
The amino acid attaches to the ……….end of the amino acid receptor arm
A. 5’
B. 3’
C. Bidirectional
D. None of the above
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint:The tRNA has many varieties. Each variety carries a specific amino acid from the amino acid pools to the mRNA on the ribosomes to form polypeptides, hence its name. the tRNA from about 15% of the total RNA of a cell. Its molecule is the smallest of all RNA types. A tRNA molecule proposed by R.W. Holley in 1965, has the form of a cloverleaf that results from self-folding and base pairing, creating paired stems and unpaired loops.
Complete answer:The tRNA has four regions.
1. Carrier end. This is the 3'end of the molecule. Here a specific amino acid joins it. It, in all cases, has a base triplet CCA with-OH at the tip. The –COOH of amino acid joins –OH
2. Recognition end. It is the opposite end of the molecule. It has 3 unpaired ribonucleotides. The bases of these ribonucleotides have complementary bases on the mRNA chain. A base triplet on mRNA chains is called a codon, and its complementary base triplet on tRNA molecules is termed as an anticodon. Anticodon reads its appropriate codon and temporarily joins it by hydrogen bonds during protein synthesis.
3. Enzyme sites. It is on one side of the molecule. It is meant for a specific charging enzyme which catalyzes the union of a specific amino acid to tRNA molecules.
4. Ribosome site. It is on the other side of the molecule. It is meant to attach to the ribosome.
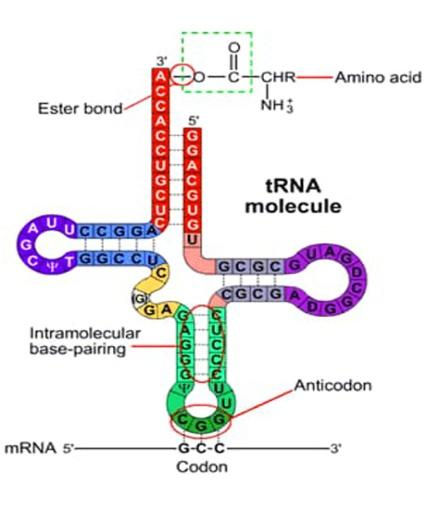
So the correct answer is option B. 3’
Note: About 15% of cells of RNA are tRNA. The length of the molecule is the shortest. The tRNA or transfer RNA has a long life and is used again and again in the translation process. The tRNA has an almost similar structure in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Complete answer:The tRNA has four regions.
1. Carrier end. This is the 3'end of the molecule. Here a specific amino acid joins it. It, in all cases, has a base triplet CCA with-OH at the tip. The –COOH of amino acid joins –OH
2. Recognition end. It is the opposite end of the molecule. It has 3 unpaired ribonucleotides. The bases of these ribonucleotides have complementary bases on the mRNA chain. A base triplet on mRNA chains is called a codon, and its complementary base triplet on tRNA molecules is termed as an anticodon. Anticodon reads its appropriate codon and temporarily joins it by hydrogen bonds during protein synthesis.
3. Enzyme sites. It is on one side of the molecule. It is meant for a specific charging enzyme which catalyzes the union of a specific amino acid to tRNA molecules.
4. Ribosome site. It is on the other side of the molecule. It is meant to attach to the ribosome.

So the correct answer is option B. 3’
Note: About 15% of cells of RNA are tRNA. The length of the molecule is the shortest. The tRNA or transfer RNA has a long life and is used again and again in the translation process. The tRNA has an almost similar structure in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




