
The budding in yeast is illustrated by the diagram:

Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: Many unicellular organisms undergo asexual reproduction through binary fusion, fission, spore formation or budding. The budding is the method of asexual reproduction which is an asymmetric division. In budding the daughter cell may or may not separate from the body.
Complete answer: Asexual reproduction is the type of reproduction in which intermixing of the genetic material does not take place. It inherits the genes of the parent.
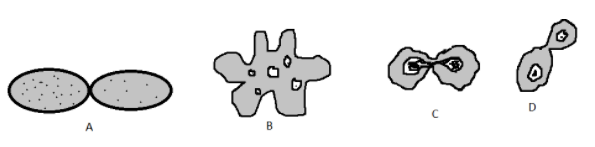
1. Figure A shows a binary fusion. It occurs in fertilisation when the male gamete is fertilized with the female gamete.
2. Figure B represents binary fission in amoeba. In this type, the parent cell divides into smaller copies of itself.
3. Figure C represents conjugation, in which two organisms of the same species join together and exchange their genetic material. One organism completely gives its genetic material to the other through the conjugation tube. This type of sexual reproduction takes place in lower organisms, i.e. bacteria, some algae, protozoa, etc.
4. Figure D shows the process of budding in yeast. It is the most common type of division in yeast. In this type, a small bud is formed from the mother cell which later becomes the daughter cell. As the daughter cell grows, the mother duplicates its DNA. The nucleus also divides and migrates to the growing bud.
Note: Budding is the most frequently used mode of reproduction. Budding also takes place in multicellular organisms like the hydra. In hydra, an outgrowth or a small bud is formed as a result of several mitotic divisions. In yeast, the bud may or may not detach from the parent but in hydra, the bud detaches as it gets matured.
Complete answer: Asexual reproduction is the type of reproduction in which intermixing of the genetic material does not take place. It inherits the genes of the parent.
1. Figure A shows a binary fusion. It occurs in fertilisation when the male gamete is fertilized with the female gamete.
2. Figure B represents binary fission in amoeba. In this type, the parent cell divides into smaller copies of itself.
3. Figure C represents conjugation, in which two organisms of the same species join together and exchange their genetic material. One organism completely gives its genetic material to the other through the conjugation tube. This type of sexual reproduction takes place in lower organisms, i.e. bacteria, some algae, protozoa, etc.
4. Figure D shows the process of budding in yeast. It is the most common type of division in yeast. In this type, a small bud is formed from the mother cell which later becomes the daughter cell. As the daughter cell grows, the mother duplicates its DNA. The nucleus also divides and migrates to the growing bud.
Note: Budding is the most frequently used mode of reproduction. Budding also takes place in multicellular organisms like the hydra. In hydra, an outgrowth or a small bud is formed as a result of several mitotic divisions. In yeast, the bud may or may not detach from the parent but in hydra, the bud detaches as it gets matured.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




