfrac{1}{18}+\dfrac{1}{9}=\dfrac{3}{18}$
So,$C=\dfrac{18}{3}=6\mu F$
Now, the effective capacitance between A and B is $6\mu F$so,
Total charge $Q$on circuit will be given by, $Q=CV$
Here, $Q$(total charge), $C$(effective capacitance between two point) and $V$(total voltage)
So,$Q=6\times 90=540$micro coulomb.
$\therefore $When capacitors in series charges remains same on capacitors and for in parallel voltage remains same.
Capacitors $18\mu F$ and $9\mu F$ are in series so charges remain the same, but potential varies from one capacitor to other so.
We know that, $V=Q/C$, so for $18\mu F$ voltage will be $V=\dfrac{540}{18}=30V$ since charge 540micro coulomb is the same for both capacitors.
Now, when we look in further circuit our $6\mu F$ and $12\mu F$ are in parallel so voltage will remains same which is equal to $30V$ and we need to calculate charge on $6\mu F$ capacitor,
$Q=CV=6\times 30=180$micro coulomb
So,$Q=180\mu C$ option (3) is correct.
Note:
When we need to find charge or potential on a capacitor in any circuit first we need to simplify the circuit to the extent till when we can calculate effective charge charge Q between point A and B and then by applying distributive properties of charge and voltage in series as well as parallel combinations of capacitors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




