
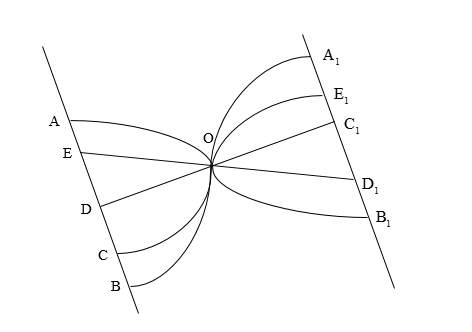
The adjoining figure shows the road plan of lines connecting two parallel roads AB and \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\]. A man walking on the road AB takes a turn at random to reach the road \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\]. It is known that he reaches the road \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] from O by taking a straight line path. The chance that he moves on a straight line from the road AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] is
(a) \[0.25\]
(b) \[0.04\]
(c) \[0.2\]
(d) None of these

Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint:
Here, we will assume \[X\] to be the event that the man takes any of the 5 paths from AB to O, and then takes one of the two straight paths from O to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\]. Again we will assume \[Y\] to be the event that the man takes any one of the 2 straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\]. We will use the formula for conditional probability to find the probability \[P\left( {Y|X} \right)\], and hence, find the required chance.
Complete step by step solution:
We can observe that from AB to O, the two straight paths are from point E, and point D.
We can also observe that form O to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\], the two straight paths are from O to \[{{\rm{C}}_1}\], or \[{{\rm{D}}_1}\].
We will use conditional probability to find the required chance.
Let \[X\] be the event that the man takes any of the 5 paths from AB to O, and then takes one of the two straight paths from O to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\].
The number of ways in which the man takes any one path of the 5 paths from AB to O is given by \[{}^5{C_1} = 5\] ways.
The number of ways in which the man takes any one path of the 2 straight paths from O to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] is given by \[{}^2{C_1} = 2\] ways.
Therefore, we get
The number of ways in which the man takes any one path of the 5 paths from AB to O, and then takes any one path of the 2 straight paths from O to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] is given by \[5 \times 2 = 10\] ways.
Thus, we get
\[P\left( X \right) = 10\]
The straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] are the paths \[{\rm{D}}{{\rm{C}}_1}\] and \[{\rm{E}}{{\rm{D}}_1}\].
Let \[Y\] be the event that the man takes any one of the 2 straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\].
The number of ways in which the man takes any one path of the 2 straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] is given by \[{}^2{C_1} = 2\] ways.
Therefore, we get
\[P\left( Y \right) = 2\]
Now, we need to find the intersection of the events \[X\] and \[Y\].
The event \[X\] is the event that the man takes any of the 5 paths from AB to O, and then takes one of the two straight paths from O to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\].
The event \[Y\] is the event that the man takes any one of the 2 straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\].
Therefore, the intersection of the events \[X\] and \[Y\] is the event that the man takes one of the two straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\].
The number of ways in which the man takes any one path of the 2 straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] is given by \[{}^2{C_1} = 2\] ways.
Therefore, we get
\[P\left( {X \cap Y} \right) = 2\]
Using the formula for conditional probability, we get
\[ \Rightarrow P\left( {Y|X} \right) = \dfrac{{P\left( {Y \cap X} \right)}}{{P\left( X \right)}}\]
Rewriting the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow P\left( {Y|X} \right) = \dfrac{{P\left( {X \cap Y} \right)}}{{P\left( X \right)}}\]
Substituting \[P\left( X \right) = 10\] and \[P\left( {X \cap Y} \right) = 2\] in the formula, we get
\[ \Rightarrow P\left( {Y|X} \right) = \dfrac{2}{{10}}\]
Therefore, we get
\[ \Rightarrow P\left( {Y|X} \right) = 0.2\]
Thus, given that the man reaches the road \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] from O by taking a straight line path, the chance that he moves on a straight line from the road AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] is the chance is \[0.2\].
The correct option is option (c).
Note:
We used the formula for conditional probability to solve the problem. If it is given that an event \[B\] has happened, then the probability that \[A\] occurs after the happening of the event \[B\] is given by the conditional probability \[P\left( {A|B} \right) = \dfrac{{P\left( {A \cap B} \right)}}{{P\left( B \right)}}\].
Here, we will assume \[X\] to be the event that the man takes any of the 5 paths from AB to O, and then takes one of the two straight paths from O to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\]. Again we will assume \[Y\] to be the event that the man takes any one of the 2 straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\]. We will use the formula for conditional probability to find the probability \[P\left( {Y|X} \right)\], and hence, find the required chance.
Complete step by step solution:
We can observe that from AB to O, the two straight paths are from point E, and point D.
We can also observe that form O to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\], the two straight paths are from O to \[{{\rm{C}}_1}\], or \[{{\rm{D}}_1}\].
We will use conditional probability to find the required chance.
Let \[X\] be the event that the man takes any of the 5 paths from AB to O, and then takes one of the two straight paths from O to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\].
The number of ways in which the man takes any one path of the 5 paths from AB to O is given by \[{}^5{C_1} = 5\] ways.
The number of ways in which the man takes any one path of the 2 straight paths from O to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] is given by \[{}^2{C_1} = 2\] ways.
Therefore, we get
The number of ways in which the man takes any one path of the 5 paths from AB to O, and then takes any one path of the 2 straight paths from O to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] is given by \[5 \times 2 = 10\] ways.
Thus, we get
\[P\left( X \right) = 10\]
The straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] are the paths \[{\rm{D}}{{\rm{C}}_1}\] and \[{\rm{E}}{{\rm{D}}_1}\].
Let \[Y\] be the event that the man takes any one of the 2 straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\].
The number of ways in which the man takes any one path of the 2 straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] is given by \[{}^2{C_1} = 2\] ways.
Therefore, we get
\[P\left( Y \right) = 2\]
Now, we need to find the intersection of the events \[X\] and \[Y\].
The event \[X\] is the event that the man takes any of the 5 paths from AB to O, and then takes one of the two straight paths from O to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\].
The event \[Y\] is the event that the man takes any one of the 2 straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\].
Therefore, the intersection of the events \[X\] and \[Y\] is the event that the man takes one of the two straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\].
The number of ways in which the man takes any one path of the 2 straight paths from AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] is given by \[{}^2{C_1} = 2\] ways.
Therefore, we get
\[P\left( {X \cap Y} \right) = 2\]
Using the formula for conditional probability, we get
\[ \Rightarrow P\left( {Y|X} \right) = \dfrac{{P\left( {Y \cap X} \right)}}{{P\left( X \right)}}\]
Rewriting the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow P\left( {Y|X} \right) = \dfrac{{P\left( {X \cap Y} \right)}}{{P\left( X \right)}}\]
Substituting \[P\left( X \right) = 10\] and \[P\left( {X \cap Y} \right) = 2\] in the formula, we get
\[ \Rightarrow P\left( {Y|X} \right) = \dfrac{2}{{10}}\]
Therefore, we get
\[ \Rightarrow P\left( {Y|X} \right) = 0.2\]
Thus, given that the man reaches the road \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] from O by taking a straight line path, the chance that he moves on a straight line from the road AB to \[{{\rm{A}}_1}{{\rm{B}}_1}\] is the chance is \[0.2\].
The correct option is option (c).
Note:
We used the formula for conditional probability to solve the problem. If it is given that an event \[B\] has happened, then the probability that \[A\] occurs after the happening of the event \[B\] is given by the conditional probability \[P\left( {A|B} \right) = \dfrac{{P\left( {A \cap B} \right)}}{{P\left( B \right)}}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




