
The ammeter reading in the circuit below is
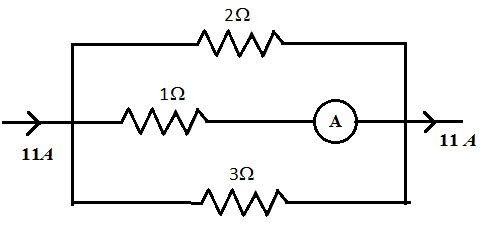
A. 2 A
B. 3 A
C. 6 A
D. 5 A

Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: We know that voltage across the parallel circuit remains constant. Use Ohm’s law to express the current through each branch in terms of voltage. Then use KCL to express the sum of currents at any junction in the circuit and substitute the values of current from the concept we discussed earlier.
Formula used:
Ohm’s law,
\[V = IR\]
Here, V is the voltage, I is the current and R is the resistance.
Complete step by step answer:
We assume the current flowing through the first branch is \[{I_1}\], the current through the second branch is \[{I_2}\] and the current through the third branch is \[{I_3}\] as shown in the figure below.
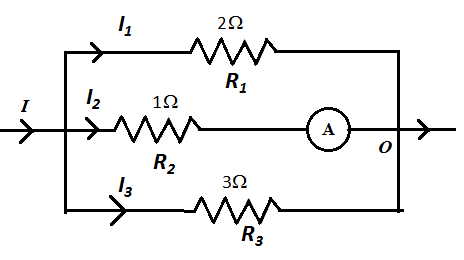
We know that in the parallel circuit, the voltage across each branch remains the same. Therefore, using Ohm’s law we can write,
\[{V_1} = {V_2} = {V_3} = V\]
\[ \Rightarrow {I_1}{R_1} = {I_2}{R_2} = {I_3}{R_3} = V\]
We substitute \[2\,\Omega \] for \[{R_1}\], \[1\,\Omega \] for \[{R_2}\] and \[3\,\Omega \] for \[{R_3}\] in the above equation.
\[2{I_1} = 1{I_2} = 3{I_3} = V\] …… (1)
We apply Kirchhoff’s current law at point O as follows,
\[{I_1} + {I_2} + {I_3} = 11\] …… (2)
Using equation (1), we can write the above equation as,
\[\dfrac{V}{2} + V + \dfrac{V}{3} = 11\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{11V}}{6} = 11\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = 6\,V\]
Now, the current flowing through the ammeter is \[{I_2}\]. Therefore, from equation (1), we have,
\[{I_2} = V\]
Therefore, the current through the ammeter is,
\[{I_2} = 6\,A\]
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Additional information: Kirchhoff’s voltage current law states that at any junction in the circuit the total incoming current is equal to the total current leaving the junction. The expression of Kirchhoff’s current law can be given as,
\[{I_{in}} = {I_{out}}\]
Note:
Students should remember that in series circuits, the current remains constant. Therefore, the total current leaves the resistor \[{R_2}\] is equal to total current leaves ammeter. KCL can be applied at any point in the circuit to determine the value of unknown current in the circuit. If we determine the values of current through each branch, the sum of the current should be 11 A.
Formula used:
Ohm’s law,
\[V = IR\]
Here, V is the voltage, I is the current and R is the resistance.
Complete step by step answer:
We assume the current flowing through the first branch is \[{I_1}\], the current through the second branch is \[{I_2}\] and the current through the third branch is \[{I_3}\] as shown in the figure below.

We know that in the parallel circuit, the voltage across each branch remains the same. Therefore, using Ohm’s law we can write,
\[{V_1} = {V_2} = {V_3} = V\]
\[ \Rightarrow {I_1}{R_1} = {I_2}{R_2} = {I_3}{R_3} = V\]
We substitute \[2\,\Omega \] for \[{R_1}\], \[1\,\Omega \] for \[{R_2}\] and \[3\,\Omega \] for \[{R_3}\] in the above equation.
\[2{I_1} = 1{I_2} = 3{I_3} = V\] …… (1)
We apply Kirchhoff’s current law at point O as follows,
\[{I_1} + {I_2} + {I_3} = 11\] …… (2)
Using equation (1), we can write the above equation as,
\[\dfrac{V}{2} + V + \dfrac{V}{3} = 11\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{11V}}{6} = 11\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = 6\,V\]
Now, the current flowing through the ammeter is \[{I_2}\]. Therefore, from equation (1), we have,
\[{I_2} = V\]
Therefore, the current through the ammeter is,
\[{I_2} = 6\,A\]
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Additional information: Kirchhoff’s voltage current law states that at any junction in the circuit the total incoming current is equal to the total current leaving the junction. The expression of Kirchhoff’s current law can be given as,
\[{I_{in}} = {I_{out}}\]
Note:
Students should remember that in series circuits, the current remains constant. Therefore, the total current leaves the resistor \[{R_2}\] is equal to total current leaves ammeter. KCL can be applied at any point in the circuit to determine the value of unknown current in the circuit. If we determine the values of current through each branch, the sum of the current should be 11 A.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




