
The amplitude of oscillation of the image is
A. A
B. 2A
C. A/2
D. image does not oscillate

Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: This question can be solved using the magnification formula used especially for the lens. The object distance equals 3 times of the focal length with a negative sign and the image distance equals three over two times of the focal length. So, when we divide these terms, object distance by image distance, we will get the amplitude of the oscillation of the image.
Formula used:
\[m=\dfrac{-v}{u}\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
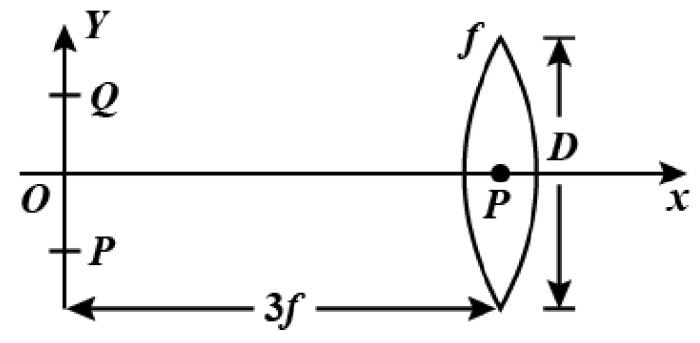
The type of lens used in the above image is a convex lens.
Therefore, the magnification formula in the case of a convex lens is as follows.
\[m=\dfrac{-v}{u}\]
Where v is the image distance (the height of the image) and u is the object distance (the height of the object).
From the data, we have the data as follows.
The object distance of the image in terms of the focal length of the lens is given as follows.
\[u=-3f\]
The negative sign represents the opposite direction.
The image distance of the image in terms of the focal length of the lens is given as follows.
\[v=\dfrac{3}{2}f\]
Substitute these values in the formula of the magnification equation. So, we get,
\[m=\dfrac{-{}^{3}/{}_{2}f}{-3f}\]
Continue further calculation.
\[\begin{align}
& m=\dfrac{-3f}{-2\times 3f} \\
& \Rightarrow m=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
The magnitude of the image represents the amplitude of the oscillation. So, we get,
As the value of the magnitude of the image reduces to half, thus, the value of the amplitude of the oscillation reduces to half.
As, the amplitude of the oscillation of the image reduces to half, thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: The given image is a bit confusing, as the question is about the amplitude of the image, but, we are given with the convex lens. In this question, we have equated the magnitude of the image to the amplitude of the oscillation. The signs of the parameters should be taken care of.
Formula used:
\[m=\dfrac{-v}{u}\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
The type of lens used in the above image is a convex lens.
Therefore, the magnification formula in the case of a convex lens is as follows.
\[m=\dfrac{-v}{u}\]
Where v is the image distance (the height of the image) and u is the object distance (the height of the object).
From the data, we have the data as follows.
The object distance of the image in terms of the focal length of the lens is given as follows.
\[u=-3f\]
The negative sign represents the opposite direction.
The image distance of the image in terms of the focal length of the lens is given as follows.
\[v=\dfrac{3}{2}f\]
Substitute these values in the formula of the magnification equation. So, we get,
\[m=\dfrac{-{}^{3}/{}_{2}f}{-3f}\]
Continue further calculation.
\[\begin{align}
& m=\dfrac{-3f}{-2\times 3f} \\
& \Rightarrow m=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
The magnitude of the image represents the amplitude of the oscillation. So, we get,
As the value of the magnitude of the image reduces to half, thus, the value of the amplitude of the oscillation reduces to half.
As, the amplitude of the oscillation of the image reduces to half, thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: The given image is a bit confusing, as the question is about the amplitude of the image, but, we are given with the convex lens. In this question, we have equated the magnitude of the image to the amplitude of the oscillation. The signs of the parameters should be taken care of.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




