
The area enclosed by a hysteresis loop is the measure of ____________ .
A) retentivity
B) susceptibility
C) permeability
D) energy loss per cycle
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint:The hysteresis loop is only exhibited by ferromagnetic materials. It represents how the magnetic field in the ferromagnetic material changes in accordance with the magnetic intensity. The material gets magnetized and demagnetized repeatedly which involves a loss of energy.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: Sketch the hysteresis loop of a ferromagnetic material.
The figure given below depicts the hysteresis loop of a ferromagnetic material.
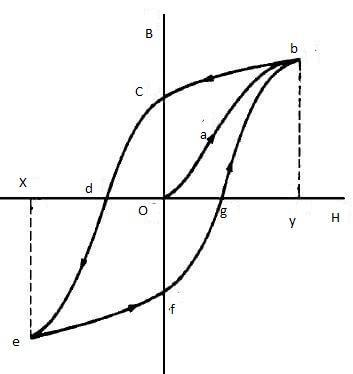
In the above figure, $B$ is the magnetic field in the material and $H$ is the magnetic intensity. The curve ${\text{ob}}$ marks the rise and saturation of the magnetic field $B$ in the material. The field then decreases along ${\text{bc}}$ as $H$ is reduced. The point $c$ represents the magnetic field in the material when $H = 0$. This is termed as retentivity. To get $B = 0$, the intensity is reversed and increased along ${\text{cd}}$. At $d$ we have $B = 0$. This is termed as coercivity. Now to attain saturation in the reverse direction, the intensity is increased in the negative direction along ${\text{de}}$. Reducing the reverse intensity gives the retentivity $f$ in the negative direction and an increase in the positive direction will make the field zero at $g$. Again saturation is achieved along ${\text{gb}}$. This constitutes one cycle.
The material thus gets magnetized and demagnetized in one cycle. Energy is lost in doing this. The lost energy is given out as heat and is referred to as the hysteresis loss. The area of the loop represents the energy lost in one cycle.
Hence the correct option is D.
Note:A narrow hysteresis loop will indicate less loss of energy and a wide loop will indicate more energy loss. The core of a transformer has to suffer minimum energy loss and so materials with narrow hysteresis like soft iron are preferred for it. However, for making permanent magnets we choose materials with high retentivity so that it is strong and high coercivity so that it cannot be demagnetized easily.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: Sketch the hysteresis loop of a ferromagnetic material.
The figure given below depicts the hysteresis loop of a ferromagnetic material.

In the above figure, $B$ is the magnetic field in the material and $H$ is the magnetic intensity. The curve ${\text{ob}}$ marks the rise and saturation of the magnetic field $B$ in the material. The field then decreases along ${\text{bc}}$ as $H$ is reduced. The point $c$ represents the magnetic field in the material when $H = 0$. This is termed as retentivity. To get $B = 0$, the intensity is reversed and increased along ${\text{cd}}$. At $d$ we have $B = 0$. This is termed as coercivity. Now to attain saturation in the reverse direction, the intensity is increased in the negative direction along ${\text{de}}$. Reducing the reverse intensity gives the retentivity $f$ in the negative direction and an increase in the positive direction will make the field zero at $g$. Again saturation is achieved along ${\text{gb}}$. This constitutes one cycle.
The material thus gets magnetized and demagnetized in one cycle. Energy is lost in doing this. The lost energy is given out as heat and is referred to as the hysteresis loss. The area of the loop represents the energy lost in one cycle.
Hence the correct option is D.
Note:A narrow hysteresis loop will indicate less loss of energy and a wide loop will indicate more energy loss. The core of a transformer has to suffer minimum energy loss and so materials with narrow hysteresis like soft iron are preferred for it. However, for making permanent magnets we choose materials with high retentivity so that it is strong and high coercivity so that it cannot be demagnetized easily.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




