
the best method for synthesis of given ether by Williamson’s ether synthesis is:
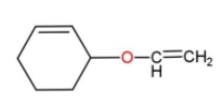
A.
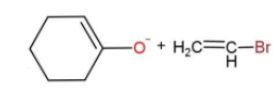
B.
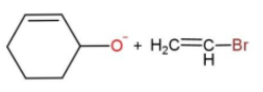
C.
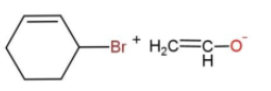
D.



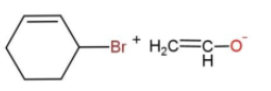

Answer
531k+ views
Hint: Williamson ether synthesis is a reaction which is used to prepare ethers. It uses an organohalide compound, which
is a compound that contains a halogen along with a carbon alkyl chain, which reacts with an alkoxide to yield ethers.
Complete answer:
Williamson synthesis for ethers involve a reaction sequence, where an alkoxide reacts with a alkyl halide through the mechanism of nucleophilic substitution reaction, which is a ${{S}_{N}}^{2}$ type of reaction. The alkoxide involved is usually a sodium alkoxide which is readily reduced to remove the sodium metal ion, the remaining is the alkoxide ion which is used in the reaction. The alkoxide ion replaces the nucleophile, bromine ion and forms an ether.
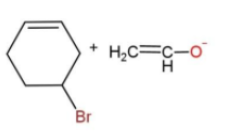
In the given reaction, the mechanism followed is ${{S}_{N}}^{2}$which is followed by inversion of configuration where the attacking nucleophile gets attached from the back side. So, reaction c favors this condition, as the removal of Br from the bulky group is easier also the alkoxide ion attacks from the opposite side to yield the product. While in other reactions, the alkoxide is the carbon ring, which does not get attached to the carbon chain due to its bulkiness, so the alkoxide attaching is favored.
The reaction is as follows:

Hence, option c is the correct way for ether synthesis.
Note:
The alkoxide is formed from the reaction of an alcohol with a metal ion. The metal ion is sodium preferably which is present as a base NaOH. The reaction uses the acidic nature of alcohols, and removes the hydrogen ion to form an alkoxide. This is the first step of Williamson ether synthesis.
is a compound that contains a halogen along with a carbon alkyl chain, which reacts with an alkoxide to yield ethers.
Complete answer:
Williamson synthesis for ethers involve a reaction sequence, where an alkoxide reacts with a alkyl halide through the mechanism of nucleophilic substitution reaction, which is a ${{S}_{N}}^{2}$ type of reaction. The alkoxide involved is usually a sodium alkoxide which is readily reduced to remove the sodium metal ion, the remaining is the alkoxide ion which is used in the reaction. The alkoxide ion replaces the nucleophile, bromine ion and forms an ether.
In the given reaction, the mechanism followed is ${{S}_{N}}^{2}$which is followed by inversion of configuration where the attacking nucleophile gets attached from the back side. So, reaction c favors this condition, as the removal of Br from the bulky group is easier also the alkoxide ion attacks from the opposite side to yield the product. While in other reactions, the alkoxide is the carbon ring, which does not get attached to the carbon chain due to its bulkiness, so the alkoxide attaching is favored.
The reaction is as follows:

Hence, option c is the correct way for ether synthesis.
Note:
The alkoxide is formed from the reaction of an alcohol with a metal ion. The metal ion is sodium preferably which is present as a base NaOH. The reaction uses the acidic nature of alcohols, and removes the hydrogen ion to form an alkoxide. This is the first step of Williamson ether synthesis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




