
The area (in sq. units) bounded by the parabola $y={{x}^{2}}-1$, the tangent at the point (2,3) to it and the y-axis is
$\begin{align}
& \left( A \right)\dfrac{14}{3} \\
& \left( B \right)\dfrac{56}{3} \\
& \left( C \right)\dfrac{8}{3} \\
& \left( D \right)\dfrac{32}{3} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: We start solving this question by finding the slope of the tangent to the curve at (2,3) by differentiating the curve and substituting the point (2,3) and we use the formula $\dfrac{d}{dx}{{x}^{n}}=n\times {{x}^{n-1}}$. From the obtained slope and point we find the equation of line using the formula, $\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$. Then we plot the graph of the curve and the tangent. Then we divide the region into two parts and find their areas by integrating them using the formula $\int{{{x}^{n}}dx}=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}$ and add them to find the total area.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that a tangent is drawn to the parabola $y={{x}^{2}}-1$ at point (2,3). So, let us find the equation of the tangent to the curve.
To find the slope of the tangent, let us differentiate the equation with respective to x.
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{2}}-1 \right) \\
& \dfrac{dy}{dx}=2x \\
\end{align}$
Then at point (2,3), slope of tangent is,
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}={{\left. 2x \right]}_{x=2}}=4$
So, slope of the tangent is equal to 4.
Now let us consider the formula for line equation from slope and point.
$\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$
So, using the above formula we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left( y-3 \right)=4\left( x-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y-3=4x-8 \\
& \Rightarrow y=4x-5 \\
\end{align}$
So, equation of the tangent at (2,3) is $y=4x-5$.
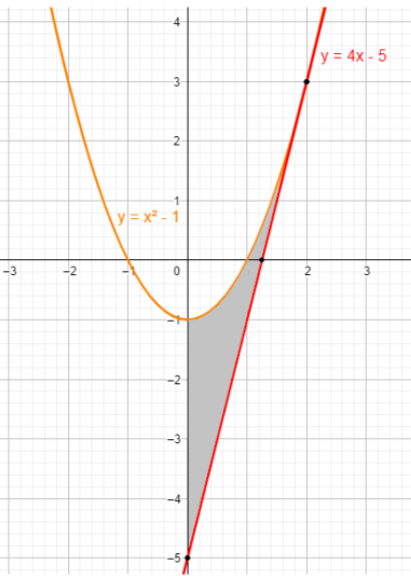
Now, let us plot the graph for the given curves.
Now, let us divide our required region into two parts, above x-axis and below x-axis. So, let us find the point where the line intersects x-axis. On x-axis y=0. So,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 4x-5=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 4x=5 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Let us use the formula for finding the area between two curves $f\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ and x-axis between x=a and x=b is
$\int\limits_{a}^{b}{\left( f\left( x \right)-g\left( x \right) \right)dx}$
Using the above formula, for the region below x-axis, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{5}{4}}{\left( \left( 4x-5 \right)-\left( {{x}^{2}}-1 \right) \right)dx} \\
& \Rightarrow \int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{5}{4}}{\left( -{{x}^{2}}+4x-4 \right)dx} \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ -\dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}+2{{x}^{2}}-4x \right]_{0}^{\dfrac{5}{4}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( -\dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right)}^{3}}}{3}+2{{\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right)}^{2}}-4\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right) \right)-\left( -\dfrac{{{0}^{3}}}{3}+2{{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 0 \right) \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( -\dfrac{\dfrac{125}{64}}{3}+2\left( \dfrac{25}{16} \right)-5 \right)-\left( 0 \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left( -\dfrac{125}{192}+\dfrac{25}{8}-5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{475}{192}-5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{475}{192}-5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow -\dfrac{485}{192} \\
\end{align}$
As the area is positive quantity, we take the area of first part as $\dfrac{485}{192}$…………(1)
Now, let us find the area of second part that is above x-axis.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \int\limits_{\dfrac{5}{4}}^{2}{\left( \left( {{x}^{2}}-1 \right)-\left( 4x-5 \right) \right)dx} \\
& \Rightarrow \int\limits_{\dfrac{5}{4}}^{2}{\left( {{x}^{2}}-4x+4 \right)dx} \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}-2{{x}^{2}}+4x \right]_{\dfrac{5}{4}}^{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( \dfrac{{{2}^{3}}}{3}-2{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+4\left( 2 \right) \right)-\left( \dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right)}^{3}}}{3}-2{{\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right)}^{2}}+4\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right) \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( \dfrac{8}{3}-8+8 \right)-\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{125}{64}}{3}-2\left( \dfrac{25}{16} \right)+5 \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{8}{3} \right)-\left( \dfrac{125}{192}-\dfrac{25}{8}+5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{8}{3} \right)-\left( -\dfrac{475}{192}+5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{8}{3}-\dfrac{485}{192} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{27}{192}.................\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Then the total area is sum of both areas. So, adding the obtained areas in equation (1) and (2) we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{485}{192}+\dfrac{27}{192} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{512}{192} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{8}{3} \\
\end{align}$
So, total area of the region bounded by given curves is $\dfrac{8}{3}$ square units.
Hence answer is Option C.
Note: There is a possibility of making a mistake while solving this question by not taking the modulus of $-\dfrac{485}{192}$, and leaving it as it is. Then they add it with $\dfrac{27}{192}$ to find the total area. But it is wrong. The first part of the region is below the x-axis that is the reason we get the area as negative. So, we need to take the modulus of the area of the first part $-\dfrac{485}{192}$, and add it to $\dfrac{27}{192}$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that a tangent is drawn to the parabola $y={{x}^{2}}-1$ at point (2,3). So, let us find the equation of the tangent to the curve.
To find the slope of the tangent, let us differentiate the equation with respective to x.
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{2}}-1 \right) \\
& \dfrac{dy}{dx}=2x \\
\end{align}$
Then at point (2,3), slope of tangent is,
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}={{\left. 2x \right]}_{x=2}}=4$
So, slope of the tangent is equal to 4.
Now let us consider the formula for line equation from slope and point.
$\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$
So, using the above formula we get,

$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left( y-3 \right)=4\left( x-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y-3=4x-8 \\
& \Rightarrow y=4x-5 \\
\end{align}$
So, equation of the tangent at (2,3) is $y=4x-5$.
Now, let us plot the graph for the given curves.
Now, let us divide our required region into two parts, above x-axis and below x-axis. So, let us find the point where the line intersects x-axis. On x-axis y=0. So,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 4x-5=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 4x=5 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Let us use the formula for finding the area between two curves $f\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ and x-axis between x=a and x=b is
$\int\limits_{a}^{b}{\left( f\left( x \right)-g\left( x \right) \right)dx}$
Using the above formula, for the region below x-axis, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{5}{4}}{\left( \left( 4x-5 \right)-\left( {{x}^{2}}-1 \right) \right)dx} \\
& \Rightarrow \int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{5}{4}}{\left( -{{x}^{2}}+4x-4 \right)dx} \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ -\dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}+2{{x}^{2}}-4x \right]_{0}^{\dfrac{5}{4}} \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( -\dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right)}^{3}}}{3}+2{{\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right)}^{2}}-4\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right) \right)-\left( -\dfrac{{{0}^{3}}}{3}+2{{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 0 \right) \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( -\dfrac{\dfrac{125}{64}}{3}+2\left( \dfrac{25}{16} \right)-5 \right)-\left( 0 \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left( -\dfrac{125}{192}+\dfrac{25}{8}-5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{475}{192}-5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{475}{192}-5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow -\dfrac{485}{192} \\
\end{align}$
As the area is positive quantity, we take the area of first part as $\dfrac{485}{192}$…………(1)
Now, let us find the area of second part that is above x-axis.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \int\limits_{\dfrac{5}{4}}^{2}{\left( \left( {{x}^{2}}-1 \right)-\left( 4x-5 \right) \right)dx} \\
& \Rightarrow \int\limits_{\dfrac{5}{4}}^{2}{\left( {{x}^{2}}-4x+4 \right)dx} \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}-2{{x}^{2}}+4x \right]_{\dfrac{5}{4}}^{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( \dfrac{{{2}^{3}}}{3}-2{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+4\left( 2 \right) \right)-\left( \dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right)}^{3}}}{3}-2{{\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right)}^{2}}+4\left( \dfrac{5}{4} \right) \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left[ \left( \dfrac{8}{3}-8+8 \right)-\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{125}{64}}{3}-2\left( \dfrac{25}{16} \right)+5 \right) \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{8}{3} \right)-\left( \dfrac{125}{192}-\dfrac{25}{8}+5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{8}{3} \right)-\left( -\dfrac{475}{192}+5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{8}{3}-\dfrac{485}{192} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{27}{192}.................\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Then the total area is sum of both areas. So, adding the obtained areas in equation (1) and (2) we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{485}{192}+\dfrac{27}{192} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{512}{192} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{8}{3} \\
\end{align}$
So, total area of the region bounded by given curves is $\dfrac{8}{3}$ square units.
Hence answer is Option C.
Note: There is a possibility of making a mistake while solving this question by not taking the modulus of $-\dfrac{485}{192}$, and leaving it as it is. Then they add it with $\dfrac{27}{192}$ to find the total area. But it is wrong. The first part of the region is below the x-axis that is the reason we get the area as negative. So, we need to take the modulus of the area of the first part $-\dfrac{485}{192}$, and add it to $\dfrac{27}{192}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




