
The active site of an enzyme is formed by a few of the enzyme’s
A. Carboxyl groups of the amino acids in \[{1^ \circ }\] and \[{2^ \circ }\] structure.
B. Amino groups of the amino acids in \[{1^ \circ }\] and \[{2^ \circ }\] structure.
C. R groups of the amino acids in \[{3^ \circ }\] structure.
D. Exposed sulphur bonds in \[{1^ \circ }\] and \[{3^ \circ }\] structure.
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: In an enzymatic reaction, the substrate binds to the specific site of the enzyme which is known as its active site, known for catalyzing the conversion of the substrate to its product.
Complete answer:
The active site of an enzyme is composed of amino acids that are present in the structure. Amino-acids are known to possess amino, carboxyl, and R-groups. It is the R-group of amino acid that provides specificity to the active site for a specific substrate. The interaction between the R-group of the active site and side chains of the substrate is only possible if the molecule is in the form of \[{3^ \circ }\] structure as this is the only conformation that provides enzyme catalytic activity.
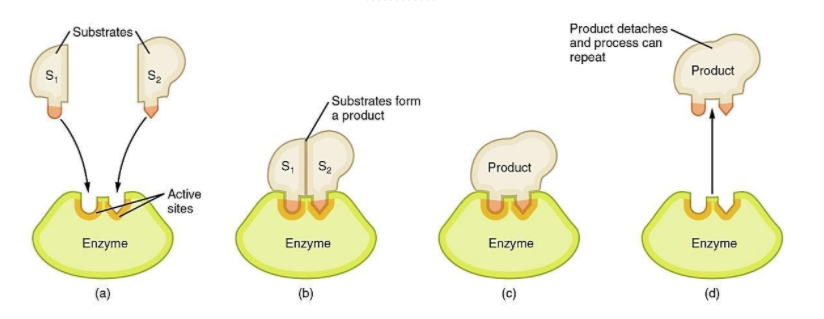
The amino and the carboxyl groups are known to perform the function of folding the protein molecule rather than providing it enzymatic activity.
The primary and secondary structures of the protein are not involved in the enzymatic activity because, to become enzymatically active, protein must take the conformation of \[{3^ \circ }\] structure.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Additional information:
The active site of an enzyme consists of two sites i.e., the binding site and catalytic site. It is the binding site which attracts the specific substrate molecule while the catalytic site is known for the conversion of substrate into product. The nature of amino acids present near the active site is responsible for determining whether or not a substrate molecule will fit in the active site. The bond formed between the active site and the side chains of the substrate molecule are temporary.
Note: The tertiary conformation of the protein molecule is known for providing enzymatic activity. The active site of the enzyme is formed by the R-groups of amino acids in the \[{3^ \circ }\] structure. It is the R-group which is different in an amino acid thereby, making it catalytic for specific substrate molecules.
Complete answer:
The active site of an enzyme is composed of amino acids that are present in the structure. Amino-acids are known to possess amino, carboxyl, and R-groups. It is the R-group of amino acid that provides specificity to the active site for a specific substrate. The interaction between the R-group of the active site and side chains of the substrate is only possible if the molecule is in the form of \[{3^ \circ }\] structure as this is the only conformation that provides enzyme catalytic activity.

The amino and the carboxyl groups are known to perform the function of folding the protein molecule rather than providing it enzymatic activity.
The primary and secondary structures of the protein are not involved in the enzymatic activity because, to become enzymatically active, protein must take the conformation of \[{3^ \circ }\] structure.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Additional information:
The active site of an enzyme consists of two sites i.e., the binding site and catalytic site. It is the binding site which attracts the specific substrate molecule while the catalytic site is known for the conversion of substrate into product. The nature of amino acids present near the active site is responsible for determining whether or not a substrate molecule will fit in the active site. The bond formed between the active site and the side chains of the substrate molecule are temporary.
Note: The tertiary conformation of the protein molecule is known for providing enzymatic activity. The active site of the enzyme is formed by the R-groups of amino acids in the \[{3^ \circ }\] structure. It is the R-group which is different in an amino acid thereby, making it catalytic for specific substrate molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




