
The box of a pinhole camera of length L, has a hole of radius a. It is assumed that when the hole is illuminated by a parallel beam of light of wavelength λ the spread of the spot (obtained on the opposite wall of the camera) is the sum of its geometrical spread and the spread due to diffraction. The spot would then have its minimum size say ${{b}_{\min }}$ when:
A. $a=\dfrac{{{\lambda }^{2}}}{L}$ and \[{{b}_{\min }}=\dfrac{2{{\lambda }^{2}}}{L}\]
B. $a=\sqrt{\lambda L}$ and \[{{b}_{\min }}=\frac{2{{\lambda }^{2}}}{L}\]
C. $a=\sqrt{\lambda L}$ and ${{b}_{\min }}=\sqrt{4\lambda L}$
D. $a=\dfrac{{{\lambda }^{2}}}{L}$ and ${{b}_{\min }}=\sqrt{4\lambda L}$
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Bending of light over the edges of an opening is known as the diffraction of light. This can be explained only by the wave nature of the light. With the overlapping of the diffracted light, the bright and the dark fringes are formed on the screen.
Formula used:
Fringe width due to diffraction (diffraction spread) is given by,
$\beta =\dfrac{D\lambda }{d}$
Complete answer:
According to the situation mentioned in the question, the box of a pinhole camera of length L, has a hole of radius a. The spread can be visualized as shown in the diagram given here,
So from the given data, we knew that the illumination spread of the light is the sum of the geometrical spread and spread due to diffraction.
Mathematically,
$b=geometrical\ spread+diffracted\ spread$
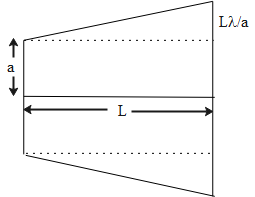
From the diagram, we can say that,
\[b=a+\dfrac{L\lambda }{a}\quad ...........\left( 1 \right)\]
For the minimum spread, the differentiation with rest to the radius of the hole should be zero.
$\dfrac{db}{da}=0$
So by differentiating equation (1) with respect to $a$,
$1-L\lambda \left( \dfrac{1}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)=0$
So here we can say the value of $a$ will be,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{L\lambda }{{{a}^{2}}}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=L\lambda \\
& \Rightarrow a=\sqrt{L\lambda } \\
\end{align}$
So for the minimum value of b (${{b}_{\min }}$) the value of $a$ should $\sqrt{L\lambda }$
So by putting the value of in equation (1) the minimum value of b will be,
$\begin{align}
& {{b}_{\min }}=\sqrt{L\lambda }+\dfrac{L\lambda }{\sqrt{L\lambda }} \\
& {{b}_{\min }}=2\sqrt{L\lambda } \\
\end{align}$
This can be also written as,
${{b}_{\min }}=\sqrt{4L\lambda }$
So, now we can say that the value of a for the least illumination spread should be $\sqrt{\lambda L}$ and the value of the minimum spread is $\sqrt{4\lambda L}$ .
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
When a monochromatic beam of light is diffracted alternative light and dark fringes are formed. The central fringe is the widest and almost equal to the size of the slit (opening). All other alternative fringes are of the same size and are dependent on the wavelength of the light, size of the slit, and the distance of the slit from the screen.
Formula used:
Fringe width due to diffraction (diffraction spread) is given by,
$\beta =\dfrac{D\lambda }{d}$
Complete answer:
According to the situation mentioned in the question, the box of a pinhole camera of length L, has a hole of radius a. The spread can be visualized as shown in the diagram given here,
So from the given data, we knew that the illumination spread of the light is the sum of the geometrical spread and spread due to diffraction.
Mathematically,
$b=geometrical\ spread+diffracted\ spread$

From the diagram, we can say that,
\[b=a+\dfrac{L\lambda }{a}\quad ...........\left( 1 \right)\]
For the minimum spread, the differentiation with rest to the radius of the hole should be zero.
$\dfrac{db}{da}=0$
So by differentiating equation (1) with respect to $a$,
$1-L\lambda \left( \dfrac{1}{{{a}^{2}}} \right)=0$
So here we can say the value of $a$ will be,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{L\lambda }{{{a}^{2}}}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=L\lambda \\
& \Rightarrow a=\sqrt{L\lambda } \\
\end{align}$
So for the minimum value of b (${{b}_{\min }}$) the value of $a$ should $\sqrt{L\lambda }$
So by putting the value of in equation (1) the minimum value of b will be,
$\begin{align}
& {{b}_{\min }}=\sqrt{L\lambda }+\dfrac{L\lambda }{\sqrt{L\lambda }} \\
& {{b}_{\min }}=2\sqrt{L\lambda } \\
\end{align}$
This can be also written as,
${{b}_{\min }}=\sqrt{4L\lambda }$
So, now we can say that the value of a for the least illumination spread should be $\sqrt{\lambda L}$ and the value of the minimum spread is $\sqrt{4\lambda L}$ .
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
When a monochromatic beam of light is diffracted alternative light and dark fringes are formed. The central fringe is the widest and almost equal to the size of the slit (opening). All other alternative fringes are of the same size and are dependent on the wavelength of the light, size of the slit, and the distance of the slit from the screen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




