
The acid which reduces Fehling’s solution is which of the following?
A.Methanoic acid
B.Ethanoic acid
C.Propanoic acid
D.Butanoic acid
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint:Fehling solution is used to detect the presence of aldehyde functional group in a molecule. It consists of Fehling solution A and Fehling solution B. It is also used as a test for detection of reducing sugars.
Complete step by step answer:
Fehling solution is made up by mixing two separate solutions- Fehling’s solution A and Fehling’s solution B. Solution A contains deep blue colored dilute solution of copper sulphate and Fehling’s solution B contains colorless aqueous solution of sodium potassium. It is prepared by mixing sodium potassium tartrate and sodium hydroxide. This solution is also called Rochelle salt.
Fehling solution is used to detect the presence of aldehyde functional groups. The active group is a bis (tartrate) complex of $C{u^{2 + }}$ . It is an oxidizing agent. The two solutions are stable separately and are mixed only when required because the $Cu(II)$ complex formed by their combination is not stable.
When Fehling solution is mixed with solution containing aldehyde, a red brown precipitate of cuprous oxide appears.
The general reaction can be stated as follows-
$RCHO + 2C{u^{2 + }} + 3O{H^ - } \to RCO{O^ - } + 2C{u^ + } + 2{H_2}O$
The blue color of Fehling solution changes to red as aldehyde reduces the $Cu(II)$ complex.
Now let us look at the acids given in the option. The structures are-
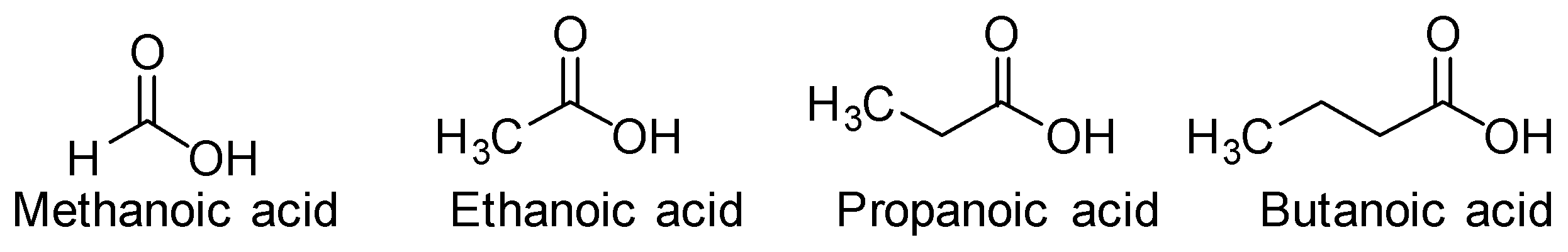
In the acids given above we can see that methanoic acid has carboxyl group $( - COOH)$ and aldehyde group $( - CHO)$ also. The other acids only have the carboxylic group. So only methanoic acid will reduce Fehling solution and give the color change.
So the correct option is A.
Note:
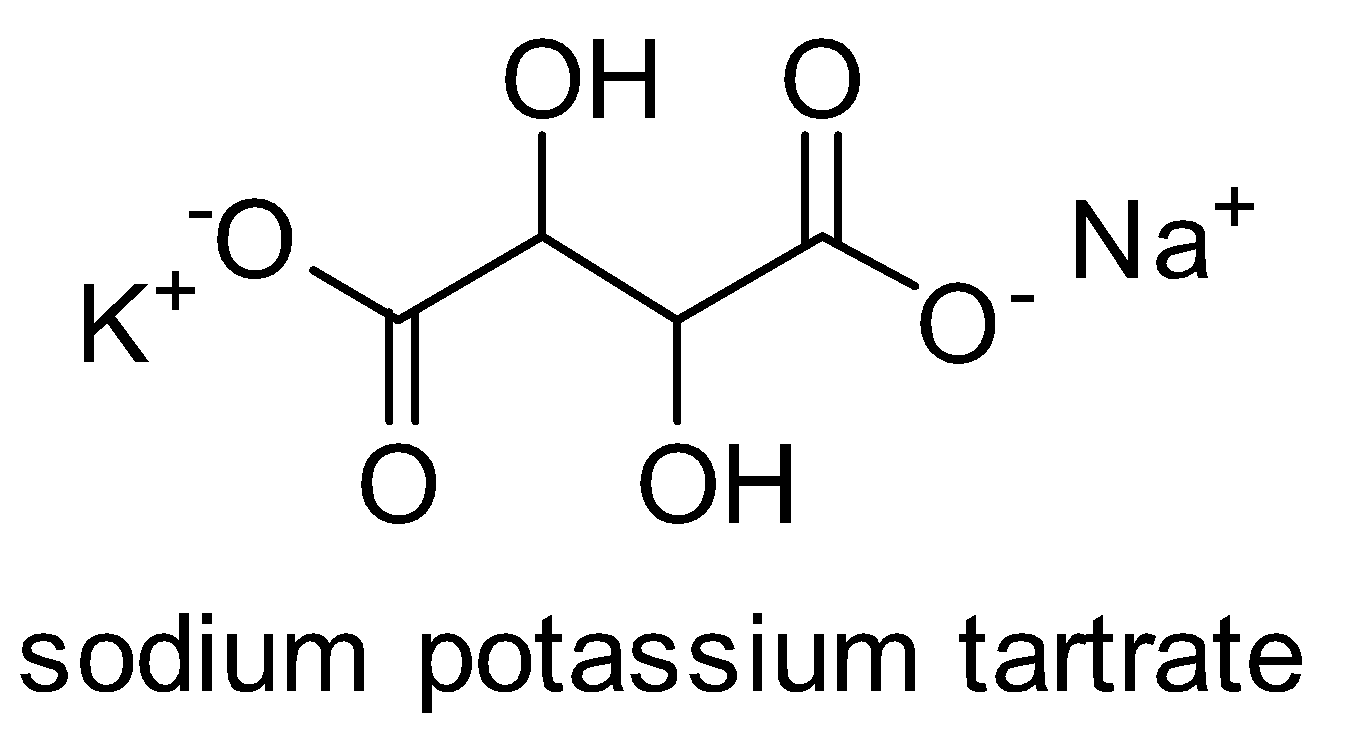
The Fehling solution is blue in color because of the copper sulphate solution. It is an oxidizing agent. Salt of sodium potassium tartrate is called Rochelle salt. It has the structure-
Fehling solution can be used to detect aldehydic groups as well as glucose(reducing sugar) in urine thus helps in detecting diabetes.
Complete step by step answer:
Fehling solution is made up by mixing two separate solutions- Fehling’s solution A and Fehling’s solution B. Solution A contains deep blue colored dilute solution of copper sulphate and Fehling’s solution B contains colorless aqueous solution of sodium potassium. It is prepared by mixing sodium potassium tartrate and sodium hydroxide. This solution is also called Rochelle salt.
Fehling solution is used to detect the presence of aldehyde functional groups. The active group is a bis (tartrate) complex of $C{u^{2 + }}$ . It is an oxidizing agent. The two solutions are stable separately and are mixed only when required because the $Cu(II)$ complex formed by their combination is not stable.
When Fehling solution is mixed with solution containing aldehyde, a red brown precipitate of cuprous oxide appears.
The general reaction can be stated as follows-
$RCHO + 2C{u^{2 + }} + 3O{H^ - } \to RCO{O^ - } + 2C{u^ + } + 2{H_2}O$
The blue color of Fehling solution changes to red as aldehyde reduces the $Cu(II)$ complex.
Now let us look at the acids given in the option. The structures are-

In the acids given above we can see that methanoic acid has carboxyl group $( - COOH)$ and aldehyde group $( - CHO)$ also. The other acids only have the carboxylic group. So only methanoic acid will reduce Fehling solution and give the color change.
So the correct option is A.
Note:
The Fehling solution is blue in color because of the copper sulphate solution. It is an oxidizing agent. Salt of sodium potassium tartrate is called Rochelle salt. It has the structure-

Fehling solution can be used to detect aldehydic groups as well as glucose(reducing sugar) in urine thus helps in detecting diabetes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




