
The anion of acetylacetone $acac$ forms $Co{\left( {acac} \right)_3}$ chelate with $C{o^{3 + }}$. The rings of the chelate are:
A.five membered
B.four membered
C.six membered
D.three membered.
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:
Acetylacetone is a bidentate ligand that is found in metal that can form octahedral complexes. It can combine with the central metal at two regions and forms a ring while doing so. The central metal atom usually bonds to the oxygen of the ligand.
Complete step by step answer:
Chelate rings are formed when a single ligand binds with a central metal using more than one bonding site thus forming a ring. Acetylacetone ligand is a bidentate ligand meaning that for a tetrahedral complex a maximum of two ligands can bond and for an octahedral complex only three ligands can form bonds with the central metal atom.
The acetylacetone which acts as a ligand is derived from $C{H^{}}_3COCHCOC{H^ - }_3$ which is the acetylacetonate anion.
The ligand uses its oxygen atoms to bind to the cobalt metal. It does so at two sites per ligand. Therefore, the ligand is said to have a six membered ring. The complex is represented by $M{\left( {aa} \right)_3}$ where $M$ is cobalt or the metal atom and $aa$ is the bidentate ligand acetylacetonate.
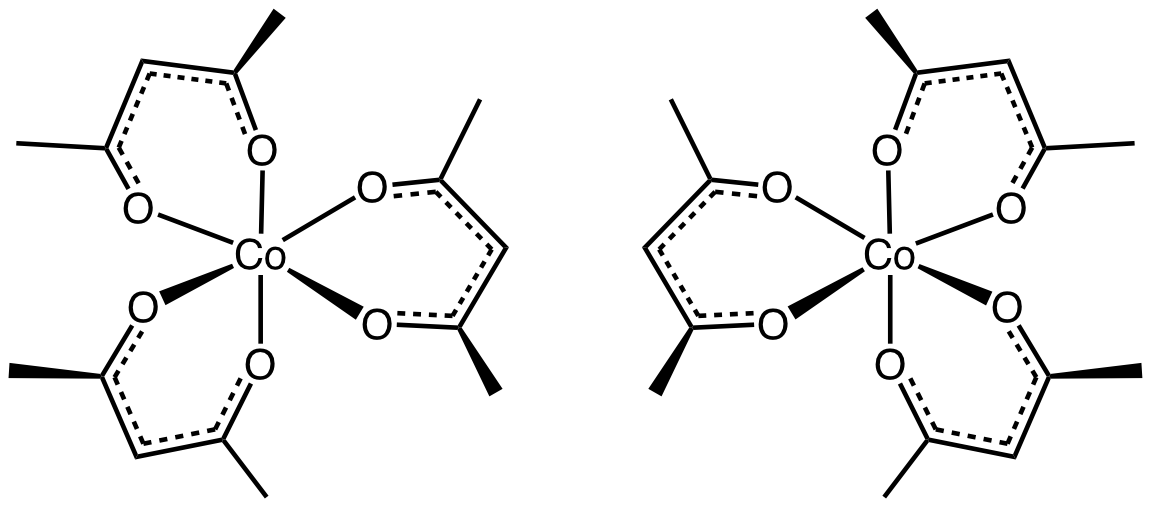
The IUPAC name of the compound is tris-acetylacetonato$\left( {III} \right)$. This complex contains three symmetrical ligands. It has two types of optical isomers. One is dextrorotatory and the other is laevorotatory, that is, the complexes are right and left handed respectively.
It cannot form geometric isomers.
Therefore, the answer to the question is option C, that is, six membered.
Note: Chelate rings are formed when the ligand is either bidentate, tridentate and so on.
-The number of sites at which they bond is known as a member site.
-Acetylacetonate ligand has two optical isomers and does not form geometric isomers.
Acetylacetone is a bidentate ligand that is found in metal that can form octahedral complexes. It can combine with the central metal at two regions and forms a ring while doing so. The central metal atom usually bonds to the oxygen of the ligand.
Complete step by step answer:
Chelate rings are formed when a single ligand binds with a central metal using more than one bonding site thus forming a ring. Acetylacetone ligand is a bidentate ligand meaning that for a tetrahedral complex a maximum of two ligands can bond and for an octahedral complex only three ligands can form bonds with the central metal atom.
The acetylacetone which acts as a ligand is derived from $C{H^{}}_3COCHCOC{H^ - }_3$ which is the acetylacetonate anion.
The ligand uses its oxygen atoms to bind to the cobalt metal. It does so at two sites per ligand. Therefore, the ligand is said to have a six membered ring. The complex is represented by $M{\left( {aa} \right)_3}$ where $M$ is cobalt or the metal atom and $aa$ is the bidentate ligand acetylacetonate.

The IUPAC name of the compound is tris-acetylacetonato$\left( {III} \right)$. This complex contains three symmetrical ligands. It has two types of optical isomers. One is dextrorotatory and the other is laevorotatory, that is, the complexes are right and left handed respectively.
It cannot form geometric isomers.
Therefore, the answer to the question is option C, that is, six membered.
Note: Chelate rings are formed when the ligand is either bidentate, tridentate and so on.
-The number of sites at which they bond is known as a member site.
-Acetylacetonate ligand has two optical isomers and does not form geometric isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




